数据结构--循环链表与双向链表
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构--循环链表与双向链表相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一.循环链表
A.循环链表的介绍
a.概念上
1.任意数据元素都有一个前驱和一个后继
2.所有数据元素的关系构成一个逻辑上的环
b.实现上
1.循环链表是一种特殊的单链表
2.尾节点的指针域保存了首结点的地址
关系图如下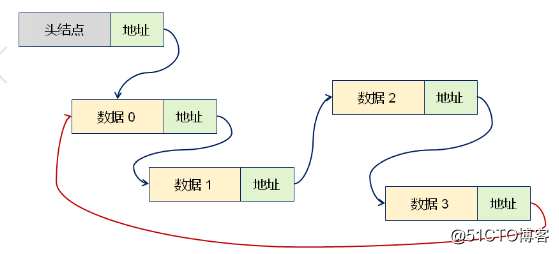 、
、
循环链表的继承层次结构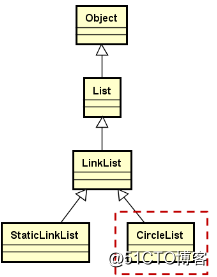
二.循环链表的实现思路
A.思路
1.通过模板定义CircleList类,继承自LinkList类
2.定义内部函数last_to_first();用于将单链表首尾相连
Node* last()const//尾节点
{
return this->position(this->m_length-1)->next;//返回尾节点(m_length-1)
}
void last_to_first()const//将链表首尾相连
{
last()->next=this->m_header.next;//尾节点的next指针指向首节点
}
int mod(int i)const//取余的实现
{
return (this->m_length==0) ? 0 : ( i % this->m_length);
}3.特殊处理:首元素的插入操作和删除操作
4.重新实现:清空操作和遍历操作
B.实现要点
a.插入位置为0时
1.头结点和尾结点均指向新结点
2.新结点成为首节点插入链表
bool insert(int i,const T& e)
{
bool ret=true;
i=i%(this->m_length+1);//i值取余
ret=LinkList<T>::insert(i,e);//调用父类的insert来实现子类的insert
if(ret&&(i==0))
{
last_to_first();
}
return ret;
}b.删除位置为0时
1.头结点和尾结点指向位置为1的结点
2.安全销毁首结点
bool remove(int i)
{
bool ret= true;
i= mod(i);
if(i==0)
{
Node *toDel=this->m_header.next;
if(toDel!=NULL)
{
this->m_header.next=toDel->next;
this->m_length--;
//链表不为空
if(this->m_length>0)
{
last_to_first();
if(this->m_current==toDel)
{
this->m_current=toDel->next;
}
}
else
{ //链表为空,置空
this->m_header.next=NULL;
this->m_current=NULL;
}
this->destroy(toDel);//在最后一步删除首节点 避免了异常安全
}
else
{
ret=false;
}
}
else
{
ret=LinkList<T>::remove(i);
}
return ret;
}
循环链表的完整实现代码如下
#include "LinkList.h"
namespace MyLib
{
template <typename T>
class CircleList:public LinkList<T>
{
protected:
typedef typename LinkList<T>::Node Node;
Node* last()const//尾节点
{
return this->position(this->m_length-1)->next;//返回尾节点(m_length-1)
}
void last_to_first()const//将链表首尾相连
{
last()->next=this->m_header.next;//尾节点的next指针指向首节点
}
int mod(int i)const
{
return (this->m_length==0) ? 0 : ( i % this->m_length);
}
public:
bool insert(const T& e)//重载
{
return insert(this->m_length,e);//调用重载的版本
}
bool insert(int i,const T& e)
{
bool ret=true;
i=i%(this->m_length+1);//i值取余
ret=LinkList<T>::insert(i,e);//调用父类的insert来实现子类的insert
if(ret&&(i==0))
{
last_to_first();
}
return ret;
}
bool remove(int i)
{
bool ret= true;
i= mod(i);
if(i==0)
{
Node *toDel=this->m_header.next;
if(toDel!=NULL)
{
this->m_header.next=toDel->next;
this->m_length--;
//链表不为空
if(this->m_length>0)
{
last_to_first();
if(this->m_current==toDel)
{
this->m_current=toDel->next;
}
}
else
{ //链表为空,置空
this->m_header.next=NULL;
this->m_current=NULL;
}
this->destroy(toDel);//在最后一步删除首节点 避免了异常安全
}
else
{
ret=false;
}
}
else
{
ret=LinkList<T>::remove(i);
}
return ret;
}
bool set(int i, const T &e)
