Java IO基础总结
Posted poorguy
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java IO基础总结相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Java中使用IO(输入输出)来读取和写入,读写设备上的数据、硬盘文件、内存、键盘......
根据数据的走向可分为输入流和输出流,这个走向是以内存为基准的,即往内存中读数据是输入流,从内存中往外写是输出流。
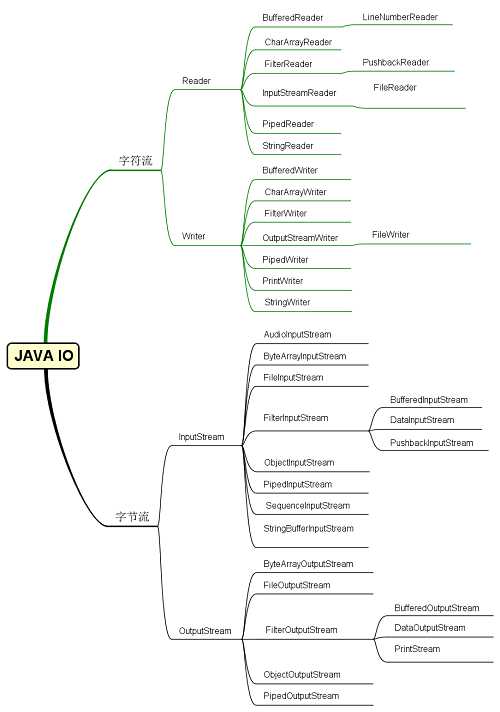
根据处理的数据类型可分为字节流和字符流
1.字节流可以处理所有数据类型的数据,在java中多以Stream结尾
2.字符流处理文本数据,在java中以Reader和Writer结尾。
读取控制台输入
Java 的控制台输入由 System.in 完成。(JDK 5 后的版本我们也可以使用 Java Scanner 类来获取控制台的输入。)
为了获得一个绑定到控制台的字符流,你可以把 System.in 包装在一个 BufferedReader 对象中来创建一个字符流。
下面是创建 BufferedReader 的基本语法:
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new
InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferReader的常用方法:
- read: 读取一个字符,返回值为读取的字符数,读到文件末尾返回-1
- readline:读取一行字符,返回类型String,当读取到结尾时返回Null
- skip:跳过字符,返回值为:跳过的字符数
注意:每次调用 read() 方法,它从输入流读取一个字符并把该字符作为整数值返回。 当流结束的时候返回 -1。该方法抛出 IOException。
public int read(char[] cbuf,
int off,
int len)
上述方法的参数的意义为,将读到的字符存入chuf数组(缓冲区)
FileInputStream
该流用于从文件读取数据,它的对象可以用关键字 new 来创建。
有多种构造方法可用来创建对象。
可以使用字符串类型的文件名来创建一个输入流对象来读取文件:
InputStream f = new FileInputStream("C:/java/hello");
也可以使用一个文件对象来创建一个输入流对象来读取文件。我们首先得使用 File() 方法来创建一个文件对象:
File f = new File("C:/java/hello");
InputStream out = new FileInputStream(f);
创建了InputStream对象,就可以使用下面的方法来读取流或者进行其他的流操作。
| 序号 | 方法及描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | public void close() throws IOException{} 关闭此文件输入流并释放与此流有关的所有系统资源。抛出IOException异常。 |
| 2 | protected void finalize()throws IOException {} 这个方法清除与该文件的连接。确保在不再引用文件输入流时调用其 close 方法。抛出IOException异常。 |
| 3 | public int read(int r)throws IOException{} 这个方法从 InputStream 对象读取指定字节的数据。返回为整数值。返回下一字节数据,如果已经到结尾则返回-1。 |
| 4 | public int read(byte[] r) throws IOException{} 这个方法从输入流读取r.length长度的字节。返回读取的字节数。如果是文件结尾则返回-1。 |
| 5 | public int available() throws IOException{} 返回下一次对此输入流调用的方法可以不受阻塞地从此输入流读取的字节数。返回一个整数值。 |
FileOutputStream
该类用来创建一个文件并向文件中写数据。
如果该流在打开文件进行输出前,目标文件不存在,那么该流会创建该文件。
有两个构造方法可以用来创建 FileOutputStream 对象。
使用字符串类型的文件名来创建一个输出流对象:
OutputStream f = new FileOutputStream("C:/java/hello")
也可以使用一个文件对象来创建一个输出流来写文件。我们首先得使用File()方法来创建一个文件对象:
File f = new File("C:/java/hello");
OutputStream f = new FileOutputStream(f);
创建OutputStream 对象完成后,就可以使用下面的方法来写入流或者进行其他的流操作。
| 序号 | 方法及描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | public void close() throws IOException{} 关闭此文件输入流并释放与此流有关的所有系统资源。抛出IOException异常。 |
| 2 | protected void finalize()throws IOException {} 这个方法清除与该文件的连接。确保在不再引用文件输入流时调用其 close 方法。抛出IOException异常。 |
| 3 | public void write(int w)throws IOException{} 这个方法把指定的字节写到输出流中。 |
| 4 | public void write(byte[] w) 把指定数组中w.length长度的字节写到OutputStream中。 |
下面给出一个Java IO的例子:
代码中有很多个函数:
- maxFolderNumber:测试最多可以创建多少个文件夹
- processfile:用于对文件进行处理,筛选出.c和.h结尾的文件
- caculateCode:用来计算代码中代码行数,空行行数和注释行数
- fileNumber:统计一个文件夹中文件的个数
- folderNumber:统计一个文件夹中,文件夹的个数
- length:统计文件的大小
- deleteFolder:使用递归删除一个文件夹
- Fileinfo:一次性计算文件和文件夹的个数
- copyfile:文件复制操作
- TextLinuxCnt:测试linux源码
package cn.csuftacm.poorguy.io.reader;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileFilter;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.channels.FileLock;
