第2章 ***********sed***********. 1目 录
2.1 -------sed命令小结及小结图---- 1
2.2 -------第几行---------- 2
2.3 -------最后一行---------- 2
2.4 ---------从哪行到哪行-------- 3
2.5 -------某几行--------- 3
2.6 ---------上插入行----------- 3
2.7 -----------不包含oldboy(条件)----- 4
2.8 -----sed不显示空行----------- 4
2.9 ------------把所有小写字母()起来----- 4
2.10 -----变量运用------ 5
2.11 --------------命令行chkconfig优化开机自启----- 6
2.12 ----------找特定行替换某一些内容----- 6
2.13 -----------显示和不显示,要取消默认输出... 7
2.14 --------------chkconfig 用sed优化----------- 8
第3章 -------shell基础------- 9
3.1 --------写脚本---- 9
3.2 -------------变量-------- 9
3.3 -----------永久生效有几种-- 10
3.4 --------- 普通变量,环境变量与脚本---------- 10
3.5 ------------------vim批量加内容v Ctrl+v---- 11
3.6 ----------awk支持小数的计算------------ 11
3.7 ---------read与计算应用----------- 12
3.8 --------------test和[ ] 进行条件判断----------------- 14
3.9 ----&& || 条件判断---------- 14
3.10 ------------如果---- 15
3.11 -----------if条件判断------- 15
3.12 -------------- 参数个数判断------------- 15
3.13 ------------for循环------- 18
3.14 ------------chkconfig优化开机自启动服务的脚本----- 19
3.15 ------------出错暂时无法解决的脚本-------- 19
3.16 ------------应该再来一个对是否是数字的判断----- 20
3.17 ------------查看脚本执行的状况- sh -x --------- 21
第4章 **************awk*******. 21
4.1 ------awk执行流程图... 21
4.2 -----------awk数组结构-------- 22
4.3 ------awk执行过程表--------- 22
4.4 ---------awk分隔符哪行哪列-------- 24
4.5 --------awk题---------- 24
4.6 -----------awk替换------------ 26
4.7 ----企业案例3:统计/etc/services文件里面的空行数量--- 27
4.8 --------awk 数组----------- 28
4.9 -------企业面试题1:统计域名访问次数---- 处理以下文件内容,将域名取出并根据域名进行计数排序处理:(百度和sohu面试题) http://www.etiantian.org/index.html http://www.etiantian.org/1.html http://post.etiantian.org/index.html http://mp3.etiantian.org/index.html http://www.etiantian.org/3.html http://post.etiantian.org/2.html 30
4.10 ---------awk统计的课后题------- 31
4.11 ----------awk识别花括号加条件---- 34
4.12 ----- a[$1]=a[$1]+$2----- 35
4.13 5. ip出现次数及使用流量... 36
4.14 ------awk 中的begin---------- 40
4.15 ------------awk版本4以上有替换功能----- 41
第5章 ---------总结大集合----- 41
5.1 -------查看端口总结 踢死了妮妮(tslnn)------- 42
5.2 ----------- 排查无法上网总结 3p----- 43
5.3 -------------- vi/vim快捷方式总结---- 44
5.4 ---sed总结-------- 46
5.5 ------awk总结--------- 46
5.6 ------rename----- 47
第2章 ***********sed***********
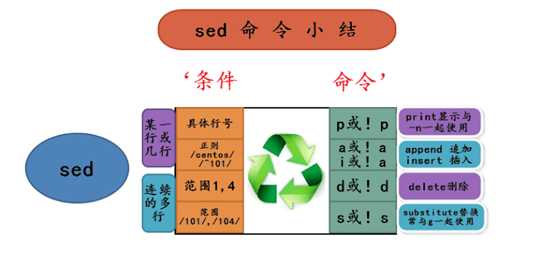
2.1 -------sed命令小结及小结图----
sed 参数 条件 命令(sed内置命令) 文件
命令:i,a,d,s,p
默认输出,取消默认输出;找谁做什么,不做什么,(替换不替换,显示不显示,可以插加不插加吗,可以删不删吗)
!:放在命令前吗?
