Lombok使用
Posted zjfjava
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Lombok使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. Lombok简介
Lombok是一个可以通过简单的注解形式来帮助我们简化消除一些必须有但显得很臃肿的Java代码的工具,通过使用对应的注解,可以在编译源码的时候生成对应的方法。
2. 使用方法
在IDEA中使用,首先安装插件,这样才能在添加注解之后看到类的改变
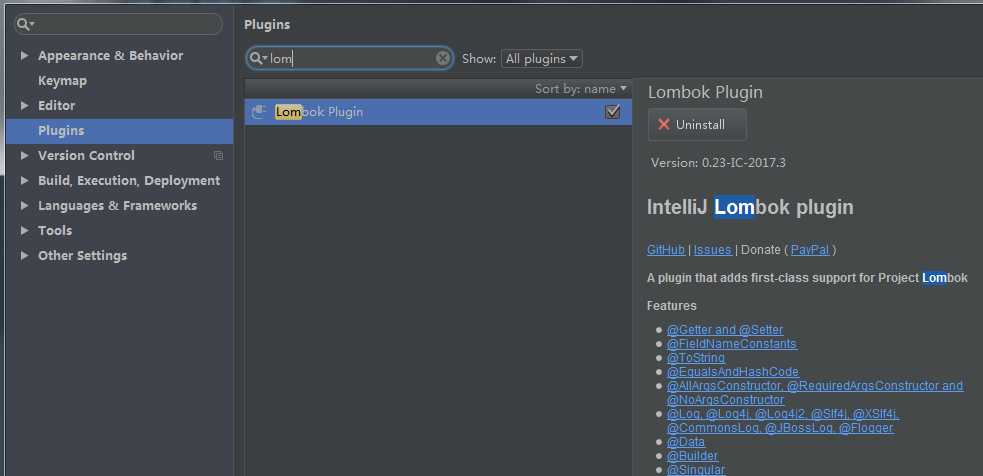
之后引入jar包即可
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.projectlombok/lombok --> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <version>1.18.4</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency>
3. 相关注解
官方注解的介绍:https://projectlombok.org/features/all
3.1 @Getter and @Setter
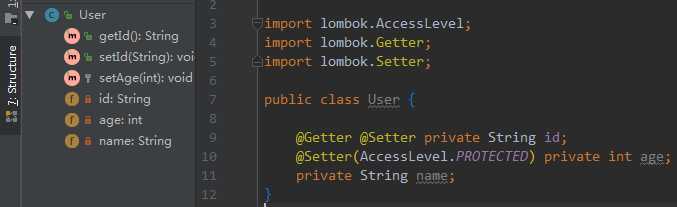
默认生成的方法是public的,如果要修改方法修饰符可以设置AccessLevel的值,例如:@Getter(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
字段上的注解示例:
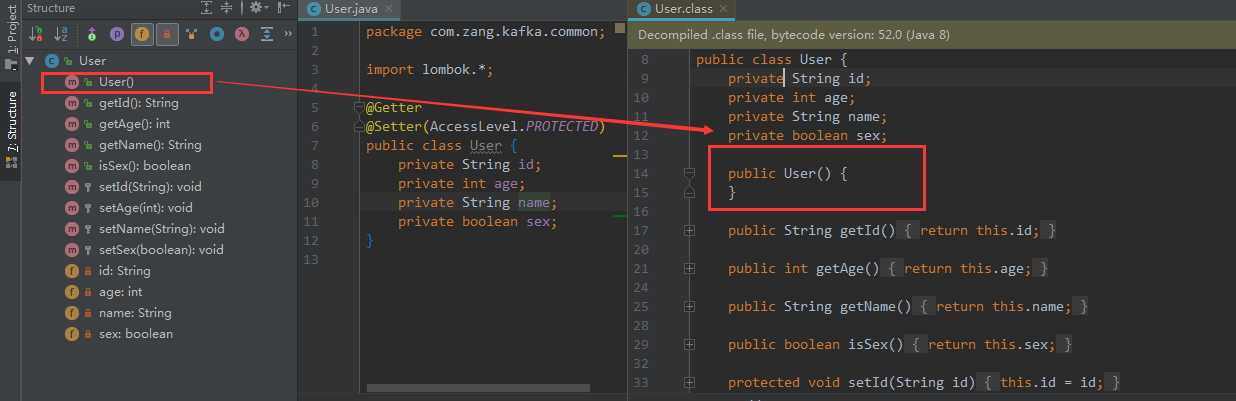
类上的注解示例:(使用类上的注解时,会默认生成一个无参构造)
3.2 @ToString
- 可以这样设置不包含哪些字段,例如:@ToString(exclude = "id") / @ToString(exclude = {"id","name"})
- 如果继承的有父类的话,可以设置callSuper 让其调用父类的toString()方法,例如:@ToString(callSuper = true)
- 如果需要可以通过注释参数
includeFieldNames来控制输出中是否包含的属性名称。,例如:@ToString(includeFieldNames= false)
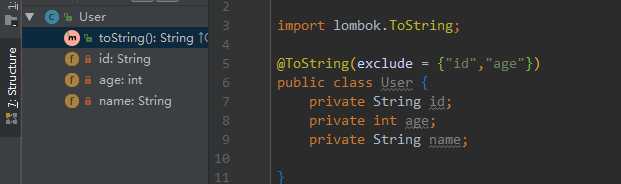
上面添加的注解映射到代码中为
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name=‘" + name + ‘‘‘ +
‘}‘;
}
