第八章 常用实用类
Posted araysel
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了第八章 常用实用类相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、String类
- String类在java.lang包中,专门处理字符序列,为final类,不可扩展。
- String常量对象放在常量池中,有自己的引用和实体。
- String对象放在动态区,可声明和创建对象:
String s = new String("we are student"); String t = new String("we are student");
对象变量s中存放着引用,所以s==t的值为false。用户无法输出对象的引用,只能输出实体。
- 也可以用已创建的String对象创建另一个String对象。
String tom = new String(s); - 用字符数组创建String对象
char a[] = {‘J‘,‘a‘,‘v‘,‘a‘}; String s = new String(a);
用String(char a[],int startIndex,int count)提取字符数组a中一部分字符创建String对象
char a[] = {‘‘J,‘a‘,v‘‘a,‘s‘,c,‘r‘,‘i‘,‘p‘,‘t‘}; String s = new String(a,2,4);
- 将String常量的引用赋值给String对象
String s1,s2; s1 = "你好"; s2 = "你好";
s1,s2中存放的是常量池中"你好"的引用,故s1==s2为true。再进行s1 = "boy"的运算时,s1中的值发生变化。
字符串用“+”实现字符串并置,参与并置的字符串只要有一个为变量,新String对象的引用就存放到变量区。
public class Example8_1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String hello = "你好"; //两个常量进行并置,其引用在常量池 String testOne = "你"+"好"; //hello和testOne的引用均为"你好"在常量池中的引用 System.out.println(hello==testOne); //true System.out.println("你好"==testOne); //true System.out.println("你好"==hello); //true String you = "你"; String hi = "好" ; //两个变量进行并置,其引用在动态区 String testTwo = you+hi; System.out.println(hello==testTwo); //false //在动态区诞生新对象 String testThree = you+hi; System.out.println(testTwo==testThree); //false } }
二、String类常用方法
- public int length():获取String对象字符序列长度。
- public boolean equals(String s):比较两个String对象的字符串是否相同。
- public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String s):比较两个String对象的字符串是否相同,忽略大小写。
- public boolean startsWith(String s):判断当前字符的前缀是否为s。
- public boolean endsWith(String s):判断当前字符的后缀是否为s。
- public int compareTo(String s):按字典序判断当前字符与s的序列比较大小,大于则返回正值,小于则返回负值,等于则返回0。
- public int compareToIgnoreCase(String s):按字典序判断当前字符与s的序列比较大小,大于则返回正值,小于则返回负值,等于则返回0,忽略大小写。
- public static void sort(String [] a):在java.util包中的Arrays类中,将String数组a按照字典序排列。
- public boolean contains(String s):当前对象是否包含s。
- public int indexOf(String s):从0索引位置检索首次出现s的位置,返回该位置,若没有检索到,则返回-1。
- public int lastIndexOf(String s) :从0索引位置检索最后一次出现s的位置,返回该位置,若没有检索到,则返回-1。
- public int IndexOf(String s,int startpoint):startpoint指定检索的开始位置。
- String对象的字符序列中如果使用目录符,windows目录符必须写成"//"。
- public String subString(int startpoint):获得新的String对象,复制当前对象startpoint位置至最后位置的字符序列。