import javax.management.ListenerNotFoundException;
public class HomeWork {
/**
* 测试最多可以创建多少个文件夹
* @param path
* @return
* 能嵌套创建多少个文件夹取决于文件的名字所占字符有关
* 文件的全名大小在不同的系统中有限制
*/
public static int maxFolderNumber(File path,String name) {
int cnt = 0;
while(path.mkdir()) {
cnt++;
path = new File(path.getPath()+"/"+name);
}
return cnt;
}
private static void TextMaxFolderNumber() {
System.out.println("测试最大可嵌套文件夹个数:");
File file1 = new File("Text1");//创建了255个文件夹 文件名new
File file2 = new File("Text2");//创建了510个文件夹 文件名n
File file3 = new File("Text3");//创建了510个文件夹 文件名1
File file4 = new File("Text4"); //创建了146个文件夹 文件名newnew
System.out.print("文件名new:"+maxFolderNumber(file1,"new"));
System.out.print(" 文件名n:"+maxFolderNumber(file2,"n"));
System.out.print(" 文件名1:"+maxFolderNumber(file3,"1"));
System.out.println(" 文件名newnew:"+maxFolderNumber(file4,"newnew"));
//删除文件夹操作
deleteFolder(file1);
deleteFolder(file2);
deleteFolder(file3);
deleteFolder(file4);
}
public static class Filter implements FileFilter{
@Override
public boolean accept(File pathname){
return pathname.getName().endsWith(".c")
||pathname.getName().endsWith(".h")
||pathname.isDirectory();
}
}
/**
* 用来处理文件,挑选出代码的文件,进行计算
* @param file
*/
public static Fileinfo processfile(File file) {
long codetemp = 0;
long nodetemp = 0;
long blanktemp = 0;
Fileinfo info = new Fileinfo();
if(file.isFile()&&(file.getName().endsWith(".h")
||file.getName().endsWith(".c"))) {
return caculateCode(file);
}else if(file.isDirectory()){
File []files = file.listFiles(new Filter());
for (File f : files) {
codetemp+=processfile(f).getCode();
nodetemp+=processfile(f).getNode();
blanktemp+=processfile(f).getBlank();
}
}
info.setBlank(blanktemp);
info.setCode(codetemp);
info.setNode(nodetemp);
return info;
}
/**
* 用来计算代码中代码行数,空行行数和注释行数
* @param file
*/
private static Fileinfo caculateCode(File file) {
Fileinfo info = new Fileinfo();
try (BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file))){
String string;
int cnt = 0;
int blank = 0;
int node = 0;
while(null!=(string = in.readLine())){
String temp = string.trim();
//空行行数
if(temp.length()==0) {
blank++;
//两种注释的行数
}else if(temp.startsWith("/**")||temp.startsWith("*")
||temp.startsWith("*/")||temp.startsWith("//")){
node++;
}
cnt++;
}
info.setNode(node);
info.setBlank(blank);
info.setCode(cnt-node-blank);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return info;
}
/**
* 统计文件的个数
* @param folder
* @return
*/
public static int fileNumber(File folder) {
int cnt = 0;
if(folder.isFile()) {
return 1;
}
File []file = folder.listFiles();
for (File f : file) {
cnt+=fileNumber(f);
}
return cnt;
}
/**
* 统计文件夹的个数
* @param folder
* @return
*/
public static int folderNumber(File folder) {
if(folder.isFile()) {
return 0;
}
int cnt = 0;
cnt++;
File []files = folder.listFiles();
for (File f : files) {
cnt+=folderNumber(f);
}
return cnt;
}
/**
* 统计文件的大小(字节)
*
* @param file 文件或文件夹
* @return
*/
public static long length(File file) {
if (file.isFile())
return file.length();
// 文件夹
long size = 0;
// 遍历文件夹
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File f : files) {
size += length(f);