3.3 @EqualsAndHashCode
生成hashCode()和equals()方法,默认情况下,它将使用所有非静态,非transient字段。但可以通过在可选的exclude参数中来排除更多字段。或者,通过在parameter参数中命名它们来准确指定希望使用哪些字段。
import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode;
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class EqualsAndHashCodeExample {
private transient int transientVar = 10;
private String name;
private double score;
@EqualsAndHashCode.Exclude private Shape shape = new Square(5, 10);
private String[] tags;
@EqualsAndHashCode.Exclude private int id;
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
@EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper=true)
public static class Square extends Shape {
private final int width, height;
public Square(int width, int height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
}
}
映射到代码中为
import java.util.Arrays;
public class EqualsAndHashCodeExample {
private transient int transientVar = 10;
private String name;
private double score;
private Shape shape = new Square(5, 10);
private String[] tags;
private int id;
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
@Override public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) return true;
if (!(o instanceof EqualsAndHashCodeExample)) return false;
EqualsAndHashCodeExample other = (EqualsAndHashCodeExample) o;
if (!other.canEqual((Object)this)) return false;
if (this.getName() == null ? other.getName() != null : !this.getName().equals(other.getName())) return false;
if (Double.compare(this.score, other.score) != 0) return false;
if (!Arrays.deepEquals(this.tags, other.tags)) return false;
return true;
}
@Override public int hashCode() {
final int PRIME = 59;
int result = 1;
final long temp1 = Double.doubleToLongBits(this.score);
result = (result*PRIME) + (this.name == null ? 43 : this.name.hashCode());
result = (result*PRIME) + (int)(temp1 ^ (temp1 >>> 32));
result = (result*PRIME) + Arrays.deepHashCode(this.tags);
return result;
}
protected boolean canEqual(Object other) {
return other instanceof EqualsAndHashCodeExample;
}
public static class Square extends Shape {
private final int width, height;
public Square(int width, int height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
@Override public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) return true;
if (!(o instanceof Square)) return false;
Square other = (Square) o;
if (!other.canEqual((Object)this)) return false;
if (!super.equals(o)) return false;
if (this.width != other.width) return false;
if (this.height != other.height) return false;