增:(行号i 行号a 内容)上插下追,insert append ,加多行操作\\n cat也能多行追加
删:d 同,命令改d
改(替换):‘Ms###Ng‘ M查找s 替换, g 全局替换 缺省替换行第一个,加数字几就是找到的第几个进行替换,ng从哪个到最后替换。变化的定义成变量,再替换,双引号解析,双引号变量替换成变量。找到哪行替换,找到不包含谁的行不替换(排除哪行其他行替换)
四组长吴 2017/9/19 9:02:59
可以sed ‘2s#[0-9]#<&>#2p‘ 精准定位到第二行的第二个匹 配项
查:p,-n打印经常要取消默认输出, ;单行,多行,第几行到第几行,哪儿到哪儿,逗号隔开,;某几行,分号隔开条件加命令;日志第一个15到第一个08,最后一行$
p和d显示不显示谁,d相当于排除显示
cat
>person.txt <<EOF
101,oldboy,CEO
102,zhangyao,CTO
103,Alex,COO
104,yy,CFO
105,feixue,CIO
EOF
2.2 -------第几行----------
[[email protected]小马过河 old]# sed -n ‘3p‘ person.txt
103,Alex,COO
[[email protected]小马过河 old]# sed -n ‘/oldboy/p‘ person.txt
101,oldboy,CEO
2.3 -------最后一行----------
方法一:
[[email protected]小马过河 old]# sed -n ‘$p‘ person.txt
105,feixue,CIO
方法二:
[[email protected]小马过河 old]# sed -n "\\$p" person.txt
105,feixue,CIO
2.4 ---------从哪行到哪行--------
[[email protected]小马过河 old]# sed -n ‘2,4p‘ person.txt
102,zhangyao,CTO
103,Alex,COO
104,yy,CFO
[[email protected]小马过河 old]# sed -n ‘/zhangyao/,/yy/p‘ person.txt
102,zhangyao,CTO
103,Alex,COO
104,yy,CFO
[[email protected]小马过河 old]#
2.5 -------某几行---------
[[email protected]小马过河 old]# sed -n ‘2p;3p;5p‘ person.txt
102,zhangyao,CTO
103,Alex,COO
105,feixue,CIO
lrzsz zip文件两个系统均能用,xshell属性指定下载/加载路径
离开死s,过来ri
[[email protected]小马过河 old]# zip -r a.zip /etc/services
adding: etc/services (deflated 80%)
压缩了百分比
2.6 ---------上插入行-----------
[[email protected]小马过河 old]# sed ‘/zhangyao/i wo shi machangwei‘ person.txt
101,oldboy,CEO
wo shi machangwei
102,zhangyao,CTO
2.7 -----------不包含oldboy(条件)-----
方法一:
[[email protected]小马过河 old]# sed -n ‘/oldboy/!p‘ person.txt
102,zhangyao,CTO
103,Alex,COO
104,yy,CFO
105,feixue,CIO
方法二:
[[email protected]小马过河 old]# sed ‘/oldboy/d‘ person.txt
102,zhangyao,CTO
103,Alex,COO
104,yy,CFO
105,feixue,CIO
2.8 -----sed不显示空行-----------
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# cat 1.txt |sed ‘/[a-z0-9:/]/!d‘
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
2.9 ------------把所有小写字母()起来-----
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# sed ‘s#([a-z])#(\\1)#g‘ 1.txt -r
(r)(o)(o)(t):(x):0:0:(r)(o)(o)(t):/(r)(o)(o)(t):/(b)(i)(n)/(b)(a)(s)(h)
(b)(i)(n):(x):1:1:(b)(i)(n):/(b)(i)(n):/(s)(b)(i)(n)/(n)(o)(l)(o)(g)(i)(n)
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# sed ‘s#[0-9]#<&>#3‘ person.txt
10<1>,oldboy,CEO
10<2>,zhangyao,CTO
10<3>,Alex,COO
10<4>,yy,CFO
10<5>,feixue,CIO
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# sed ‘s#,#(,)#‘ person.txt
101(,)oldboy,CEO
102(,)zhangyao,CTO
103(,)Alex,COO
104(,)yy,CFO
105(,)feixue,CIO
2.10 -----变量运用------
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# sed "s#$ma#m#g" person.txt
101,oldboy,mEO
102,zhangyao,mTO
103,Alex,mOO
104,yy,mFO
105,feixue,mIO
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# sed "s#$ma#m$mam#g" person.txt
101,oldboy,mEO
102,zhangyao,mTO
103,Alex,mOO
104,yy,mFO
105,feixue,mIO
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# sed "s#$ma#m$ma#g" person.txt
101,oldboy,mCEO
102,zhangyao,mCTO
103,Alex,mCOO
104,yy,mCFO
105,feixue,mCIO
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# sed "s#$ma#$ma#g" person.txt
101,oldboy,CEO
102,zhangyao,CTO
103,Alex,COO
104,yy,CFO
105,feixue,CIO
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# sed "s#$ma#$mam#g" person.txt
101,oldboy,EO
102,zhangyao,TO
103,Alex,OO
104,yy,FO
105,feixue,IO
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]#
2.11 --------------命令行chkconfig优化开机自启-----
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# chkconfig|sed -rn ‘/sshd|network|rsyslog|crond|systat/!s#^(.*)0:.*$#chkconfig \\1 off#gp‘|bash
找到!不替换,取消它的默认输出,
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]#
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# chkconfig|sed -r ‘/sshd|network|rsyslog|crond|systat/d‘|sed -r ‘s#^(.*)0:.*$#chkconfig \\1 off#g‘|bash
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# chkconfig
2.12 ----------找特定行替换某一些内容-----
其他行为默认输出
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# sed ‘/yy/s#[0-9]##g‘ person.txt
101,oldboy,CEO
102,zhangyao,CTO
103,Alex,COO
,yy,CFO
105,feixue,CIO
不包含yy的行前面的数字替换,默认输出和取消默认输出
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# sed -n ‘/yy/s#[0-9]##gp‘ person.txt
,yy,CFO
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# sed -n ‘/yy/!s#[0-9]##gp‘ person.txt
,oldboy,CEO
,zhangyao,CTO
,Alex,COO
,feixue,CIO
[email protected]小马过河 ~]# sed ‘/yy/!s#[0-9]##g‘ person.txt
,oldboy,CEO
,zhangyao,CTO
,Alex,COO
104,yy,CFO
,feixue,CIO
2.13 -----------显示和不显示,要取消默认输出
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# sed -n ‘/old/!p‘ person.txt
102,zhangyao,CTO
103,Alex,COO
104,yy,CFO
105,feixue,CIO
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# sed -n ‘/old/p‘ person.txt
101,oldb
除了要找的显示一次其余的显示两次
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# sed ‘/old/!p‘ person.txt
101,oldboy,CEO
102,zhangyao,CTO
102,zhangyao,CTO
103,Alex,COO
103,Alex,COO
104,yy,CFO
104,yy,CFO
105,feixue,CIO
105,feixue,CIO
找到谁不删除和找到谁删除,不需要取消默认输出,可以用来显示哪行不显示哪行(不要空要空呢?)
