Huffman coding
Posted lab601
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Huffman coding相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Huffman coding
1、Basic Technique
Huffmam coding是David A. Huffman在MIT上学期间发明的一种编码方式,并以他的名字命名。Huffman coding 和 Shannon-Fano coding方法正好相反,Huffman coding是从下到上,Shannon-Fano coding 是从上到下。
编码步骤
- 1 为每个符号建立一个叶子节点,将它们放到一个队列中,并为每个节点分配权重(符号出现次数);
- 2 当队列中的符号个数大于1:
- 2.1 将权重最低的两个节点从队列中移除;
- 2.2 为这两个节点分配符号0和1;
- 2.3 新建一个新节点,作为上面两个节点的父节点,权重是子节点的权重和;
- 2.4 将新节点加入队列
3 剩下的一个节点是根节点,编码结束。
2、Example
Symbol A B C D E count 15 7 6 6 5 probabilities 0.38461538 0.17948718 0.15384615 0.15384615 0.12830513
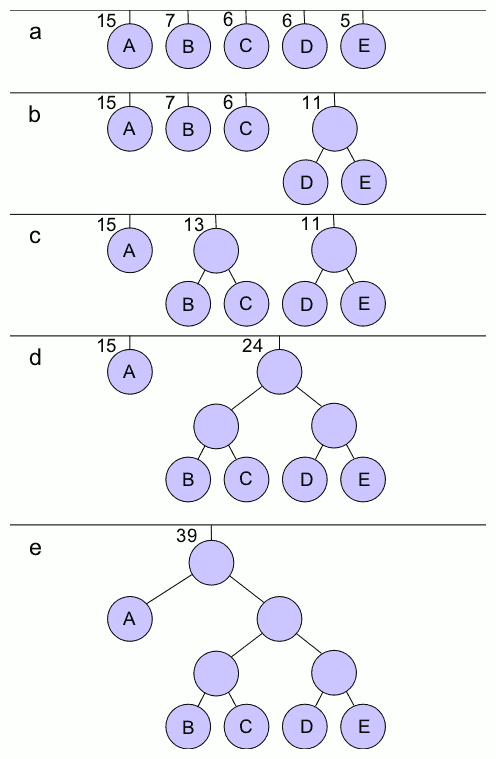
首先,D&E权重最小,将它们相加构成新的节点,权重0.28205128, 两个子节点分配0和1,如上图b所示.
| Symbol | A | D&E | B | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| count | 15 | 11 | 7 | 6 |
| probabilities | 0.38461538 | 0.28205128 | 0.17948718 | 0.15384615 |
然后,合并最小的两个符号B&C,组成新节点B&C,权重0.33333333,两个子节点分配0和1,如上图c所示
| Symbol | A | B&C | D&E |
|---|---|---|---|
| count | 15 | 13 | 11 |
| probabilities | 0.38461538 | 0.33333333 | 0.28205128 |
再将B&C和D&E合并,组成新节点B&C&D&E,如上图d所示;最后,将A和B&C&D&E合并组成root节点。最后得到编码如下表所示
| Symbol | A | B | C | D | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| code | 0 | 100 | 101 | 110 | 111 |
计算得到平均字长:[frac{1 bits*15+3 bits*(7+6+6+5)}{39 symbols} approx 2.23 bits per symbol]
3、实验
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
char word[10] = {‘A‘, ‘B‘, ‘C‘, ‘D‘, ‘E‘, ‘F‘, ‘G‘, ‘H‘, ‘I‘, ‘J‘};
int weight[10] = {10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
typedef struct HuffmanNode{
int word;
int weight;
int parrent, lchild, rchild;
}HN;
HN *HT=NULL;
int Select(HN *H, int n, int *s1, int *s2)
{
/*寻找权值最小节点*/
/*先找到第一个没有父母节点的节点*/
int i=0;
for(; i<n; i++){
if(H[i].parrent==0) {
*s1 = i;
break;
}
}
/*寻找权值最小节点*/
for(; i<n; i++){
if(H[i].parrent == 0 && H[i].weight < H[*s1].weight){
*s1=i;
}
}
/*寻找权值次小节点*/
int j=0;
for(; j<n; j++){
if(H[j].parrent==0 && *s1!=j) {
*s2 = j;
break;
}
}
for(; j<n; j++){
if(H[j].parrent == 0 && *s1!=j && H[j].weight < H[*s2].weight){
*s2=j;
}
}
}
int creatHuffmanTree(int n)
{
/*分配并初始化节点*/
int m=2*n-1;
HT = (HN*)malloc(sizeof(HN)*m);
for(int i=0; i<m; i++) {
HT[i].parrent=0;
HT[i].lchild=0;
HT[i].rchild=0;
}
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
HT[i].weight=weight[i];
HT[i].word=word[i];
}
//printf("init is OK.
");
/*构造Huffman树*/
for(int i=n; i<m; i++){
int s1, s2;
/*寻找前i个数据中的最小值*/
Select(HT, i, &s1, &s2);
HT[i].weight=HT[s1].weight+HT[s2].weight;
HT[i].lchild=s1;
HT[i].rchild=s2;
HT[s1].parrent=i;
HT[s2].parrent=i;
//printf("%d and %d have some parents %d!
", s1, s2, i);
}
}
int main() {
printf("Huffman coding test!
");
creatHuffmanTree(10);
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
int j=i;
/*编码从叶子节点遍历到根节点,逆序输出编码*/
while(HT[j].parrent != 0){
if(HT[HT[j].parrent].lchild == j)
printf("0");
else if(HT[HT[j].parrent].rchild == j)
printf("1");
else {
printf("ERROR! Parents‘ child is not me.");
free(HT);
return 1;
}
j=HT[j].parrent;
}
/*输出编码对应字符*/
printf(" word is %c
", HT[i].word);
}
free(HT);
return 0;
}4、参考文献
以上是关于Huffman coding的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章