SPLAY or SPALY ?
Posted 2017ssy
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了SPLAY or SPALY ?相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
写在前面:
由我们可爱的Daniel Sleator和Robert Tarjan提出的一种数据结构,平衡树的一种,本质是二叉树。
至于到底是splay还是spaly,我认为可能splay更对一些
毕竟splay是有实意的单词,更有可能一点。而且WIKI百科页也是splay
以下是本人学习splay的一点过程,请多指教喽
SPLAY
那么我在这里复习整理一下spaly的代码相关吧
例题:http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=3224
参考博客:http://blog.csdn.net/clove_unique/article/details/50636361

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #define maxn 500100 3 using namespace std; 4 int root,N,tot; 5 inline int read(){ 6 register int x=0,t=1; 7 register char ch=getchar(); 8 while((ch<‘0‘||ch>‘9‘)&&ch!=‘-‘)ch=getchar(); 9 if(ch==‘-‘){t=-1;ch=getchar();} 10 while(ch>=‘0‘&&ch<=‘9‘){x=x*10+ch-48;ch=getchar();} 11 return x*t; 12 } 13 struct node{ 14 int ch[2],ff,cnt,val,sum; 15 }t[maxn]; 16 void pushup(int u){ 17 t[u].sum=t[t[u].ch[0]].sum+t[t[u].ch[1]].sum+t[u].cnt; 18 } 19 void rotate(int x){ 20 register int y=t[x].ff; 21 register int z=t[y].ff; 22 register int k=t[y].ch[1]==x; 23 t[z].ch[t[z].ch[1]==y]=x;t[x].ff=z; 24 t[y].ch[k]=t[x].ch[k^1];t[t[x].ch[k^1]].ff=y; 25 t[x].ch[k^1]=y;t[y].ff=x; 26 pushup(y),pushup(x); 27 } 28 void splay(int x,int goal){ 29 while(t[x].ff!=goal){ 30 int y=t[x].ff; 31 int z=t[y].ff; 32 if(z!=goal) 33 (t[y].ch[0]==x)^(t[z].ch[0]==y)?rotate(x):rotate(y); 34 rotate(x); 35 } 36 if(goal==0) 37 root=x; 38 } 39 void insert(int x){ 40 int u=root,ff=0; 41 while(u&&t[u].val!=x){ 42 ff=u; 43 u=t[u].ch[x>t[u].val]; 44 } 45 if(u) 46 t[u].cnt++; 47 else{ 48 u=++tot; 49 if(ff) 50 t[ff].ch[x>t[ff].val]=u; 51 t[tot].ch[0]=0; 52 t[tot].ch[1]=0; 53 t[tot].ff=ff;t[tot].val=x; 54 t[tot].cnt=t[tot].sum=1; 55 } 56 splay(u,0); 57 } 58 void find(int x){ 59 int u=root; 60 if(!u)return; 61 while(t[u].ch[x>t[u].val]&&x!=t[u].val) 62 u=t[u].ch[x>t[u].val]; 63 splay(u,0); 64 } 65 int next(int x,int f){ 66 find(x); 67 int u=root; 68 if((t[u].val>x&&f)||(t[u].val<x&&!f))return u; 69 u=t[u].ch[f]; 70 while(t[u].ch[f^1])u=t[u].ch[f^1]; 71 return u; 72 } 73 void del(int x){ 74 int la=next(x,0); 75 int ne=next(x,1); 76 splay(la,0),splay(ne,la); 77 int d=t[ne].ch[0]; 78 if(t[d].cnt>1){ 79 t[d].cnt--; 80 splay(d,0); 81 } 82 else 83 t[ne].ch[0]=0; 84 } 85 int K_th(int x){ 86 int u=root; 87 if(t[u].sum<x) 88 return 0; 89 while(1){ 90 int y=t[u].ch[0]; 91 if(x>t[y].sum+t[u].cnt){ 92 x-=t[y].sum+t[u].cnt; 93 u=t[u].ch[1]; 94 } 95 else if(t[y].sum>=x) 96 u=y; 97 else 98 return t[u].val; 99 } 100 } 101 int main(){ 102 insert(-2147483647); 103 insert(+2147483647); 104 N=read(); 105 while(N--){ 106 int opt=read(); 107 if(opt==1)insert(read()); 108 else if(opt==2)del(read()); 109 else if(opt==3){ 110 find(read()); 111 printf("%d ",t[t[root].ch[0]].sum); 112 } 113 else if(opt==4)printf("%d ",K_th(read()+1)); 114 else if(opt==5)printf("%d ",t[next(read(),0)].val); 115 else if(opt==6)printf("%d ",t[next(read(),1)].val); 116 } 117 return 0; 118 }
上面那份代码其实是洛谷上的。。。本来想自己写的,但是怎么调都过不去5555(;′д`)ゞ
算了吧,既然抄了代码就要抄的明明白白,这里让我们看看splay到底是怎么维护的吧
首先是一些基本操作:
1.rotate
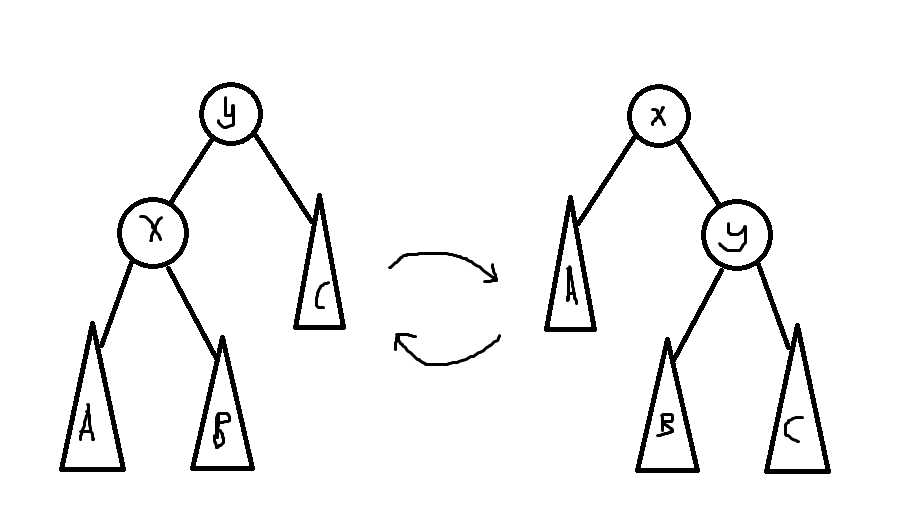
就是这个东西,保证了二叉树储存的元素顺序不变,大小顺序不变,总之转它就对了。

