最短路径问题---Floyd算法详解
Posted seatop
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了最短路径问题---Floyd算法详解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
Genius only means hard-working all one’s life.
Name:Willam
Time:2017/3/8
1、最短路径问题介绍
问题解释:
从图中的某个顶点出发到达另外一个顶点的所经过的边的权重和最小的一条路径,称为最短路径
解决问题的算法:
- 迪杰斯特拉算法(Dijkstra算法)
- 弗洛伊德算法(Floyd算法)
- SPFA算法
之前已经对Dijkstra算法做了介绍(不懂的可以看这篇博客:Dijkstra算法详解),所以这篇博客打算对Floyd算法做详细的的介绍。
2、Floyd算法的介绍
-
算法的特点:
弗洛伊德算法是解决任意两点间的最短路径的一种算法,可以正确处理有向图或有向图或负权(但不可存在负权回路)的最短路径问题,同时也被用于计算有向图的传递闭包。 -
算法的思路
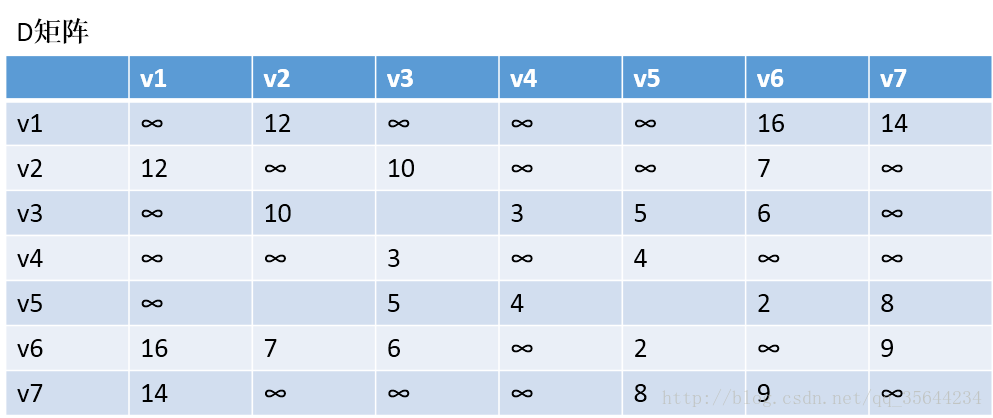
通过Floyd计算图G=(V,E)中各个顶点的最短路径时,需要引入两个矩阵,矩阵S中的元素a[i][j]表示顶点i(第i个顶点)到顶点j(第j个顶点)的距离。矩阵P中的元素b[i][j],表示顶点i到顶点j经过了b[i][j]记录的值所表示的顶点。
假设图G中顶点个数为N,则需要对矩阵D和矩阵P进行N次更新。初始时,矩阵D中顶点a[i][j]的距离为顶点i到顶点j的权值;如果i和j不相邻,则a[i][j]=∞,矩阵P的值为顶点b[i][j]的j的值。 接下来开始,对矩阵D进行N次更新。第1次更新时,如果”a[i][j]的距离” > “a[i][0]+a[0][j]”(a[i][0]+a[0][j]表示”i与j之间经过第1个顶点的距离”),则更新a[i][j]为”a[i][0]+a[0][j]”,更新b[i][j]=b[i][0]。 同理,第k次更新时,如果”a[i][j]的距离” > “a[i][k-1]+a[k-1][j]”,则更新a[i][j]为”a[i][k-1]+a[k-1][j]”,b[i][j]=b[i][k-1]。更新N次之后,操作完成!