{
i=mod(i);
return LinkList<T>::set(i,e);//调用父类函数
}
T get(int i)const
{
i=mod(i);
return LinkList<T>::get(i);
}
T get(int i,const T&e) const
{
i=mod(i);
return LinkList<T>::get(i,e);
}
int find(const T &e)const
{
int ret=-1;
Node* slide=this->m_header.next;//指针slide指向首节点
for(int i=0;i<this->m_length;i++)//slide指针遍历每个元素
{
if(slide->value==e)
{
ret=i;
break;
}
slide=slide->next;
}
return ret;
}
void clear()
{
while(this->m_length>1)
{
remove(1);//这里取1的原因是效率更高
}
if(this->m_length==1)
{
Node* toDel=this->m_header.next;
this->m_header.next=NULL;
this->m_current=NULL;
this->m_length=0;
this->destroy(toDel);
}
}
bool move(int i, int step)//i表示位置
{
i=mod(i);
return LinkList<T>::move(i,step);
}
bool end()
{
return (this->m_length==0)||(this->m_current==NULL);
}
~CircleList()//析构函数直接调用clear()函数
{
clear();
}
};
}三.小结
1.循环链表是一种特殊的单链表
2.尾结点的指针域保存了首结点的地址
3.特殊处理首元素的插入操作和删除操作
4.重新实现清空操作和遍历操作
四.双向链表
由之前的单链表我们可以看到单链表存在的缺陷
1.单向性==>只能从头结点开始高效访问链表中的数据元素
2.缺陷==>如果需要逆向访问单链表中的数据元素将极其低效
新的线性表实现
设计思路:在单链表的结点中增加一个指针pre,用于指向当前结点的前驱结点
示意图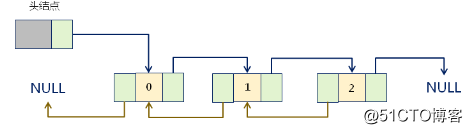
双向链表的继承层次结构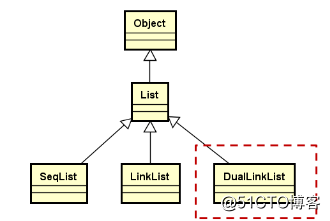
简单的图示来说明双向链表的插入和删除操作
插入操作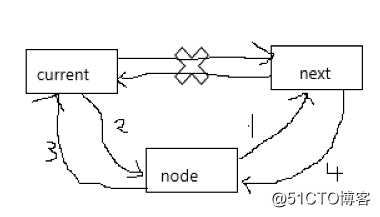
如图所示四个步骤完成操作
1.将插入结点的next指向next
2.current的next指向插入的结点
3.插入结点的pre指向curret
4.next的pre指向node
实现代码
bool insert(int i,const T&e)
{
bool ret=((0<=i)&&(i<= m_length));
if(ret)
{
Node* node=creat();
if(node!=NULL)
{
Node* current=positon();
Node* next=current->next;
node->value=e;
node->next=next;//步骤1
current->next=node;//步骤2
if(current!=reinterpret_cast<Node*>(&m_header))
{
node->pre=current;//步骤3
}
else
{
node->pre=NULL;
}
if(next!=NULL)
{
next-pre=node;
}
m_length++;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEoughMemoryException,"NoEoughMemory");
}
}
return ret;
}删除操作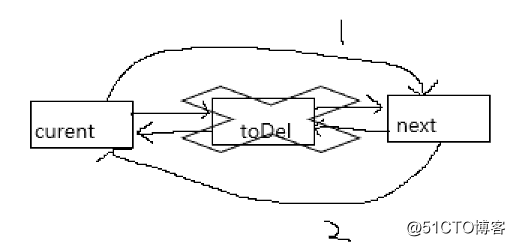
删除部分3个步骤
1.将current的next指向next
2.将next的pre指向current
3.删除toDel
代码实现如下
bool remove(int i)
{
bool ret=((0<=i)&&(i<m_length));
if(ret)
{
Node* current=position(i);
Node* toDel=current->next;
Node* next=toDel->next;
if(m_current==toDel)
{
m_current=next;
}
current->next=next;//步骤1
if(next!=NULL)
{
next->pre=toDel->pre;//步骤2
}
m_length--;
destroy(toDel);//步骤3
//m_length--;
}
return ret;
}双向链表的具体实现
#include "List.h"
#include "Exception.h"
namespace MyLib
{
template <typename T>
class DuaLinkList:public List<T>
{
protected:
struct Node :public Object
{
T value;//数据域 保存数据的值
Node* next;//指针域 指向后继节点的指针
Node* pre;
};
mutable struct:public Object//没有类型名的结构
{
char reserved[sizeof(T)];
Node* next;
Node* pre;
} m_header;//头节点 辅助定位元素
int m_length;
int m_step;
Node* m_current;
Node* position(int i) const//程序优化