1 void rotate(int x){ 2 register int y=t[x].ff; 3 register int z=t[y].ff; 4 register int k=t[y].ch[1]==x; 5 t[z].ch[t[z].ch[1]==y]=x;t[x].ff=z; 6 t[y].ch[k]=t[x].ch[k^1];t[t[x].ch[k^1]].ff=y; 7 t[x].ch[k^1]=y;t[y].ff=x; 8 pushup(y),pushup(x); 9 }
2.splay
splay是依靠平均操作来降低复杂度的,其实有点玄学,splay这个操作就是要把每次查询和修改的中心重新改变成根,
在这个过程中尽可能的让树的大小平衡,即尽可能打断原先树上存在的链,把他们压成树。。。
反正挺神的,记住写双旋时有先后就对了,尽量让树平衡。

1 void splay(int x,int goal){ 2 while(t[x].ff!=goal){ 3 int y=t[x].ff; 4 int z=t[y].ff; 5 if(z!=goal) 6 (t[y].ch[0]==x)^(t[z].ch[0]==y)?rotate(x):rotate(y); 7 rotate(x); 8 } 9 if(goal==0) 10 root=x; 11 }
em。。。接下来挑一些重点(我蒙过的)讲吧。。。
3.del
删除操作,为了精确定位我们想删掉的那个点,我们选择找到他的前驱,旋到根上,再找他的后继,旋到前驱下面
这样的话这个点只能在后继的左儿子上了
但是如果这个点没有前驱和后继岂不是药丸???
那我们就干脆插入一个+inf和-inf,保证有前驱和后继,但是相对的作为代价我们还要修改其他的几个函数

1 void del(int x){ 2 int la=next(x,0); 3 int ne=next(x,1); 4 splay(la,0),splay(ne,la); 5 int d=t[ne].ch[0]; 6 if(t[d].cnt>1){ 7 t[d].cnt--; 8 splay(d,0); 9 } 10 else 11 t[ne].ch[0]=0; 12 }
4.查询排名
查找这个数在这里的第几名?首先把他找到再旋到根上(这时候如果这个数不在树里,会发生什么呢?表示蒙圈= ̄ω ̄=)
然后理论上是应该所有比他小的数的个数+1,也就是左儿子sum+1
但是因为咱插了个-inf还得-1,所以就直接是左儿子sum
5.查询排名位k的是谁
同理,还是因为极值的问题,查询第k名就要变成查询k+1名