3、Floyd算法的实例过程
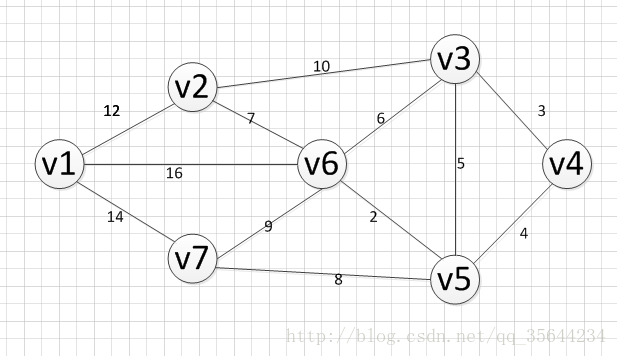
上面,我们已经介绍了算法的思路,如果,你觉得还是不理解,那么通过一个实际的例子,把算法的过程过一遍,你就明白了,如下图,我们求下图的每个点对之间的最短路径的过程如下:
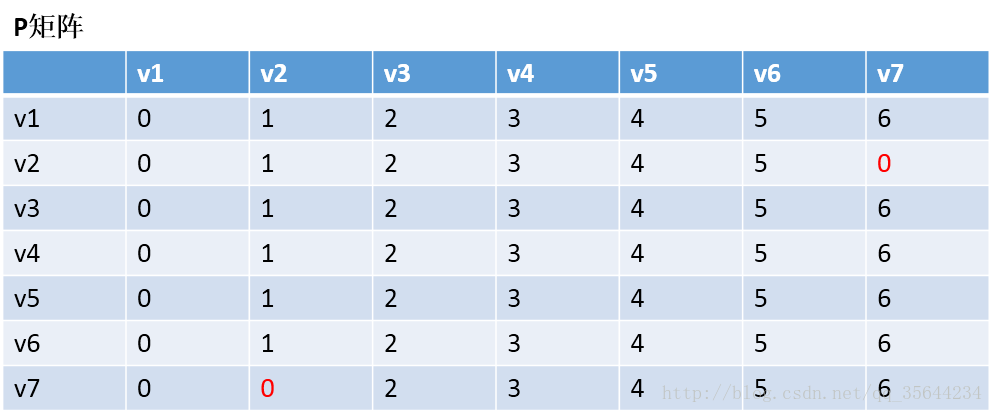
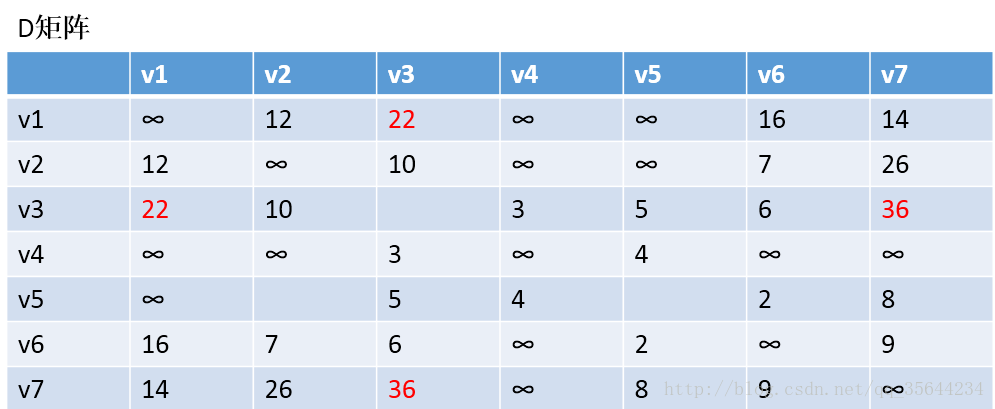
第一步,我们先初始化两个矩阵,得到下图两个矩阵:
、
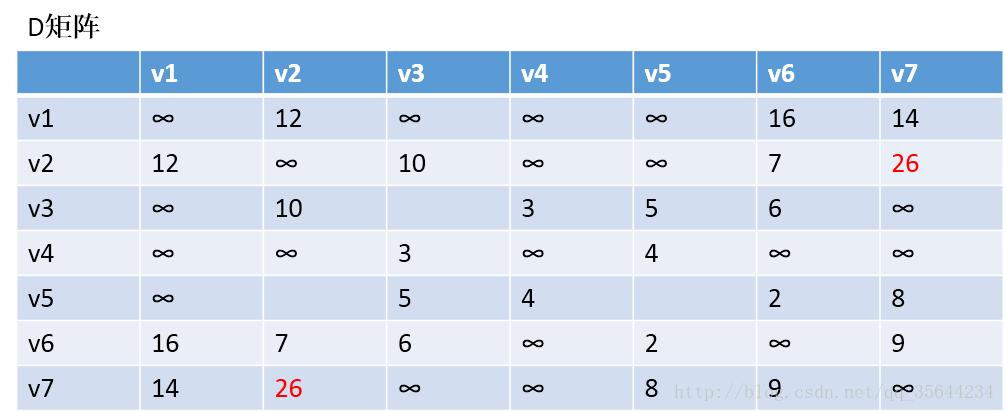
第二步,以v1为中阶,更新两个矩阵:
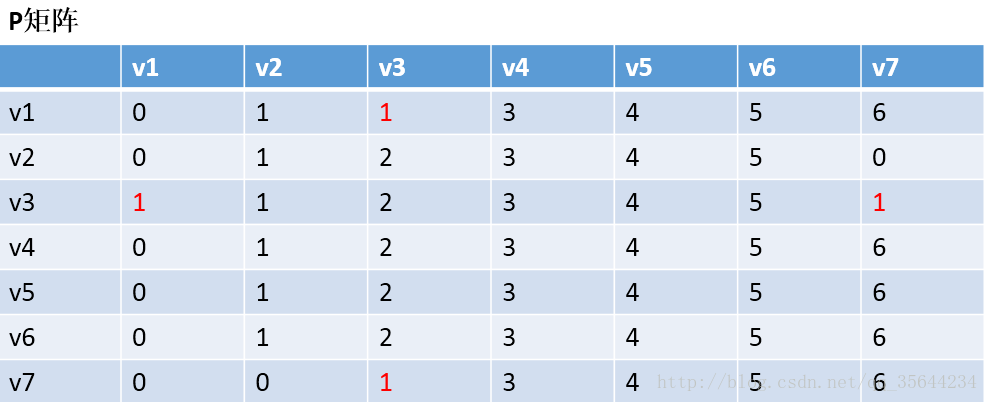
发现,a[1][0]+a[0][6] < a[1][6] 和a[6][0]+a[0][1] < a[6][1],所以我们只需要矩阵D和矩阵P,结果如下:
通过矩阵P,我发现v2–v7的最短路径是:v2–v1–v7
第三步:以v2作为中介,来更新我们的两个矩阵,使用同样的原理,扫描整个矩阵,得到如下图的结果:
OK,到这里我们也就应该明白Floyd算法是如何工作的了,他每次都会选择一个中介点,然后,遍历整个矩阵,查找需要更新的值,下面还剩下五步,就不继续演示下去了,理解了方法,我们就可以写代码了。
4、Floyd算法的代码实现
- Floyd.h文件代码
/************************************************************/
/* 程序作者:Willam */
/* 程序完成时间:2017/3/11 */
/* 有任何问题请联系:[email protected] */
/************************************************************/
//@尽量写出完美的程序
#pragma once
//#pragma once是一个比较常用的C/C++杂注,
//只要在头文件的最开始加入这条杂注,
//就能够保证头文件只被编译一次。
/*
本博客开始对Floyd算法的使用邻接矩阵实现的
*/
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Graph_DG {
private:
int vexnum; //图的顶点个数
int edge; //图的边数
int **arc; //邻接矩阵
int ** dis; //记录各个顶点最短路径的信息
int ** path; //记录各个最短路径的信息
public:
//构造函数
Graph_DG(int vexnum, int edge);
//析构函数
~Graph_DG();
// 判断我们每次输入的的边的信息是否合法
//顶点从1开始编号
bool check_edge_value(int start, int end, int weight);
//创建图
void createGraph(int);
//打印邻接矩阵
void print();
//求最短路径
void Floyd();
//打印最短路径
void print_path();
};
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- Floyd.cpp文件代码
#include"Floyd.h"
//构造函数
Graph_DG::Graph_DG(int vexnum, int edge) {
//初始化顶点数和边数
this->vexnum = vexnum;
this->edge = edge;
//为邻接矩阵开辟空间和赋初值
arc = new int*[this->vexnum];
dis = new int*[this->vexnum];
path = new int*[this->vexnum];
for (int i = 0; i < this->vexnum; i++) {
arc[i] = new int[this->vexnum];
dis[i] = new int[this->vexnum];
path[i] = new int[this->vexnum];