- public String subString(int start,int end):获得新的String对象,复制当前对象start位置至end-1位置的字符序列。
- public String trim():获得新的String对象,为当前对象去掉前后空格的字符序列。
三、字符串转化
- public static int parseInt(String s):在java.lang包中的Integer类中,可将数字字符转化成int数据。
- 类似的,有parseByte()、praseShort()等方法。
- public static String valueOf(int/byte/long/float/double n):在java.lang包中的String类中,可将int数据转化成String。
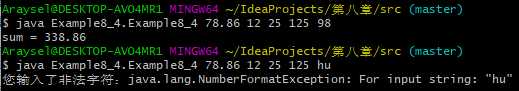
public class Example8_4 { public static void main(String[] args) { double sum = 0,item = 0; boolean computable = true; for (String s:args) { //应用程序的main方法中参数args能接受用户从键盘输入的字符序列 try { item = Double.parseDouble(s); sum = sum + item; } catch (NumberFormatException e) { System.out.println("您输入了非法字符:" + e); computable = false; } } if (computable) System.out.println("sum = "+sum); } }
- public String toString():在Object类中,可以被任意对象调用,返回的String对象的一般形式为:
创建对象的类名字@对象引用的字符串表示
Object的直接或间接子类也可以重写toString()方法,如java.util包中的Date类就重写了toString()方法。
四、字符串与字符数组、字节数组
- public void getChars(int start,int end,char c[],int offset):在String类中,将String从start到end-1位置上的字符复刻到参数c制定的数组中,从c的offset处开始存放这些字符。
- public char[] toCharArray():将String的全部字符存放在一个字符数组中。
- String(byte[]):String类的构造方法,用指定的字节数组构造一个String对象。
- String(byte[],int offset,int length):用指定的字节数组的一部分,从offset开始取length个字节,构造String对象。
- public byte[] getByte():使用平台默认字符编码,将当前的String对象的字符序列存放到字节数组中,并返回数组引用。
- public byte[] getByte(String charsetName):使用参数指定字符编码。
五、正则表达式及字符串的替换和分解
- 正则表达式是String对象的字符序列,含有特殊意义字符(称作元字符)。
"0cat"、"1cat"、"2cat"、"3cat"等都是和正则表达式"\\dcat"匹配的字符序列
- public boolean matches(String regex):在String类中的方法,判断当前String对象是否和正则表达式regex相匹配。
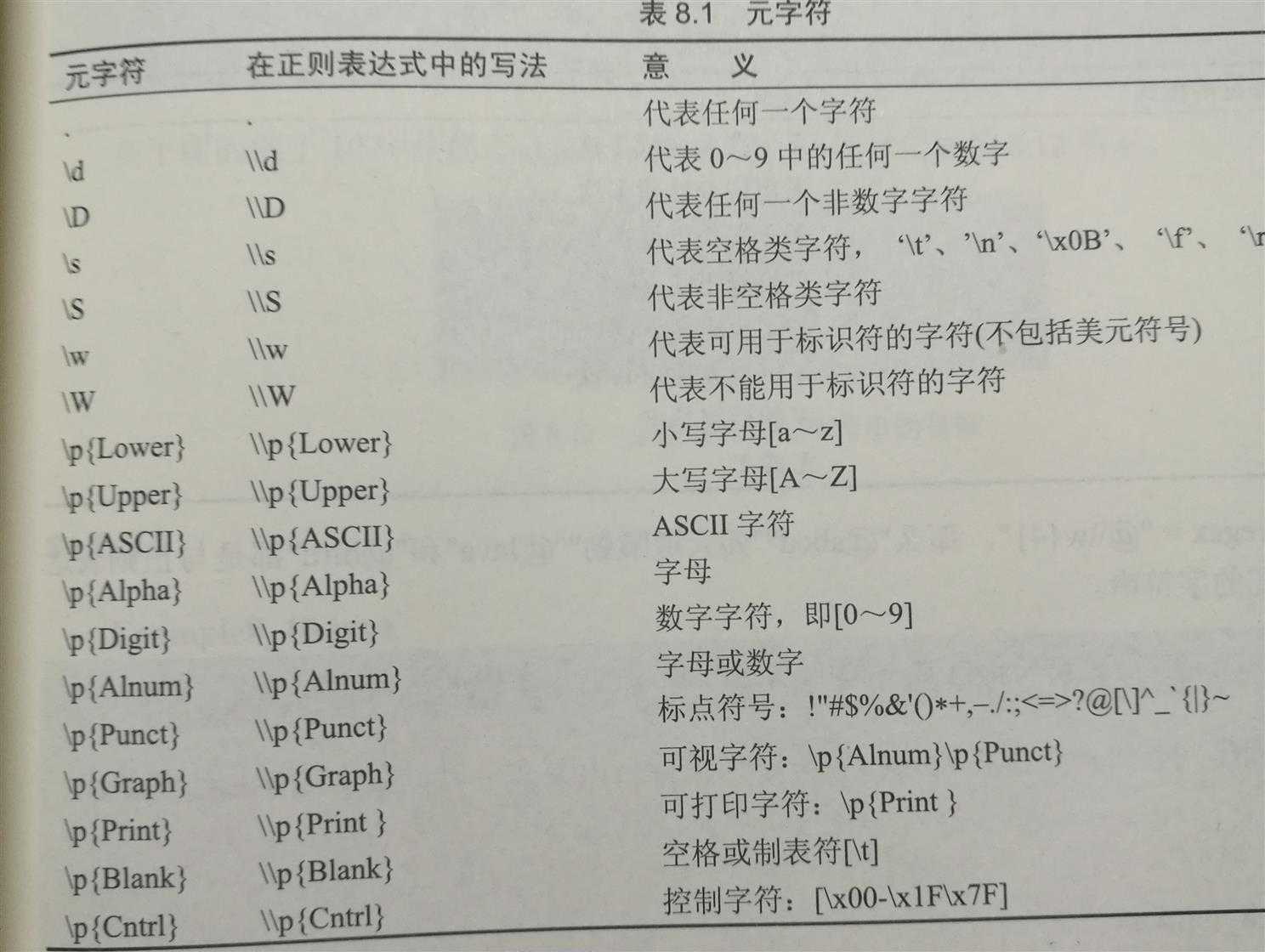
- 常用元字符及其意义:

- 在正则表达式可以使用限定修饰符:
若regex = "@\\w{4}",那么"@abcd"、"@天道酬勤"、"@Java"、"@bird"都与正则表达式regex相匹配

- public String replaceAll(String regex,String replacement):返回一个新的String对象,将当前String对象的字符序列中所有和参数regex匹配的字符序列,用replacement的字符序列替换。
String str = "12hello567bird".replaceAll("[a-zA-Z]+","你好"); 得到str字符序列是"12你好567你好" - public String[] spilt(String regex):String类中,使用regex作为分隔标记,分解当前String对象,分解出的单词存放在String数组。
String str = "1949年10月1日是中华人民共和国成立的日子"; String digitWord[] = str.spilt(regex); 那么,digitWord[0]、digitWord[1]、digitWord[2]分别是"1949"、"10"、"1"
注意:split方法认为分隔标记的左右侧都应该是单词。
六、StringTokenizer类
- 在java.util包中,有两种构造方法。
- StringTokenizer(String s):为s构造一个分析器,使用默认的空格符、换行符、回车符、Tab符、进纸符作分隔标记。
- StringTokenizer(String s,String delim):为s构造一个分析器,使用delim中字符的任意排列作分隔标记。