return true;
}
@Override public int hashCode() {
final int PRIME = 59;
int result = 1;
result = (result*PRIME) + super.hashCode();
result = (result*PRIME) + this.width;
result = (result*PRIME) + this.height;
return result;
}
protected boolean canEqual(Object other) {
return other instanceof Square;
}
}
}
3.4 @NoArgsConstructor, @RequiredArgsConstructor, @AllArgsConstructor
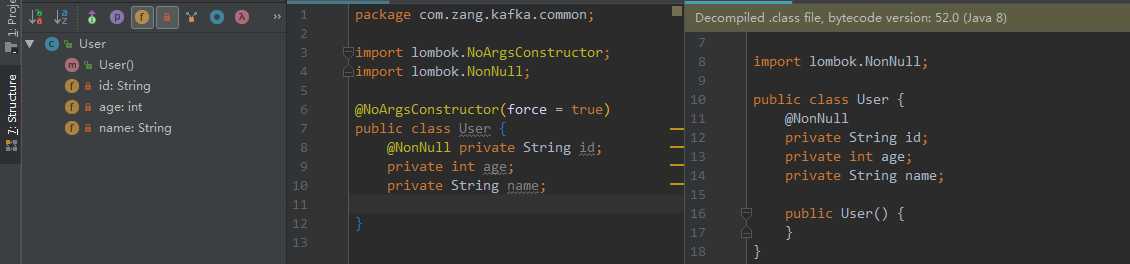
3.4.1 @NoArgsConstructor
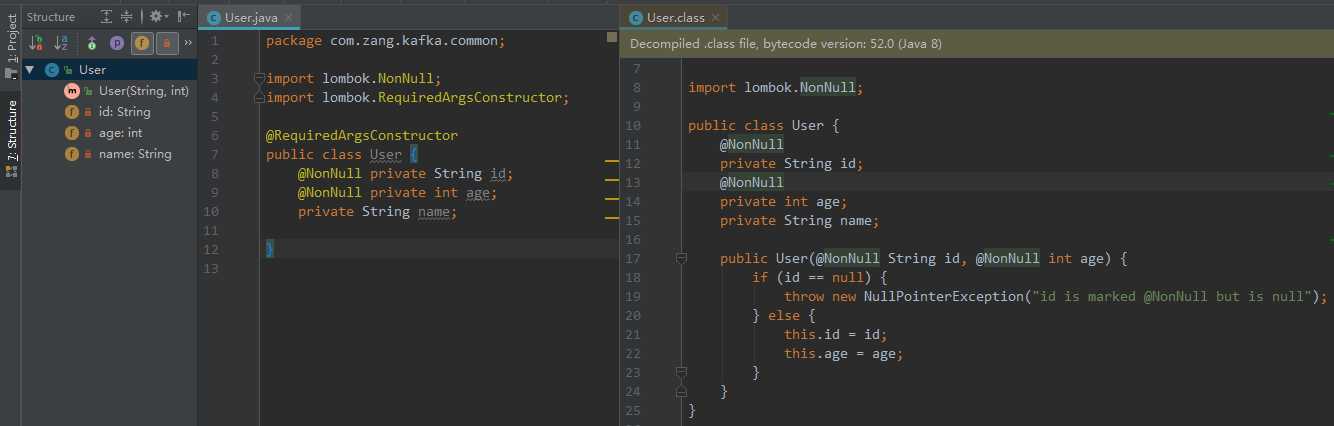
3.4.2 @RequiredArgsConstructor
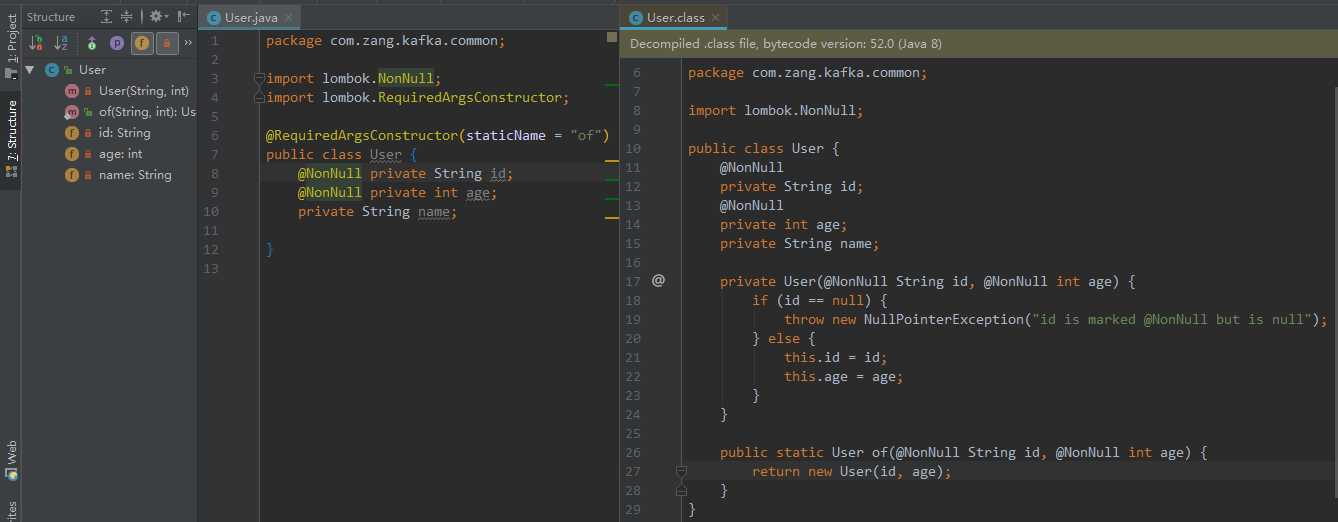
@RequiredArgsConstructor(staticName = "of")会生成一个of()的静态方法,并把构造方法设置为私有的
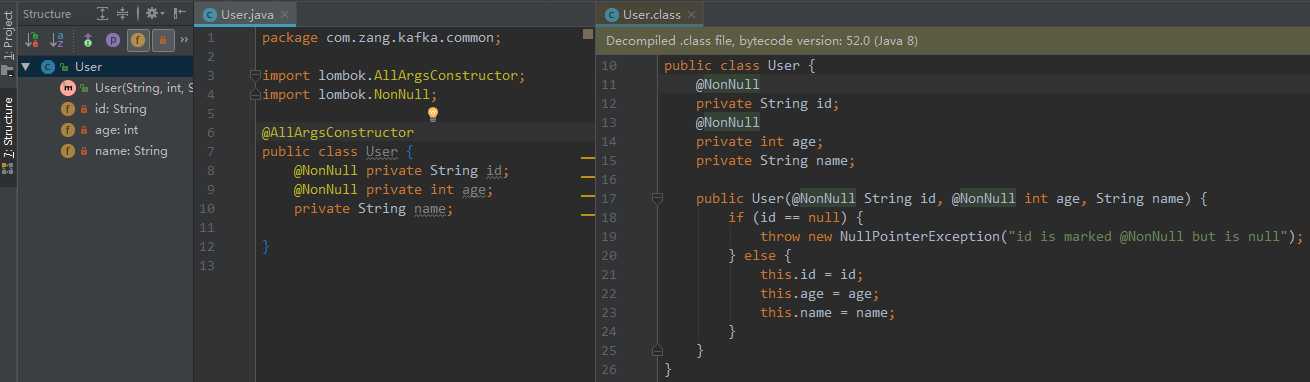
3.4.3 @AllArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor 生成一个全参数的构造方法,默认不提供无参构造。
3.5 @Data
该注解使用在类上,该注解会提供getter、setter、equals、canEqual、hashCode、toString方法。
虽然@Data注解非常有用,但是它没有与其他注解相同的控制粒度。@Data提供了一个可以生成静态工厂的单一参数,将staticConstructor参数设置为所需要的名称,Lombok自动生成的构造函数设置为私有,并提供公开的给定名称的静态工厂方法。
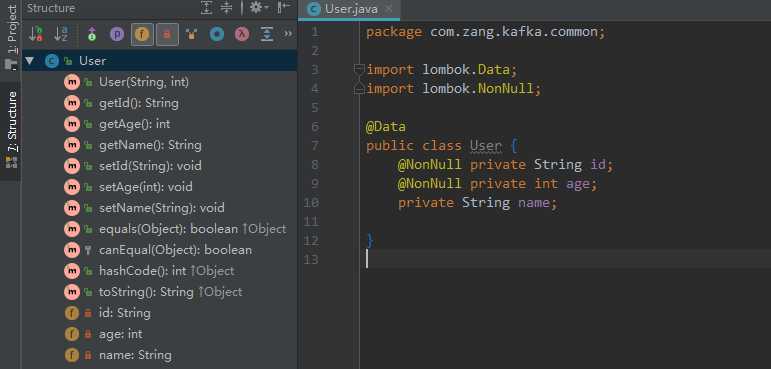
3.6 @NonNull
该注解使用在属性上,该注解用于属性的非空检查,当放在setter方法的字段上,将生成一个空检查,如果为空,则抛出NullPointerException。
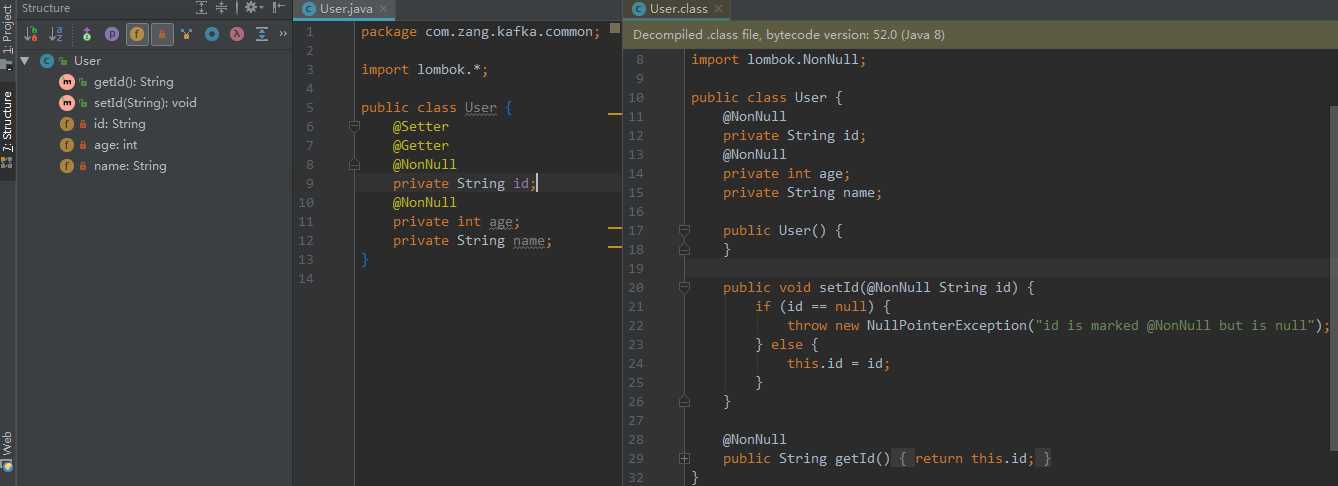
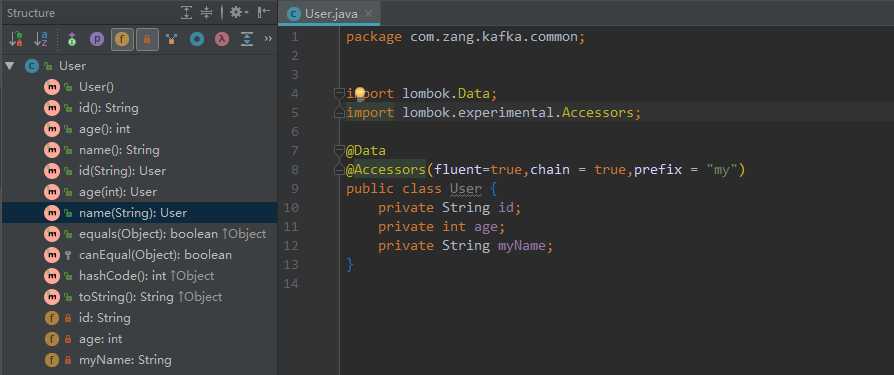
3.7 @Accessors
@Accessors 主要用于控制生成的getter和setter