for (int k = 0; k < this->vexnum; k++) {
//邻接矩阵初始化为无穷大
arc[i][k] = INT_MAX;
}
}
}
//析构函数
Graph_DG::~Graph_DG() {
for (int i = 0; i < this->vexnum; i++) {
delete this->arc[i];
delete this->dis[i];
delete this->path[i];
}
delete dis;
delete arc;
delete path;
}
// 判断我们每次输入的的边的信息是否合法
//顶点从1开始编号
bool Graph_DG::check_edge_value(int start, int end, int weight) {
if (start<1 || end<1 || start>vexnum || end>vexnum || weight < 0) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
void Graph_DG::createGraph(int kind) {
cout << "请输入每条边的起点和终点(顶点编号从1开始)以及其权重" << endl;
int start;
int end;
int weight;
int count = 0;
while (count != this->edge) {
cin >> start >> end >> weight;
//首先判断边的信息是否合法
while (!this->check_edge_value(start, end, weight)) {
cout << "输入的边的信息不合法,请重新输入" << endl;
cin >> start >> end >> weight;
}
//对邻接矩阵对应上的点赋值
arc[start - 1][end - 1] = weight;
//无向图添加上这行代码
if(kind==2)
arc[end - 1][start - 1] = weight;
++count;
}
}
void Graph_DG::print() {
cout << "图的邻接矩阵为:" << endl;
int count_row = 0; //打印行的标签
int count_col = 0; //打印列的标签
//开始打印
while (count_row != this->vexnum) {
count_col = 0;
while (count_col != this->vexnum) {
if (arc[count_row][count_col] == INT_MAX)
cout << "∞" << " ";
else
cout << arc[count_row][count_col] << " ";
++count_col;
}
cout << endl;
++count_row;
}
}
void Graph_DG::Floyd() {
int row = 0;
int col = 0;
for (row = 0; row < this->vexnum; row++) {
for (col = 0; col < this->vexnum; col++) {
//把矩阵D初始化为邻接矩阵的值
this->dis[row][col] = this->arc[row][col];
//矩阵P的初值则为各个边的终点顶点的下标
this->path[row][col] = col;
}
}
//三重循环,用于计算每个点对的最短路径
int temp = 0;
int select = 0;
for (temp = 0; temp < this->vexnum; temp++) {
for (row = 0; row < this->vexnum; row++) {
for (col = 0; col < this->vexnum; col++) {
//为了防止溢出,所以需要引入一个select值
select = (dis[row][temp] == INT_MAX || dis[temp][col] == INT_MAX) ? INT_MAX : (dis[row][temp] + dis[temp][col]);