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# sed ‘/old/d‘ person.txt
102,zhangyao,CTO
103,Alex,COO
104,yy,CFO
105,feixue,CIO
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# sed ‘/old/!d‘ person.txt
101,oldboy,CEO
2.14 --------------chkconfig 用sed优化-----------
方法总结:如果想要引用一堆东西中的某一列然后批量生成其它的东西,一个方法是用sed找到找一列,保护起来反向引用替换成想要的批量命令,交给bash执行。即是用sed批量生成含有某一列变量的各种内容
先批量显示一下做得命令,不要忘了交给bash执行。for循环哪里也有一个方法
sshd 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
svnserve 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
sysstat 0:off 1:on 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
udev-post 0:off 1:on 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# chkconfig|sed -nr ‘/sshd|network|crond|sysstat|rsyslog/!s#(.*)0:.*#chkconfig \\1 off#gp‘|bash
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# chkconfig
abrt-ccpp 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
abrtd 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
acpid 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
atd 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
auditd 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
blk-availability 0:off 1:on 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
cpuspeed 0:off 1:on 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
crond 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
条件,判断,循环,变量
定义函数,case判断执行
第3章 -------shell基础-------
3.1 --------写脚本----
命令解释器:(几个人,交给bash执行)
注释:路径,作者
脚本
---------
绝对路径,相对路径执行脚本 相对要有执行权限
3.2 -------------变量--------
环境变量 普通变量 特殊变量
sed 外面删除内容
3.3 -----------永久生效有几种--
3.4 --------- 普通变量,环境变量与脚本----------
执行脚本使用变量,普通变量放入脚本或(export)定义成环境变量才可以
a=213
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# sh a
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# export a=213
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# sh a
213
unset 变量 取消变量,环境的也可以
用户登录显示的东西,运行的脚本/etc/profile.d/
/etc/profile、/etc/bashrc、
/etc/profile.d/
~/.bash_profile ~/.bashrc
[[email protected]小马过河 profile.d]# ma=2
[[email protected]小马过河 profile.d]# echo $ma
2
[[email protected]小马过河 profile.d]# echo $mam
[[email protected]小马过河 profile.d]# echo $ma m
2 m
[[email protected]小马过河 profile.d]# echo "$ma"m 方法一
2m
[[email protected]小马过河 profile.d]# echo ${ma}m 方法二
2m
[[email protected]小马过河 profile.d]# echo ·$m·am 错误一
··am
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# echo `$a`a 错误二
-bash: 1: command not found
a
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# echo $($a)a 错误三
-bash: 1: command not found
a
3.5 ------------------vim批量加内容v Ctrl+v----
单用户进入,救援模式进入
vi从第几行到最后一行,:n,$s###g
当前行到最后一行: :.$
所有航
批量加内容v Ctrl+v 上下左右选中输入内容,按Esc退出,不能用Alt选中,因为Alt是xshell功能,不是vim的功能
3.6 ----------awk支持小数的计算------------
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# awk -va=1 -vb=3 ‘BEGIN{print a/b}‘
0.333333
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# vim 1.t
#!/bin/bash
echo $1 $3 $0 $# 怎么使用参数
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# sh 1.t
1.t 0
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# sh 1.t a b c d e
a c 1.t 5
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# echo $? #$?看上一个命令执行的状况
可以看命令行的,可以看脚本执行情况的
0
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# s 1.t a b c d e
-bash: s: command not found
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# echo $?
127
$?有脚本?
:noh
3.7 ---------read与计算应用-----------
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# vim cal.sh
#!/bin/bash
read -t40 -p "输入你的游戏帐号:" a \\n
read -t40 -p "输入你的游戏帐号:" b \\n
#a=$1
#b=$2
#echo a + b|bc
#echo a - b|bc
#echo a \\* b|bc
#echo a \\/ b|bc
#echo a \\% b|bc
#echo a \\^ b|bc
awk -va=$a -vb=$b ‘BEGIN{print a+b}‘
awk -va=$a -vb=$b ‘BEGIN{print a-b}‘
awk -va=$a -vb=$b ‘BEGIN{print a*b}‘
awk -va=$a -vb=$b ‘BEGIN{print a/b}‘
awk -va=$a -vb=$b ‘BEGIN{print a%b}‘
awk -va=$a -vb=$b ‘BEGIN{print a^b}‘
~
~
"cal.sh" 17L, 434C written
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# sh cal.sh
输入你的游戏帐号:4
输入你的游戏帐号:3
7
1
12
1.33333
1
64
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# vim cal.sh
#!/bin/bash
read -t40 -p "输入你的游戏帐号:" a \\n
read -t40 -p "输入你的游戏帐号:" b \\n
echo $a + $b|bc
echo $a - $b|bc
echo $a \\* $b|bc
echo $a \\/ $b|bc
echo $a \\% $b|bc
echo $a \\^ $b|bc
#awk -va=$a -vb=$b ‘BEGIN{print a+b}‘
#awk -va=$a -vb=$b ‘BEGIN{print a-b}‘
#awk -va=$a -vb=$b ‘BEGIN{print a*b}‘
#awk -va=$a -vb=$b ‘BEGIN{print a/b}‘
#awk -va=$a -vb=$b ‘BEGIN{print a%b}‘
#awk -va=$a -vb=$b ‘BEGIN{print a^b}‘
~
~
~
~
"cal.sh" 15L, 434C written
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# sh cal.sh
输入你的游戏帐号:4
输入你的游戏帐号:3
7
1
12
1
1
64
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]#
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# find . -name "machangwei"
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# echo $?