- fluent boolean值,默认为false。此字段主要为控制生成的getter和setter方法前面是否带get/set
- chain boolean值,默认false。如果设置为true,setter返回的是此对象,方便链式调用方法
- prefix 设置前缀 例如:@Accessors(prefix = "my") private String myName 当生成get/set方法时,会把此前缀去掉
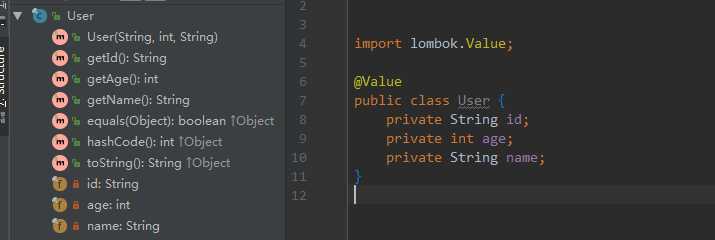
3.8 @Value
这个注解用在 类 上,会生成含所有参数的构造方法,get 方法,此外还提供了equals、hashCode、toString 方法。
注意:没有setter 方法
3.9 @Synchronized
该注解使用在类或者实例方法上,Synchronized在一个方法上,使用关键字可能会导致结果和想要的结果不同,因为多线程情况下会出现异常情况。Synchronized
关键字将在this示例方法情况下锁定当前对象,或者class讲台方法的对象上多锁定。这可能会导致死锁现象。一般情况下建议锁定一个专门用于此目的的独立锁,而不是允许公共对象进行锁定。该注解也是为了达到该目的。
// 注解方法 @Synchronized public int answerToLife() { return 42; } //等同于加锁 public int answerToLife() { synchronized($lock) { return 42; } }
3.10 @SneakyThrows
该注解使用在方法上,这个注解用在 方法 上,可以将方法中的代码用 try-catch 语句包裹起来,捕获异常并在 catch 中用 Lombok.sneakyThrow(e) 把异常抛出,可以使用 @SneakyThrows(Exception.class) 的形式指定抛出哪种异常。该注解需要谨慎使用。
3.11 @Cleanup
该注解使用在属性前,该注解是用来保证分配的资源被释放。在本地变量上使用该注解,任何后续代码都将封装在try/finally中,确保当前作用于中的资源被释放。默认@Cleanup清理的方法为close,可以使用value指定不同的方法名称。
3.12 @Wither
提供了给final字段赋值的一种方法
3.13 @onXxx
在注解里面添加注解的方式
import lombok.Getter; import lombok.Setter;public class User { @Getter(onMethod = @_({@Id,@Column(name="id",nullable=false),@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.AUTO)})) @Setter private Integer id; @Getter(onMethod = @_(@Column(name="age"))) @Setter private int age; @Getter(onMethod = @_(@Column(name="name"))) @Setter private String name; }