}
return size;
}
/**
* 删除一个文件夹
* @param args
*/
public static void deleteFolder(File file) {
if(file.isFile()) {
file.delete();
}else {
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File f : files) {
deleteFolder(f);
}
}
file.delete();
}
/**
* 一次性计算文件和文件夹的个数
* @param file
* @return
*/
public static Fileinfomation Fileinfo(File file) {
Fileinfomation info = new Fileinfomation();
long length = 0;
long filecnt = 0;
long foldercnt = 0;
if(file.isFile()) {
info.setFilecnt(1);
info.setLength(file.length());
return info;
}
foldercnt++;
File []files = file.listFiles();
for (File f : files) {
Fileinfomation info1 = Fileinfo(f);
length+=info1.getLength();
filecnt+=info1.getFilecnt();
foldercnt+=info1.getFoldercnt();
}
info.setLength(length);
info.setFilecnt(filecnt);
info.setFoldercnt(foldercnt);
return info;
}
/**
* 文件复制操作
* copyfile
* @param args
*/
public static void copyfile(File file1,File file2) {
if(!file2.exists()) {
try {
file2.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
String string;
try (BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file1))){
while(null!=(string=in.readLine())) {
try (BufferedWriter out = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file2,true))){
out.write(string);
out.write("
");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试最大可以迭代的文件夹层次
TextMaxFolderNumber();
//计算linux文件夹内文件的数量,文件夹数量和文件夹大小
File file1 = new File("/Users/poorguy/linux-4.19.8");
TextLinuxCnt(file1);
//代码分析,分析注释,空行和代码行的行数
System.out.println("
linux-4.19.8 中 lib目录下,代码信息统计");
File file2 = new File("/Users/poorguy/linux-4.19.8/lib");
//CaculateProcess(file2);
//测试文件复制操作
File f1 = new File("Text/abc.txt");
File f2 = new File("bcd.txt");
//copyfile(f1, f2);
//System.out.println("文件复制完毕");
deleteFolder(new File("bcd"));
}
private static void CaculateProcess(File file) {
Fileinfo info = processfile(file);
System.out.println("代码行数:"+info.getCode());
System.out.println("注释行数:"+info.getNode());
System.out.println("空行行数:"+info.getBlank());
}
private static void TextLinuxCnt(File file) {
//分开计算部分
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.print("文件个数:"+fileNumber(file)+" ");
System.out.print("文件夹个数:"+folderNumber(file)+" ");
System.out.print("文件大小:"+length(file)+" ");
t1 = System.currentTimeMillis()-t1;
System.out.println("运行时间:"+t1);
//合并计算
long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
Fileinfomation f = Fileinfo(file);
System.out.print("文件个数:"+f.getFilecnt()+" ");
System.out.print("文件夹个数:"+f.getFoldercnt()+" ");
System.out.print("文件大小:"+f.getLength()+" ");
t2 = System.currentTimeMillis()-t2;
System.out.println("运行时间:"+t2);
}
}
Fileinfomation类:
package cn.csuftacm.poorguy.io.reader;
public class Fileinfomation {
private long length = 0;
private long filecnt = 0;
private long foldercnt = 0;
public long getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(long length) {
this.length = length;
}
public long getFilecnt() {
return filecnt;
}
public void setFilecnt(long filecnt) {
this.filecnt = filecnt;
}
public long getFoldercnt() {
return foldercnt;
}
public void setFoldercnt(long foldercnt) {