0
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# cat machangwei
cat: machangwei: No such file or directory
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# echo $?
1
3.8 --------------test和[ ] 进行条件判断-----------------
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# test -f changwei
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# echo $?
1
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# test -f a
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# echo $?
0
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# [ -d ma ]
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# echo $?
1
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# mkdir changwei
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# [ -d changwei ]
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# echo $?
0
3.9 ----&& || 条件判断----------
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# [ -d changwei ]&&echo dir exit
dir exit
我感觉机子在前一个命令结束之后有一个对返回值的判断
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# [ -f sss ]||touch sss
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# ls
1.t a cal.sh cal.sh.bak changwei date.sh html.sh ip.sh sss tar.sh
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# [ -d xiaoma ]&&echo dir exit
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]#
3.10 ------------如果----
如果文件不存在就干啥,如果文件存在就不干啥了
3.11 -----------if条件判断-------
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# sh if.sh
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# ll maxiaowei
total 0
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# cat if.sh
#!/bin/bash
if [ -d maxiaowei ];
then
echo maxiaowei exit
else
mkdir maxiaowei
fi
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]#
3.12 -------------- 参数个数判断-------------
"canshu.sh" 10L, 135C written
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# sh canshu.sh 2 3
5
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# sh canshu 2
sh: canshu: No such file or directory
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# sh canshu.sh 2 3
5
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# sh canshu.sh 2
canshu wei 2
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# cat canshu.sh
#!/bin/bash
a=$1
b=$2
if [ $# -ne 2 ];
then
echo canshu wei 2
exit
else
awk -va=$a -vb=$b ‘BEGIN{print a+b}‘
fi
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]#
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# sh canshu.yuan 4 3
7
1
12
1.33333
1
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# sh canshu.yuan 4
canshu wei 2
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# cat anshu.yuan
cat: anshu.yuan: No such file or directory
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# cat canshu.yuan
#!/bin/bash
a=$1
b=$2
if [ $# -ne 2 ];
then
echo canshu wei 2
exit
else
awk -va=$a -vb=$b ‘BEGIN{print a+b}‘
awk -va=$a -vb=$b ‘BEGIN{print a-b}‘
awk -va=$a -vb=$b ‘BEGIN{print a*b}‘
awk -va=$a -vb=$b ‘BEGIN{print a/b}‘
awk -va=$a -vb=$b ‘BEGIN{print a%b}‘
fi
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]#
高超的脚本:
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# sh gaochao.sh
命令错误 请输入两个数字
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# sh gaochao.sh 4 5
I love you 开始输出结果
相加结果
9
相减结果
-1
相乘结果
20
相除结果
0.8
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# cat gaochao.sh
#!/bin/bash
num=$#
if [ "$num" -ne "2" ] ; then
echo "命令错误 请输入两个数字"
exit 1
else
echo -e "I love you 开始输出结果\\n"
fi
a=$1
b=$2
echo "相加结果"
awk -vnum1=$1 -vnum2=$2 ‘BEGIN{print num1+num2}‘
echo "相减结果"
awk -vnum1=$1 -vnum2=$2 ‘BEGIN{print num1-num2}‘
echo "相乘结果"
awk -vnum1=$1 -vnum2=$2 ‘BEGIN{print num1*num2}‘
echo "相除结果"
awk -vnum1=$1 -vnum2=$2 ‘BEGIN{print num1/num2}‘
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]#
结合一下 read
结合函数
3.13 ------------for循环-------
多个变量就循环
for n in xx
do
done
定义变量在哪,
对每一个变量值循环操作
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# vim wenjian.sh
#!/bin/bash
for hd in {01..20}
do
date -s "201705$hd"
touch /tmp/taojin-$(date +%F).txt
done
for hd in 2017-05-{01..20}
do
date -s $hd
filename=$(date +%F)
touch $filename".txt"
done
3.14 ------------chkconfig优化开机自启动服务的脚本-----
a=里面的命令放在命令行执行要|bash,在这里不需要应该是因为它在脚本里,执行脚本时就已经使用执行命令了
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# cat youhuakaiji.sh
#!/bin/bash
a=`chkconfig|sed -nr ‘/sshd|network|cron|sysstat|rsyslog/!s#(.*)0:.*#\\1#gp‘`
for machangwei in $a
do
chkconfig $machangwei off
done
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]#
同学的脚本
#!/bin/bash
for n in $(chkconfig|sed -r ‘/sshd|network|crond|sysstat|rsyslog/d‘|sed -r ‘s#^(.*)0:.*$#\\1#g‘)
do
chkconfig $n off
done
3.15 ------------出错暂时无法解决的脚本--------
问题:有read命令,但是无法使后面的计算得到执行
思路拓展:是否需要有个对输入是数字的判断呢
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# vim canshu.sh
#!/bin/bash
read -p "请输入两个数字:" a
read -p "请输入两个数字:" b
a=$1
b=$2
if [ $# -ne 1 ];
then
echo 警告:应输入两个数字!!
