Focal Loss 的理解
Posted houjun
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Focal Loss 的理解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
论文:《Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection》
Focal Loss 是何恺明设计的为了解决one-stage目标检测在训练阶段前景类和背景类极度不均衡(如1:1000)的场景的损失函数。它是由二分类交叉熵改造而来的。
标准交叉熵
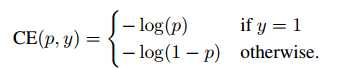
其中,p是模型预测属于类别y=1的概率。为了方便标记,定义:
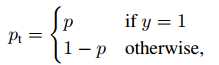
交叉熵CE重写为:
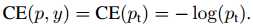
α-平衡交叉熵:
有一种解决类别不平衡的方法是引入一个值介于[0; 1]之间的权重因子α:当y=1时,取α; 当y=0时,取1-α。
这种方法,当y=0(即背景类)时,随着α的增大,会对损失进行很大惩罚(降低权重),从而减轻背景类
太多对训练的影响。
类似Pt,可将α-CE重写为:
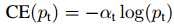
Focal Loss定义
虽然α-CE起到了平衡正负样本的在损失函数值中的贡献,但是它没办法区分难易样本的样本对损失的贡献。因此就有了Focal Loss,定义如下:
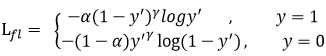
其中,alpha和gamma均为常熟,是一个超参数。y‘为模型预测,其值介于(0-1)之间。
当y=1时,y‘->1,表示easy positive,它对权重的贡献->0;
当y=0是,y‘->0,表示easy negative,它对权重的贡献->0.
因此,Focal Loss不仅降低了背景类的权重,还降低了easy positive/negative的权重。
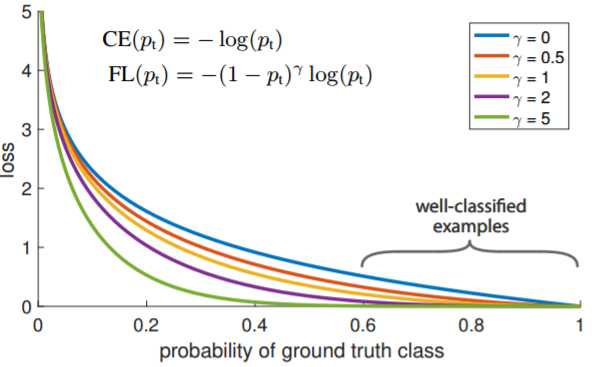
gamma是对损失函数的调节,当gamma=0是,Focal Loss与α-CE等价。以下是gamma
对Focal Loss的调节。
Focal Loss的Pytorch实现(蓝色字体)
以下Focal Loss=Focal Loss + Regress Loss;
代码来自:https://github.com/yhenon/pytorch-retinanet
1 import numpy as np 2 import torch 3 import torch.nn as nn 4 5 def calc_iou(a, b): 6 area = (b[:, 2] - b[:, 0]) * (b[:, 3] - b[:, 1]) 7 8 iw = torch.min(torch.unsqueeze(a[:, 2], dim=1), b[:, 2]) - torch.max(torch.unsqueeze(a[:, 0], 1), b[:, 0]) 9 ih = torch.min(torch.unsqueeze(a[:, 3], dim=1), b[:, 3]) - torch.max(torch.unsqueeze(a[:, 1], 1), b[:, 1]) 10 11 iw = torch.clamp(iw, min=0) 12 ih = torch.clamp(ih, min=0) 13 14 ua = torch.unsqueeze((a[:, 2] - a[:, 0]) * (a[:, 3] - a[:, 1]), dim=1) + area - iw * ih 15 16 ua = torch.clamp(ua, min=1e-8) 17 18 intersection = iw * ih 19 20 IoU = intersection / ua 21 22 return IoU 23 24 class FocalLoss(nn.Module): 25 #def __init__(self): 26 27 def forward(self, classifications, regressions, anchors, annotations): 28 alpha = 0.25 29 gamma = 2.0 30 batch_size = classifications.shape[0] 31 classification_losses = [] 32 regression_losses = [] 33 34 anchor = anchors[0, :, :] 35 36 anchor_widths = anchor[:, 2] - anchor[:, 0] 37 anchor_heights = anchor[:, 3] - anchor[:, 1] 38 anchor_ctr_x = anchor[:, 0] + 0.5 * anchor_widths 39 anchor_ctr_y = anchor[:, 1] + 0.5 * anchor_heights 40 41 for j in range(batch_size): 42 43 classification = classifications[j, :, :] 44 regression = regressions[j, :, :] 45 46 bbox_annotation = annotations[j, :, :] 47 bbox_annotation = bbox_annotation[bbox_annotation[:, 4] != -1] 48 49 if bbox_annotation.shape[0] == 0: 50 regression_losses.append(torch.tensor(0).float().cuda()) 51 classification_losses.append(torch.tensor(0).float().cuda()) 52 53 continue 54 55 classification = torch.clamp(classification, 1e-4, 1.0 - 1e-4) 56 57 IoU = calc_iou(anchors[0, :, :], bbox_annotation[:, :4]) # num_anchors x num_annotations 58 59 IoU_max, IoU_argmax = torch.max(IoU, dim=1) # num_anchors x 1 60 61 #import pdb 62 #pdb.set_trace() 63 