//分隔标记为空格 StringTokenizer fenxi = new StringTokenizer("You are welcome"); //分隔标记为#*的任意排列 StringTokenizer fenxi = new StringTokenizer("You#*are*##welcome","#*");
- 一个StringTokenizer对象为一个字符串分析器,可使用nextToken()方法逐个获取String对象中的单词,每调用一次nextToken(),获得下一个单词,分析器中负责计时的变量就减1,初始值为单词个数。
- 可运用while循环来获取单词,利用hasMoreTokens()方法,计数变量>0时,返回true,否则返回false。
- countTokens()方法得到计数变量的值。
七、Scanner类
- Scanner(String s):构造一个Scanner对象。
- useDelimiter(正则表达式):Scanner调用此方法,将此正则表达式作为分隔标记。若不指定分隔标记,默认用空白字符作分隔标记。
- Scanner对象调用next()方法返回被解析的单词。
- hasNext():若单词未全部返回,则返回true,否则返回false。
- hasInt()、hasDouble():将数字型单词转化为int、double返回。若发生InputMismatchException异常,可调用next()返回非数字单词。
八、StringBuffer类
- String对象的字符序列的字符不能被修改、删除,即String对象的实体不能再发生变化。
- StringBuffer()类的对象的实体的内存空间可以自动改变大小,便于存放一个可变的字符序列。
- StringBuffer对象可以调用append()方法追加字符序列。
- StringBuffer():分配的初始容量为16个字符,当实体的长度大于16时,自动增加。
- StringBuffer(int size):指定初始容量为size个字符。
- StringBuffer(String s):初始容量为s的长度加上16个字符。
- length():StringBuffer对象调用,获取字符序列的长度。
- capacity():StringBuffer对象调用,当前实体的实际容量。
- StringBuffer append(String s):将s追加到当前StringBuffer对象后,返回当前StringBuffer对象的引用。
- StringBuffer append(int n):将n转化为String对象,再追加到当前StringBuffer对象后,返回当前StringBuffer对象的引用。
- StringBufferappend(Object o):将Object对象o的字符序列表示追加到当前StringBuffer对象后,返回当前StringBuffer对象的引用。
- public charcharAt(int n):得到StringBuffer对象的位置n上的字符。
- public char setCharAt(int n,char ch):将StringBuffer对象的位置n上的字符替换为ch。
- StringBuffer insert(int index,String str):将str的字符序列插入到index指定的位置。
- public StringBuffer reverse():将当前对象的字符序列翻转,返回当前对象的引用。
- StringBuffer delete(int startIndex,int endIndex):删除startIndex位置到endIndex-1位置处的字符序列,返回当前对象的引用。
- deleteCharAt():删除index位置上的一个字符。
- StringBuffer replace(int startIndex,int endIndex,String str):将startIndex位置到endIndex-1位置处的字符序列替换为str,返回当前对象的引用。
九、Date类与Calendar类
- Date类在java.util包中,使用无参构造方法Date()可获得本机当前的日期和时间。
Date nowTime = new Date(); System.out.println(nowTime); //Date类重写了Object类的toString方法,输出实体而不是引用
输出 Sat Oct 01 14:39:22 CST 2016
- 计算机系统自身的时间为“公元”,为1970年1月1日0时(格林威治时间),北京时间为08时。
- 使用构造方法Date(long time):负数为公元后time毫秒,正数为公元前time毫秒。
Date date1 = new Date(1000); //北京时间1970年1月1日08时00分01秒 Date date2 = new Date(-1000); //北京时间1970年1月1日07时59分59秒
可用System.currentTimeMillis()获取当前系统时间,返回从“公元”走到现在的毫秒数。
- Calendar类在java.util包中,使用此类的static方法getInstance()初始化一个日历对象。