exit
else
awk -va=$a -vb=$b ‘BEGIN{print a+b}‘
awk -va=$a -vb=$b ‘BEGIN{print a-b}‘
awk -va=$a -vb=$b ‘BEGIN{print a*b}‘
awk -va=$a -vb=$b ‘BEGIN{print a/b}‘
awk -va=$a -vb=$b ‘BEGIN{print a%b}‘
fi
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# sh canshu.sh
请输入两个数字:1 3
请输入两个数字:3
警告:应输入两个数字!!
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# sh canshu.sh
请输入两个数字:1
请输入两个数字:3
警告:应输入两个数字!
3.16 ------------应该再来一个对是否是数字的判断-----
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# sh canshu.sh # # # # # # # #
警告:应输入两个数字!!
[[email protected]小马过河 scripts]# sh canshu.sh nishi shui?
0
0
0
awk: fatal: division by zero attempted
awk: fatal: division by zero attempted in `%‘
3.17 ------------查看脚本执行的状况- sh -x ---------
计算器加上判断参数个数,扩展判断这两个参数是否为数字。
课后练习题:批量创建用户并设置随机密码
第4章 **************awk*******
------------awk--------
4.1 ------awk执行流程图
4.2 -----------awk数组结构--------
4.3 ------awk执行过程表---------
取列计算(统计)
条件行(可用行列),哪列,
awk 内置变量 指定分隔符FS,指定输出分隔符OFS,最后一列NF,倒数第几列$(NF-n),只要哪列可以最好以这列前后作为分隔符 多个相同字符加+(+正则表达),指定行分隔符RS,支持正则表达式,
可加字符""
算多少行,‘{i++}END print i‘
算每行数量相加 ‘{i=i+$0($1)}END print i‘
取哪列 $数字,$0所有列就是全行内容
像平面直角坐标系,找列^$
替换sed好
计算awk
!可放在~前
mkdir -p /server/files/
cat >>/server/files/reg.txt <<EOF
Zhang Dandan 41117397 :250:100:175
Zhang Xiaoyu 390320151 :155:90:201
Meng Feixue 80042789 :250:60:50
Wu Waiwai 70271111 :250:80:75
Liu Bingbing 41117483 :250:100:175
Wang Xiaoai 3515064655 :50:95:135
Zi Gege 1986787350 :250:168:200
Li Youjiu 918391635 :175:75:300
Lao Nanhai 918391635 :250:100:175
EOF
m 第一列是姓氏
m 第二列是名字
m 第一第二列合起来就是姓名
m 第三列是对应的ID号码
m 最后三列是三次捐款数量
4.4 ---------awk分隔符哪行哪列--------
条件:
模糊找行
找列有模糊条件的行
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# awk ‘$2~/waiwai/‘ /server/files/reg.txt
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# awk ‘$2~/X/‘ /server/files/reg.txt
Zhang Xiaoyu 390320151 :155:90:201
Wang Xiaoai 3515064655 :50:95:135
Zhang Xiaoyu 390320151 :155:90:201
Wang Xiaoai 3515064655 :50:95:135
4.5 --------awk题----------
1显示Xiaoyu的姓氏和ID号码
2显示所有ID号码最后一位数字是1或5的人的全名
3姓氏是Zhang的人,显示他的第二次捐款金额及她的名字
4显示Xiaoyu的捐款.每个值时都有以$开头.如$520$200$135
1
[[email protected]小马过河 files]# awk ‘$2~/Xiaoyu/{print $1,$3}‘ reg.txt
Zhang 390320151
Zhang 390320151
2.
方法一:
[[email protected]小马过河 files]# awk ‘$3~/(1|5)$/{print $1$2,$3}‘ reg.txt
ZhangXiaoyu 390320151
WuWaiwai 70271111
WangXiaoai 3515064655
方法二:
[[email protected]小马过河 files]# awk ‘$3~/[15]$/{print $1$2,$3}‘ reg.txt
ZhangXiaoyu 390320151
WuWaiwai 70271111
WangXiaoai 3515064655
3.
[[email protected]小马过河 files]# awk -F "[ :]+" ‘$1~/Zhang/{print $(NF-1),$2}‘ reg.txt
100 Dandan
90 Xiaoyu
100 Dandan
90 Xiaoyu
[[email protected]小马过河 files]# echo 12312312|tr "123" "abc"
abcabcab
4.