1 int K_th(int x){ 2 int u=root; 3 if(t[u].sum<x) 4 return 0; 5 while(1){ 6 int y=t[u].ch[0]; 7 if(x>t[y].sum+t[u].cnt){ 8 x-=t[y].sum+t[u].cnt; 9 u=t[u].ch[1]; 10 } 11 else if(t[y].sum>=x) 12 u=y; 13 else 14 return t[u].val; 15 } 16 }
但是以上只是个平衡树板子,splay作为平衡树中独特的一员,有着自己独特的闪光点(出难题的坑点╰(‵□′)╯
让我们对splay自己独到的用法再进一步探究
P3391 【模板】文艺平衡树(Splay)
这道题是splay裸题,利用的就是splay可以维护区间翻转
具体实现就是首先以每个数的位置作为比较大小的权值,再附上一个标记,表示这个节点及其所有儿子都要交换他们的左右儿子,但谁还都没换(包括自己
这样交换了左右儿子后,就相当于改变了比较大小的方式,原先较小的反而在较大的位置上,就实现了区间反转
例如要翻转(l,r),那么把前驱l旋到根上,后继旋到他后面,这段区间自然就卡成一段子树了,打个标记即可~
对应的K_th函数也有些改动,最后遍历一遍就是答案啦
注意,
所有自上到下的函数(K_th,go)都应该每次pushdown,但insert因为是之前做的,与标记无关,就不用了
而splay这种自下而上的函数则要先把一路的节点记下来,再从上往从下传标记,然后再旋,详细看代码吧
代码(我自己YY了半天才弄出来(ノへ ̄、)好弱啊):

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<algorithm> 3 using namespace std; 4 int n,m,root,tot; 5 struct node{ 6 int f,val,ch[2],sum; 7 bool rev; 8 }t[200005]; 9 void pushup(int x){ 10 t[x].sum=t[t[x].ch[0]].sum+t[t[x].ch[1]].sum+1; 11 } 12 void pushdown(int x){ 13 if(t[x].rev){ 14 t[t[x].ch[0]].rev^=1; 15 t[t[x].ch[1]].rev^=1; 16 t[x].rev^=1;swap(t[x].ch[0],t[x].ch[1]); 17 } 18 } 19 void rotate(int x){ 20 register int y=t[x].f; 21 register int z=t[y].f; 22 register int k=t[y].ch[1]==x; 23 t[z].ch[t[z].ch[1]==y]=x;t[x].f=z; 24 t[y].ch[k]=t[x].ch[k^1];t[t[x].ch[k^1]].f=y; 25 t[x].ch[k^1]=y;t[y].f=x; 26 pushup(y),pushup(x); 27 } 28 int st[200005],top; 29 void splay(int x,int goal){ 30 top=1;st[1]=x; 31 for(int i=x;t[i].f!=goal;i=t[i].f)st[++top]=t[i].f; 32 for(int i=top;i>=1;i--)pushdown(st[i]); 33 while(t[x].f!=goal){ 34 int y=t[x].f; 35 int z=t[y].f; 36 if(z!=goal) 37 (t[z].ch[0]==y)^(t[y].ch[0]==x)?rotate(x):rotate(y); 38 rotate(x); 39 } 40 if(goal==0) 41 root=x; 42 } 43 void insert(int x){ 44 int u=root,ff=0; 45 while(u&&t[u].val!=x){ 46 ff=u; 47 u=t[u].ch[x>t[u].val]; 48 } 49 u=++tot; 50 if(ff) 51 t[ff].ch[x>t[ff].val]=u; 52 t[u].f=ff;t[u].val=x; 53 t[u].rev=0; 54 t[u].ch[0]=0;t[u].ch[1]=0; 55 splay(u,0); 56 } 57 int K_th(int x){ 58 int u=root; 59 while(1){ 60 pushdown(u); 61 int y=t[u].ch[0]; 62 if(x>t[y].sum+1){ 63 x-=t[y].sum+1; 64 u=t[u].ch[1]; 65 } 66 else if(x<=t[y].sum)u=y; 67 else return u; 68 } 69 } 70 void go(int x){ 71 if(!x)return; 72 pushdown(x); 73 go(t[x].ch[0]); 74 st[++top]=t[x].val; 75 go(t[x].ch[1]); 76 } 77 int main(){ 78 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 79 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)insert(i); 80 insert(-2147483647); 81 insert(+2147483647); 82 for(int i=1,l,r;i<=m;i++){ 83 scanf("%d%d",&l,&r); 84 l--;r++; 85 l=K_th(l+1),splay(l,0); 86 r=K_th(r+1),splay(r,l); 87 t[t[r].ch[0]].rev^=1; 88 89 } 90 top=0; 91 go(root); 92 printf("%d ",st[2]); 93 for(int i=3;i<=n+1;i++) 94 printf("%d ",st[i]); 95 return 0; 96 }
以上是关于SPLAY or SPALY ?的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