- set(int year,int month,int date,[int hour,int minute,[int second]]):将日历翻到任何时间,year为负标明是公元前(实际)。
- public int get(int field):获取年份、月份、星期等信息,field为Calendar类的静态常量:
Calendar calendar = Calender.getInstance(); calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH); //获取月份,0表示一月,1表示二月 calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK); //获取星期信息,1表示星期日,2表示星期一
public long getTimeInMillis()返回当前对象的毫秒计时(与“公元”的差值)。
十、Math类、BigInteger类、Random类
- Math类在java.lang包中,有两个static常量E和PI。
- public static long abs(double a)、double max(double,double)、min(double,double)、random()[产生0~1的随机数,不包括1]、pow(double,double)、sqrt()、log()、sin()、asin()、ceil()、floor()、long round()[四舍五入]。
- BigInteger类在java.math包中,其对象用来处理特别大的整数。
- BigInteger(String val):构造BigInteger类的对象,若val含有非数字,则发生NumberFormatException异常。
- public BigInteger add/subtract/multiply/divide/remainder(BigInteger val):返回当前对象与val的和/差/积/商/余。
- public int compareTo(BigInteger val):返回当前对象与val的比较结果,1(大于)、-1(小于)、0(等于)。
- public BigInteger abs():返回绝对值。
- public BigInteger pows(int a):当前对象的n次幂。
- public String toString(int p):当前对象的p进制的字符串表示,无参时,为十进制。
- Random类在java.util包中,更灵活地获得随机数。
- Random()或Random(long seed):构造Random对象,即随机数生成器,seed为种子,可调用nextInt()或nextInt(int m)返回一个随机整数。
Random random = new Random(); random.nextInt(); //返回一个整数 random.nextInt(int m); //返回一个0~m的整数,不包括m
- public boolean nextBoolean():得到ture或false。
十一、数字格式化
- 数字格式化,就是按照指定的格式得到一个字符序列。
- 使用String类调用format方法对数字进行格式化。
例: String s = String.format("%.2f",3.141592); //得到3.14 - 加号修饰符“+”:强制加上正号。
- 逗号修饰符“,”:格式化整数时,按“千”分组。
- %e(%E):格式化为科学记数法的十进制的浮点数。
十二、Class类与Console类
- Class类在java.lang包中,帮助程序创建其他类的实例。
- 使用Class的类方法public static Class forName(String className)创建一个和ClassName指定的类相关的Class对象
public static Class forName(String className) throws ClassNotFoundException
如果类在某个包中,className必须带有包名,例:className = "java.util.Date"。
- 使用public Object newInstance()方法得到一个className类的对象
public Object newInstance() throws InstantiationException,IllegalAccessException
className类必须有无参数的构造方法。
十三、Console类
- Console类在java.io包中,在键盘输入一行文本时,是文本不回显(不再命令行显示)。
- 使用System类中的static方法console()返回Console类的一个对象
Console cons = System.console();
cons调用方法readPassword()方法读取用户在键盘上输入的一行文本,将文本以char数组返回
char [] passwd = cons.readPassword();
十四、Pattern类与Matcher类
- Pattern类和Matcher类在java.util.regex包中,用来进行模式匹配,也就是检索和指定模式匹配的字符序列。
String input = "hello,good morning,this is a good idea";