[[email protected]小马过河 files]# awk ‘$2~/Xiaoyu/{gsub(/:/,"$",$NF);print $2,$NF}‘ reg.txt
Xiaoyu $155$90$201
4.6 -----------awk替换------------
[[email protected]小马过河 files]# awk ‘{gsub(/:/,"$",$NF);print $0}‘ reg.txt
Zhang Dandan 41117397 $250$100$175
Zhang Xiaoyu 390320151 $155$90$201
Meng Feixue 80042789 $250$60$50
~ !~
判断当前系统上所有用户的shell是否为可登录shell(即用户的shell不是/sbin/nologin),如果是显示用户名字
[[email protected]小马过河 files]# awk -F ":" ‘$NF!~/nologin$/{print $1}‘ /etc/passwd
root
sync
shutdown
[[email protected] files]# awk ‘{gsub(/:/,"$",$NF) ; print $0}‘ reg.txt |column -t
Zhang Dandan 41117397 $250$100$175
Zhang Xiaoyu 390320151 $155$90$201
awk读取之前就执行
4.7 ----企业案例3:统计/etc/services文件里面的空行数量---
不用end显示过程
用途:可以统计行数
[[email protected]小马过河 files]# awk ‘/^$/‘ /etc/services |wc -l
16
[[email protected]小马过河 files]# awk ‘/^$/‘ /etc/services |uniq -c
16
[[email protected]小马过河 files]# awk ‘/^$/{i++} ; END{print i}‘ /etc/services
16
[[email protected]小马过河 files]# awk ‘/^$/{++i} ; END{print i}‘ /etc/services
16
[[email protected]小马过河 files]# awk ‘/^$/{i++} ; END{print i}‘ /etc/services
16
[[email protected]小马过河 files]# awk ‘/^$/{i=i+1} ; END{print i}‘ /etc/services
16
用途: 可以对一列内容进行累加
seq 10 >num.txt 计算这个文件每一行数字相加的结果
i=i+$0 ===累积相加 累加
[[email protected] files]# awk ‘{i=i+$0;print i}‘ num.txt
1
3
6
10
15
21
28
36
45
55
[[email protected] files]# awk ‘{i=i+$0}END{print i}‘ num.txt
55
[[email protected]小马过河 files]# awk ‘{i=i+$0};END {print i}‘ num.txt
5050
[[email protected]小马过河 files]# awk ‘{i=i+$1};END {print i}‘ num.txt
5050
算多少行,‘{i++}END print i‘
算每行数量相加 ‘{i=i+$0($1)}END print i‘
‘{hotel[$2]++;END print hotel["www"]}‘
hotel[]数组,$2为awk找到的第二列内容,将它放进hotel数组作为变量,++为将数组里面的相同变量进行统计,然后统计结果作为变量值。
4.8 --------awk 数组-----------
‘{hotel[$2]++;END print hotel["www"]}‘
‘{hotel[$2]++}END {for (ma in hotel) print ma,hotel[ma]}‘
{hotel[$2]++}:hotel[]数组,$2为awk找到的第二列内容,将它放进hotel数组作为变量,++为将数组里面的相同变量进行统计,然后统计结果作为变量值。
END: 没有的话就会显示awk命令执行过程
for (ma in hotel): 定义变量ma 在数组hotel里
print ma,hotel[ma] : 打印变量ma,以及变量值
用途:(简化:计算列重复值)
对ip地址去重并统计重复数
即对一列重复的内容去重并统计重复数.
[[email protected]小马过河 files]# awk -F "[/]+" ‘{hao[$2]++}END{for (ma in hao)print hao[ma],ma}‘ 1
1 mp3.etiantian.org
2 post.etiantian.org
3 www.etiantian.org
定义数组,定义变量为数组元素,打印变量名及变量值
[[email protected]小马过河 files]# awk ‘BEGIN{hotel[110]="lidao" ;hotel[119]="tanjiaoshou";hotel[121]="taojin";
print hotel[110],hotel[119],hotel[121]}‘
lidao tanjiaoshou taojin
[[email protected]小马过河 files]#
4.9 -------企业面试题1:统计域名访问次数----
处理以下文件内容,将域名取出并根据域名进行计数排序处理:(百度和sohu面试题)
http://www.etiantian.org/index.html
http://www.etiantian.org/1.html
http://post.etiantian.org/index.html
http://mp3.etiantian.org/index.html
http://www.etiantian.org/3.html
http://post.etiantian.org/2.html
方法一:
[[email protected]小马过河 files]# cat 1
http://www.etiantian.org/index.html
http://www.etiantian.org/1.html
http://post.etiantian.org/index.html
http://mp3.etiantian.org/index.html
http://www.etiantian.org/3.html
http://post.etiantian.org/2.html
[[email protected]小马过河 files]# awk -F "[/]+" ‘{print $2}‘ 1|sort|uniq -c|sort -r
3 www.etiantian.org
2 post.etiantian.org
1 mp3.etiantian.org
方法二:
[[email protected]小马过河 files]# awk -F "[/]+" ‘{hao[$2]++}END{for (ma in hao)print hao[ma],ma}‘ 1
1 mp3.etiantian.org
2 post.etiantian.org
3 www.etiantian.org
4.10 ---------awk统计的课后题-------
echo ;echo 可以不换行输出吗?
课后题目:
#secure.zip access.zip
1.统计secure文件中谁在破解你的密码(统计出破解你密码的ip地址出现的次数)
2.统计access.log文件中对ip地址去重并统计重复数
3.统计access.log文件中网站一共使用了多少流量
4.统计access.log文件中每个ip地址使用了多少流量
- awk统计有失败的ip并计算个数
[[email protected]小马过河 machangwei]# awk ‘$6~/Failed/{heike[$(NF-3)]++}END{for(ip in heike) print heike[ip]" "ip }‘ secure-20161219|sort -nr
68652 218.65.30.25
34326 218.65.30.53
21201 218.87.109.154
18065 112.85.42.103
17164 112.85.42.99
17163 218.87.109.151
17163 218.87.109.150
2
[[email protected]小马过河 machangwei]# awk ‘{print $1}‘ access.log|sort|uniq -c|sort -nr|head
12049 58.220.223.62
10856 112.64.171.98
1982 114.83.184.139
1662 117.136.66.10
1318 115.29.245.13
961 223.104.5.197
957 116.216.0.60
939 180.111.48.14
871 223.104.5.202
869 223.104.4.139
3.