64 # compute the loss for classification 65 targets = torch.ones(classification.shape) * -1 66 targets = targets.cuda() 67 68 targets[torch.lt(IoU_max, 0.4), :] = 0 69 70 positive_indices = torch.ge(IoU_max, 0.5) 71 72 num_positive_anchors = positive_indices.sum() 73 74 assigned_annotations = bbox_annotation[IoU_argmax, :] 75 76 targets[positive_indices, :] = 0 77 targets[positive_indices, assigned_annotations[positive_indices, 4].long()] = 1 78 79 alpha_factor = torch.ones(targets.shape).cuda() * alpha 80 81 alpha_factor = torch.where(torch.eq(targets, 1.), alpha_factor, 1. - alpha_factor) 82 focal_weight = torch.where(torch.eq(targets, 1.), 1. - classification, classification) 83 focal_weight = alpha_factor * torch.pow(focal_weight, gamma) 84 85 bce = -(targets * torch.log(classification) + (1.0 - targets) * torch.log(1.0 - classification)) 86 87 # cls_loss = focal_weight * torch.pow(bce, gamma) 88 cls_loss = focal_weight * bce 89 90 cls_loss = torch.where(torch.ne(targets, -1.0), cls_loss, torch.zeros(cls_loss.shape).cuda()) 91 92 classification_losses.append(cls_loss.sum()/torch.clamp(num_positive_anchors.float(), min=1.0)) 93 94 # compute the loss for regression 95 96 if positive_indices.sum() > 0: 97 assigned_annotations = assigned_annotations[positive_indices, :] 98 99 anchor_widths_pi = anchor_widths[positive_indices] 100 anchor_heights_pi = anchor_heights[positive_indices] 101 anchor_ctr_x_pi = anchor_ctr_x[positive_indices] 102 anchor_ctr_y_pi = anchor_ctr_y[positive_indices] 103 104 gt_widths = assigned_annotations[:, 2] - assigned_annotations[:, 0] 105 gt_heights = assigned_annotations[:, 3] - assigned_annotations[:, 1] 106 gt_ctr_x = assigned_annotations[:, 0] + 0.5 * gt_widths 107 gt_ctr_y = assigned_annotations[:, 1] + 0.5 * gt_heights 108 109 # clip widths to 1 110 gt_widths = torch.clamp(gt_widths, min=1) 111 gt_heights = torch.clamp(gt_heights, min=1) 112 113 targets_dx = (gt_ctr_x - anchor_ctr_x_pi) / anchor_widths_pi 114 targets_dy = (gt_ctr_y - anchor_ctr_y_pi) / anchor_heights_pi 115 targets_dw = torch.log(gt_widths / anchor_widths_pi) 116 targets_dh = torch.log(gt_heights / anchor_heights_pi) 117 118 targets = torch.stack((targets_dx, targets_dy, targets_dw, targets_dh)) 119 targets = targets.t() 120 121 targets = targets/torch.Tensor([[0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2]]).cuda() 122 123 124 negative_indices = 1 - positive_indices 125 126 regression_diff = torch.abs(targets - regression[positive_indices, :]) 127 128 regression_loss = torch.where( 129 torch.le(regression_diff, 1.0 / 9.0), 130 0.5 * 9.0 * torch.pow(regression_diff, 2), 131 regression_diff - 0.5 / 9.0 132 ) 133 regression_losses.append(regression_loss.mean()) 134 else: 135 regression_losses.append(torch.tensor(0).float().cuda()) 136 137 return torch.stack(classification_losses).mean(dim=0, keepdim=True), torch.stack(regression_losses).mean(dim=0, keepdim=True)
以上是关于Focal Loss 的理解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章