3.14 @Delegate
给类生成一些列的方法,这些方法都来自于List接口
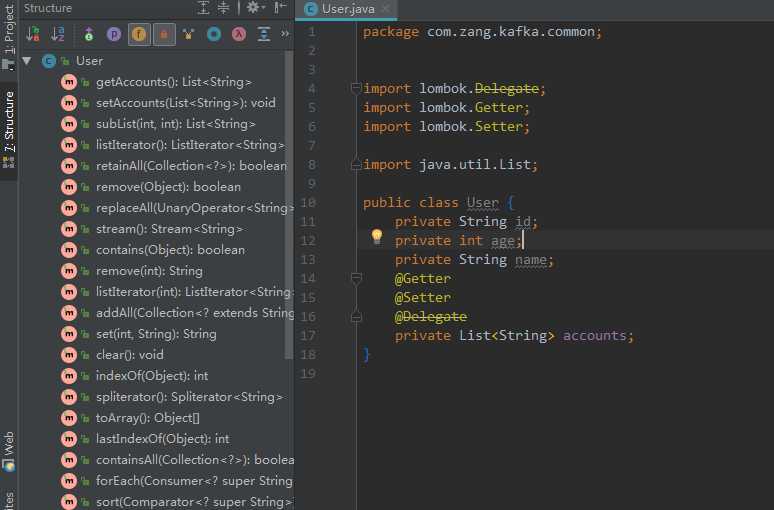
3.15 @Builder
@Builder注释为你的类生成复杂的构建器API。
3.16 @Log
注解于类上,用于满足不同的日志系统的日志使用,提供以下供选择
//@CommonsLog private static final org.apache.commons.logging.Log log = org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory.getLog(LogExample.class); //@JBossLog private static final org.jboss.logging.Logger log = org.jboss.logging.Logger.getLogger(LogExample.class); //@Log private static final java.util.logging.Logger log = java.util.logging.Logger.getLogger(LogExample.class.getName()); //@Log4j private static final org.apache.log4j.Logger log = org.apache.log4j.Logger.getLogger(LogExample.class); //@Log4j2 private static final org.apache.logging.log4j.Logger log = org.apache.logging.log4j.LogManager.getLogger(LogExample.class); //@Slf4j private static final org.slf4j.Logger log = org.slf4j.LoggerFactory.getLogger(LogExample.class); //@XSlf4j private static final org.slf4j.ext.XLogger log = org.slf4j.ext.XLoggerFactory.getXLogger(LogExample.class);
以上是关于Lombok使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章