if (this->dis[row][col] > select) {
//更新我们的D矩阵
this->dis[row][col] = select;
//更新我们的P矩阵
this->path[row][col] = this->path[row][temp];
}
}
}
}
}
void Graph_DG::print_path() {
cout << "各个顶点对的最短路径:" << endl;
int row = 0;
int col = 0;
int temp = 0;
for (row = 0; row < this->vexnum; row++) {
for (col = row + 1; col < this->vexnum; col++) {
cout << "v" << to_string(row + 1) << "---" << "v" << to_string(col+1) << " weight: "
<< this->dis[row][col] << " path: " << " v" << to_string(row + 1);
temp = path[row][col];
//循环输出途径的每条路径。
while (temp != col) {
cout << "-->" << "v" << to_string(temp + 1);
temp = path[temp][col];
}
cout << "-->" << "v" << to_string(col + 1) << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- main.cpp文件的代码
#include"Floyd.h"
//检验输入边数和顶点数的值是否有效,可以自己推算为啥:
//顶点数和边数的关系是:((Vexnum*(Vexnum - 1)) / 2) < edge
bool check(int Vexnum, int edge) {
if (Vexnum <= 0 || edge <= 0 || ((Vexnum*(Vexnum - 1)) / 2) < edge)
return false;
return true;
}
int main() {
int vexnum; int edge;
cout << "输入图的种类:1代表有向图,2代表无向图" << endl;
int kind;
cin >> kind;
//判读输入的kind是否合法
while (1) {
if (kind == 1 || kind == 2) {
break;
}
else {
cout << "输入的图的种类编号不合法,请重新输入:1代表有向图,2代表无向图" << endl;
cin >> kind;
}
}
cout << "输入图的顶点个数和边的条数:" << endl;
cin >> vexnum >> edge;
while (!check(vexnum, edge)) {
cout << "输入的数值不合法,请重新输入" << endl;
cin >> vexnum >> edge;
}
Graph_DG graph(vexnum, edge);
graph.createGraph(kind);
graph.print();
graph.Floyd();
graph.print_path();
system("pause");
return 0;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
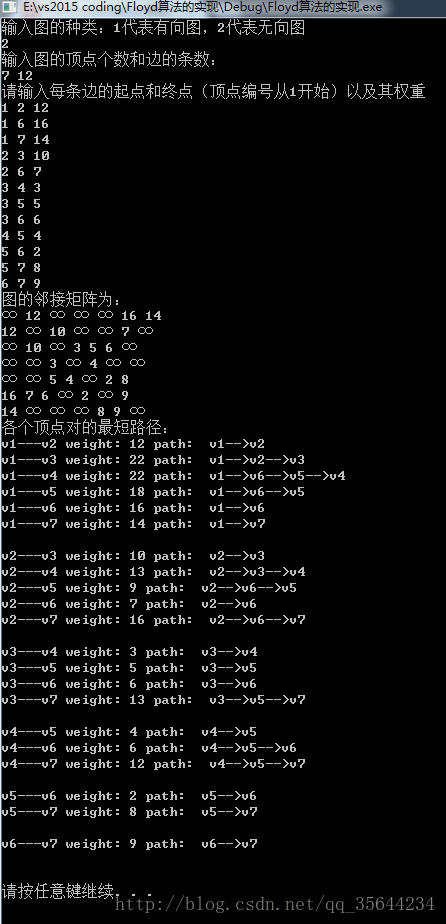
输入:
2
7 12
1 2 12
1 6 16
1 7 14
2 3 10
2 6 7
3 4 3
3 5 5
3 6 6
4 5 4
5 6 2
5 7 8
6 7 9 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
输出:
以上是关于最短路径问题---Floyd算法详解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章