若想知道good出现在input的那个位置,需使用这两个类。
- 建立Pattern对象(模式对象):
String ergex = "good"; pattern = Pattern.compile(regex);也可以调用compile(String regex,int flags):flags取Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE时,模式匹配时忽略大小写。
- 利用Matcher类得到检索String对象input的实例matcher(匹配对象)
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(input);
模式对象pattern调用matcher()方法创建Matcher类的对象。
- boolean find():返回boolean值,是否能将regex与input匹配,每次调用时,从上次结束的索引处开始。
- start()/end():返回regex出现在input中的开头和结尾的索引。
- matcher.group():返回检索到的与regex匹配的字符串。
- public String replaceAll(String replacement)/public String replaceFirst(String replacement):将regex匹配到的子字符序列替换为replacement/只替换第一个匹配到的子字符串。
习题
8.4.1
public class Practice8_4_1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = "I love you baby"; String str2 = str1.toUpperCase(); System.out.println(str2); str2 = str2.toLowerCase(); System.out.println(str2); System.out.println(str1.concat(",I miss you.")); } }

8.4.3
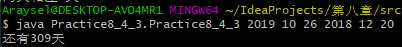
import java.util.Calendar; public class Practice8_4_3 { public static void main(String[] args) { String [] str = new String[7]; int date [] = new int[7]; for(int i = 1;i < str.length;i++) { str[i] = args[i-1]; date[i] = Integer.parseInt(str[i]); } Calendar calendarOne = Calendar.getInstance(); Calendar calendarTwo = Calendar.getInstance(); calendarOne.set(date[1],date[2]-1,date[3]); calendarTwo.set(date[4],date[5]-1,date[6]); int day = (int)((calendarOne.getTimeInMillis()-calendarTwo.getTimeInMillis())/(1000*60*60*24)); System.out.printf("还有%d天",day); } }
8.4.5
import java.util.*; public class Practice8_4_5 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); String str = scanner.nextLine(); String regex = "[^0123456789]+"; String [] s = str.split(regex); String fin = ""; for(int i = 0;i < s.length;i++) { fin = fin + s[i]; } System.out.println("fin"); } }

8.4.6
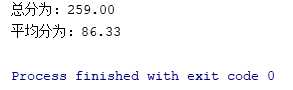
import java.util.Scanner; public class Practice8_4_6 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner("数学87分,物理76分,英语96分"); scanner.useDelimiter("[^0123456789.]+"); double sum = 0; int count = 0; while(scanner.hasNext()) { sum = sum + scanner.nextDouble(); count++; } System.out.printf("总分为:%.2f ",sum); System.out.printf("平均分为:%.2f ",sum/count); } }
以上是关于第八章 常用实用类的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章