方法一:
[[email protected]小马过河 machangwei]# awk ‘{i=i+$10}END{print i}‘ access.log
2478496663
方法二:
[[email protected]小马过河 machangwei]# sh tt
2478496663
[[email protected]小马过河 machangwei]# cat tt
#!/bin/bash
awk ‘{a[$1]++}{for (b in a)print b}‘ access.log >/machangwei/xiaoma
for i in ‘cat /machangwei/xiaoma‘
do
awk -v i="BASH" ‘/i/{d=d+$10}END{print d}‘ /machangwei/access.log
done
4.
[[email protected]小马过河 machangwei]# awk ‘{a[$1]=a[$1]+$10}{for(b in a)print b,a[b]}‘ access.log |head
101.226.61.184 24662
101.226.61.184 25188
101.226.61.184 25188
27.154.190.158 3084
101.226.61.184 32579
27.154.190.158 3084
101.226.61.184 32579
27.154.190.158 3084
114.94.29.165 491
101.226.61.184 44091
[[email protected]小马过河 machangwei]# seq 20|sort
1
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
20
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
[[email protected]小马过河 machangwei]# seq 20|sort -nr
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
4.11 ----------awk识别花括号加条件----
awk --posix ‘/[0-9]{1,5}/‘ secure-20161219
awk --re-interval ‘/[0-9]{1,5}/‘ secure-20161219
假如现在有个文本,格式如下:
a 1
b 3
c 2
d 7
b 5
a 3
g 2
f 6
d 9
即左边是随机字母,右边是随机数字,要求写个脚本使其输出格式为:
即将相同的字母后面的数字加在一起,按字母的顺序输出。
a 4
b 8
c 2
d 16
f 6
g 2
4.12 ----- a[$1]=a[$1]+$2-----
功能:某一列变化的有重复的内容对应另一列变化的数,将这个同一个东西的对应值累加并将两者对应打印出来
[[email protected]小马过河 machangwei]# awk ‘{a[$1]=a[$1]+$2}END{for (b in a)print a[b],b }‘ cc
4 a
8 b
2 c
16 d
6 f
2 g
awk ‘{a[$1]=a[$1]+$2}END{for (b in a)print a[b],b }‘ cc
{a[$1]=a[$1]+$2: 数组中很多变量,$1中第i个变量加上$2赋值给后一个第i个变量,实现第i个变量对应的$2的统计和,然后将统计和作为变量i的值
for (b in a) : 定义变量在数组a里
print a[b],b : 打印变量值,变量
4.13 5. ip出现次数及使用流量
[[email protected] files]# awk ‘{count[$1]++;sum[$1]+=$10}END{for(pol in count)print pol,count[pol],sum[pol]}‘ access.log |column -t|sort -rnk3 |head
114.83.184.139 1982 31362956
117.136.66.10 1662 22431302
116.216.30.47 506 21466000
[[email protected] files]# awk ‘BEGIN{print "访问次数","使用流量","ip地址"}{ss[$1]++;mm[$1]+=$10}END{for(nn in mm)print ss[nn],mm[nn],nn}‘ access.log |sort -n|column -t|head
访问次数 使用流量 ip地址
1 0 101.226.65.105
1 0 110.75.105.135
1 0 110.75.105.47
1 0 110.75.87.144
[[email protected]小马过河 machangwei]# awk ‘{ips[$1]++;sum[$1]+=$10}{for(b in ips)print b,ips[b],sum[b]}‘ access.log |head
101.226.61.184 1 24662
101.226.61.184 2 25188
[[email protected]]# awk ‘{sums[$1]+=$10;sus[$1]++}END{for (sum in sums) print " 访问ip===> " sum " ip访问次数=====> " sus[sum] " 每次访问的流量 "sums[sum]/sus[sum]/1024"K" " 总流量: "sums[sum]}‘ access.log |sort -nrk6 | head |column -t
访问ip===> 182.18.102.159 ip访问次数=====> 3 每次访问的流量 242.575K 总流量: 745189
访问ip===> 180.97.182.222 ip访问次数=====> 1 每次访问的流量 185.885K 总流量: 190346
访问ip===> 124.156.66.72 ip访问次数=====> 2 每次访问的流量 185.791K 总流量: 380500
访问ip===> 223.104.211.140 ip访问次数=====> 2 每次访问的流量 130.531K 总流量: 267327
访问ip===> 101.86.13.161 ip访问次数=====> 17 每次访问的流量 97.4069K 总流量: 1695660
访问ip===> 101.87.174.78 ip访问次数=====> 42 每次访问的流量 95.2861K 总流量: 4098063
访问ip===> 202.111.6.229 ip访问次数=====> 3 每次访问的流量 95.2354K 总流量: 292563
访问ip===> 61.171.38.1 ip访问次数=====> 74 每次访问的流量 92.072K 总流量: 6976851
访问ip===> 66.249.82.181 ip访问次数=====> 3 每次访问的流量 84.0768K 总流量: 258284
访问ip===> 125.86.90.242 ip访问次数=====> 19 每次访问的流量 82.5421K 总流量: 1605939
效果图
不用两个for就是这样,不好放在一起
4.14 ------awk 中的begin----------
可以|""里里面加内容,先begin,再中间,再end,如果|加在整个命令前面,begin里的内容也会加入,比如排序
[[email protected] files]# awk ‘BEGIN{print "ip","count"}{count[$1]++}END{for(pol in count)print pol,count[pol]|"sort -rnk2"}‘ access.log |head |column -t
ip count
58.220.223.62 12049
112.64.171.98 10856
114.83.184.139 1982
117.136.66.10 1662
115.29.245.13 1318
223.104.5.197 961
116.216.0.60 957
180.111.48.14 939
223.104.5.202 871
4.15 ------------awk版本4以上有替换功能-----
[[email protected]小马过河 machangwei]# awk --version
GNU Awk 3.1.7
Copyright (C) 1989, 1991-2009 Free Software Foundation.