this.foldercnt = foldercnt;
}
}
下面介绍一下MD5和SHA1和SHA256的使用:
MD5消息摘要算法(英语:MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm),一种被广泛使用的密码散列函数,可以产生出一个128位(16字节)的散列值(hash value),用于确保信息传输完整一致。
安全哈希算法(Secure Hash Algorithm)主要适用于数字签名标准 (Digital Signature Standard DSS)里面定义的数字签名算法(Digital Signature Algorithm DSA)。对于长度小于2^64位的消息,SHA1会产生一个160位的消息摘要。当接收到消息的时候,这个消息摘要可以用来验证数据的完整性。在传输的过程中,数据很可能会发生变化,那么这时候就会产生不同的消息摘要。 SHA1有如下特性:不可以从消息摘要中复原信息;两个不同的消息不会产生同样的消息摘要,(但会有1x10 ^ 48分之一的机率出现相同的消息摘要,一般使用时忽略)。
package cn.csuftacm.poorguy.io.md5;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.util.Arrays;
//使用MD5算法对字符进行关键字提取
public class TextIO {
public static void md5(String string) {
try {
byte[] out = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5").digest(string.getBytes());
String result = new BigInteger(1, out).toString(16);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(out));
System.out.println(result);
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void md5(File file) {
try (BufferedInputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream()) {
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int size;
while (-1 != (size = in.read(buf))) {
out.write(buf, 0, size);
}
byte[] data = out.toByteArray();
byte[] result = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256").digest(data);
String SHA256 = new BigInteger(result).toString(16);
System.out.println(SHA256);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 单个文件复制操作,给出两个文件的完整路径即可
*
* @param file1
* @param file2
*/
public static void cp(File file1, File file2) {
try (BufferedInputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file1));
BufferedOutputStream out = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file2))) {
// 用于记录每一次读取的实际大小
int size;
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
while (-1 != (size = in.read(buf))) {
out.write(buf, 0, size);
}
time = System.currentTimeMillis() - time;
//System.out.println("文件复制成功" + time);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
/**
* 文件的复制操作
* @param file1
* @param file2
*/
public static void copy(File file1, File file2) {
// 先建立文件夹
if (!file2.exists()) {
file2.mkdirs();
}
if (file1.isFile()) {
cp(file1, file2);
} else {
String path = file1.getPath();
File[] files = file1.listFiles();
for (File f : files) {
String temp = f.getPath();
int len = temp.length() - path.length();
String p = f.getPath().substring(path.length(), temp.length());
File tempfile = new File(file2.getPath() + p);
if (!f.isFile()) {
copy(f, tempfile);
} else {
cp(f, tempfile);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// md5("");
// md5("PoorGuy");
// md5("poorguy");
// md5("/usr/src/linux-2.4.20-8/include -Wall taoning.c");
// cp("/Users/poorguy/Downloads/linux.tar.xz", "linux2.tar.xz");
// md5(new File("linux2.tar.xz"));
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
copy(new File("/Users/poorguy/linux-4.19.8"), new File("/Users/poorguy/linux"));
time = System.currentTimeMillis()-time;
System.out.println("复制成功:"+time);
}
}
以上是关于Java IO基础总结的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章