{
Node* ret=reinterpret_cast<Node*>(&m_header);//reinterpret_cast强制类型转换
for(int p=0;p<i;p++)
{
ret=ret->next;
}
return ret;
}
virtual Node* create()
{
return new Node();
}
virtual void destroy(Node* pn)
{
delete pn;
}
public:
DuaLinkList()
{
m_header.next=NULL;
m_header.pre=NULL;
m_length=0;
m_step=1;
m_current=NULL;
}
bool insert(const T&e)
{
return insert(m_length,e);
}
bool insert(int i,const T&e)//i表示插入的位置,e表示插入的数据
{
bool ret=((0<=i)&&(i<= m_length));//m_length表示链表的长度
if(ret)
{
Node* node=create();
if(node!=NULL)
{
Node* current=position(i);//定位位置
Node* next=current->next;//表示插入的节点的后继节点
node->value=e;
node->next=next;
current->next=node;
if(current!=reinterpret_cast<Node*>(&m_header))
{
node->pre=current;
}
else
{
node->pre=NULL;
}
if(next!=NULL)
{
next->pre=node;
}
m_length++;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEoughMemoryException,"No ...");
}
}
return ret;
}
bool remove(int i)
{
bool ret=((0<=i)&&(i<m_length));
if(ret)
{
Node* current=position(i);
Node* toDel=current->next;
Node* next=toDel->next;
if(m_current==toDel)
{
m_current=next;
}
current->next=next;
if(next!=NULL)
{
next->pre=toDel->pre;
}
m_length--;
destroy(toDel);
//m_length--;
}
return ret;
}
bool set(int i,const T&e)
{
bool ret=((0<=i)&&(i<m_length));
if(ret)
{
position(i)->next->value=e;
}
return ret;
}
int find(const T&e) const
{
int ret=-1;
int i=0;
Node* node=m_header.next;
while(node)
{
if(node->value==e)
{
ret=i;
break;
}
else
{
node=node->next;
i++;
}
}
return ret;
}
virtual T get(int i)const
{
T ret;
if(get(i,ret))
{
return ret;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(indexOutOfBoundsException,"...");
}
return ret;
}
bool get(int i,T&e)const
{
bool ret=((0<=i)&&(i<m_length));
if(ret)
{
e=position(i)->next->value;
}
return ret;
}
int length()const
{
return m_length;
}
void clear()
{
while(m_length>0)
{
remove(0);
}
}
virtual bool move(int i,int step=-1)
{
bool ret= (0<=i)&&(i<m_length)&&(step>0);
if(ret)
{
m_current=position(i)->next;
m_step=step;
}
return ret;
}
virtual bool end()
{
return (m_current==NULL);
}
virtual T current()
{
if(!end())
{
return m_current->value;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException,"...");
}
}
virtual bool next()
{
int i=0;
while((i<m_step)&& !end())
{
m_current=m_current->next;
i++;
}
return (i==m_step);
}
virtual bool pre()
{
int i=0;
while((i<m_step)&& !end())
{
m_current=m_current->pre;
i++;
}
return (i==m_step);
}
~DuaLinkList()
{
clear();
}
};
}小结
1.双向链表是为了弥补单链表的缺陷而重新设计的
2.在概念上,双向链表不是单链表,没有继承关系
3.双向链表中的游标能够直接访问当前结点的前驱和后继
4.双向链表是线性表概念的最终实现
以上是关于数据结构--循环链表与双向链表的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章