This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
the Free Software Foundation; either version 3 of the License, or
(at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
along with this program. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses/.
第5章 ---------总结大集合-----
cpu一个内核同时只能做一个事情,我们看到他做很多事是因为它不断切换的。比如一个人做会这件事,做会儿那件事,把做事时间无限缩短,相当于同时在做很多事情。
reinstall
5.1 -------查看端口总结 踢死了妮妮(tslnn)-------
查看端口是否开启五个:踢死了妮妮(tslnn),telnet,ss(netstat),lsof,nmap,nc
查看22端口是否开启
1.telnet
telnet 10.0.0.200 22
2.ss
ss -lntup|grep 22
ss === netstat
3.lsof
lsof -i:22
4.nmap
[[email protected] files]# nmap -p22 10.0.0.200
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.10 seconds
[[email protected] files]# nmap -p25 10.0.0.200
PORT STATE SERVICE
25/tcp closed smtp
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 2.61 seconds
5.
[[email protected] files]# nc 10.0.0.200 22
SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_5.3
Protocol mismatch.
ps -ef |grep sshd #进程是否在运行
yum install telnet tree lrzsz nmap nc dos2unix -y
5.2 ----------- 排查无法上网总结 3p-----
2)linux无法上网
1] ping
www.baidu.com
#是否能上网
2] ping
223.5.5.5
#DNS是否有问题
3] ping 网关 #
--------查看系统默认网关
route -n =====
ifconfig
ip a
ifconfig eth0
ip a s eth0
ip address show eth0
route -n
ip route
ip r
5.3 -------------- vi/vim快捷方式总结----
vi/vim快捷方式
移动光标:
快速的达到文件的最后一行 G(shift+g)
快速达到文件的第一行 gg
快速达到文件的第100行 100gg :100
移动光标到行首 0 ^
移动光标到行尾 $
编辑:
复制 yy
粘贴 p
剪切/删除当前行 dd
删除光标所在位置到文件的最后一行 dG
删除光标所在位置到行尾 D === d$
把光标移动到文件的结尾并进入编辑模式 A
在当前行下面插入一个空行并进入编辑模式 o(小写字母O)
删除光标所在位置的一个字符 x
撤销 u
查找替换:
:1,10s#oldboy#oldgirl#g
:.,$s#oldboy#oldgirl#g #.表示当前行
:%s#oldboy#oldgirl#g #1,$====%
查找替换移动:
:1,10s#oldboy#oldgirl#g
:.,$s#oldboy#oldgirl#g #.表示当前行
:%s#oldboy#oldgirl#g #1,$====%
:1,5m[ove]10 #从第一行到底5行移动到第10行
:1,5co[py]10 #从第一行到底5行复制到第10行
批量操作:(可视块模式)
ctrl+v
ctrl+v 按I 编辑 按esc
其他:
/搜索的内容 继续搜索n 继续向上搜索N
显示行号 :set nu
取消显示行号 :set nonu
s
5.4 ---sed总结--------
1.sed ‘找谁干啥‘
删改查
d s p
5.5 ------awk总结---------
3.awk ‘找谁{干啥}‘
NR==1
NR==1,NR==20
正则表达式
/oldboy/
$2~/oldboy/
NR>=20
$3>20
gsub(/找谁/,"替换为什么",在哪个部分)
计算
i=i+1 i++
i=i+$2 i+=$2
h[$1]=h[$1]+1 h[$1]++
h[$1]=h[$1]+$2 h[$1]+=$2
[[email protected] files]# awk ‘BEGIN{for(i=1;i<=100;i++) sum=sum+i;print sum}‘
5050
2.shell
变量分类
read
循环和判断
5.6 ------rename-----
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# rename bb "cc" bb
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# ls
1.txt c d035 ett.txt install.log lrzsz-0.12.20.tar.gz passwd.txt stu.sh
2.txt cc data f032 install.log.syslog ma person.txt tandao
anaconda-ks.cfg d032 download f035 lrzsz-0.12.20 machangwei services x.t
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# rename x "e" *.t
[[email protected]小马过河 ~]# ls
1.txt c d035 e.t f035 lrzsz-0.12.20 machangwei services
2.txt cc data ett.txt install.log lrzsz-0.12.20.tar.gz passwd.txt stu.sh
anaconda-ks.cfg d032 download f032 install.log.syslog ma person.txt tandao