树及其衍生算法(Trees and tree algorithms)
Posted silence-cho
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了树及其衍生算法(Trees and tree algorithms)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1,二叉树(Binary tree)
二叉树:每一个节点最多两个子节点,如下图所示:
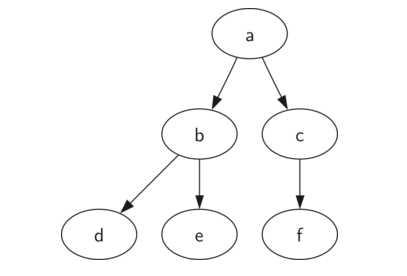
相关概念:节点Node,路径path,根节点root,边edge,子节点 children,父节点parent,兄弟节点sibling, 子树subtree,叶子节点leaf node, 度level,树高hight

节点Node:
路径path:从一个节点到拧一个节点间的边
根节点root,
边edge:节点间的连线
子节点 children,
父节点parent,
兄弟节点sibling,
子树subtree,
叶子节点leaf node,
度level:从当前节点到根节点的路径中边的数量
高度 hight:树中所有节点的最大level
二叉树可以通过多级列表的形式实现,多级列表形式如下,根节点r,有两个子节点a , b,且a, b节点没有子节点。
mytree =[ r,
[ a, [ ], [ ] ], [ b, [ ], [ ] ]
]
python实现代码如下:

#coding:utf-8 #多级列表实现 def binaryTree(r): return [r,[],[]] #root[]为根节点,root[1]左子树,root[2]右子树 def insertLeftTree(root,newbranch): t = root.pop(1) if len(t)>1: root.insert(1, [newbranch, t, []]) else: root.insert(1,[newbranch, [], []]) return root def insertRightTree(root,newbranch): t = root.pop(2) if len(t)>1: root.insert(2, [newbranch, [], t]) else: root.insert(2,[newbranch, [], []]) return root def getRootVal(root): return root[0] def setRootVal(root,val): root[0]= val def getLeftChildren(root): return root[1] def getRightChildren(root): return root[2] r = binaryTree(3) insertLeftTree(r,4) insertLeftTree(r,5) insertRightTree(r,6) insertRightTree(r,7) l = getLeftChildren(r) print(l) setRootVal(l,9) print(r) insertLeftTree(l,11) print(r) print(getRightChildren(getRightChildren(r)))
二叉树可以通过节点的形式实现,如下所示:
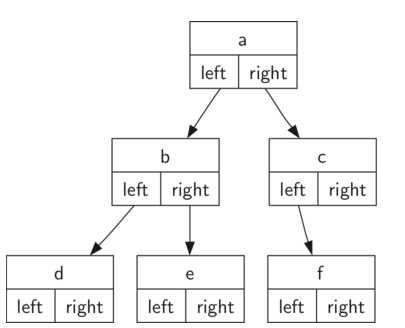
python实现代码如下:

class BinaryTree(object): def __init__(self,value): self.key = value self.leftChild = None self.rightChild = None def insertLeft(self,newNode): if self.leftChild != None: temp = BinaryTree(newNode) temp.leftChild = self.leftChild self.leftChild = temp else: self.leftChild = BinaryTree(newNode) def insertRight(self,newNode): if self.rightChild != None: temp = BinaryTree(newNode) temp.rightChild= self.rightChild self.rightChild = temp else: self.rightChild = BinaryTree(newNode) def getRootVal(self): return self.key def setRootVal(self,value): self.key = value def getLeftChild(self): return self.leftChild def getRightChild(self): return self.rightChild
2,二叉树的应用
2.1 解析树(parse tree)
解析树常用于表示真实世界的结构表示,如句子和数学表达式。如下图是((7+3)*(5-2))的解析树表示,根据解析树的层级结构,从下往上计算,能很好的代替括号的表达式中括号的作用
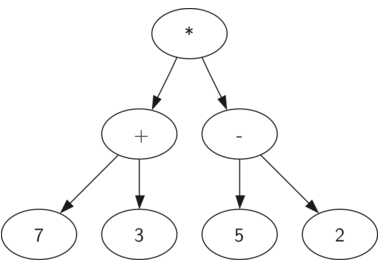
将一个全括号数学表达式转化为解析树的过程如下:
遍历表达式:
1,若碰到“(”,为当前节点插入左节点,并移动到左节点
2,若碰到 + ,- ,* , /,设置当前节点的值为该符号,并为当前节点插入右节点,并移动到右节点
3,若碰到数字,设置当前节点的值为该数字,并移动到其父节点
4,若碰到“)”,移动到当前节点的父节点
python实现代码如下:(Stack 参见数据结构之栈 )

from stackDemo import Stack #参见数据结构之栈 def buildParseTree(expstr): explist = expstr.split() s = Stack() t = BinaryTree(‘‘) s.push(t) current = t for token in explist: #token = token.strip() if token ==‘(‘: current.insertLeft(‘‘) s.push(current) current = current.getLeftChild() elif token in [‘*‘,‘/‘,‘+‘,‘-‘]: current.setRootVal(token) current.insertRight(‘‘) s.push(current) current = current.getRightChild() elif token not in [‘(‘,‘*‘,‘/‘,‘+‘,‘-‘,‘)‘]: current.setRootVal(token) current = s.pop() elif token==‘)‘: current = s.pop() else: raise ValueError return t t = buildParseTree("( ( 10 + 5 ) * 3 )")
计算解析树:数学表达式转化为解析树后,可以对其进行计算,python代码如下:

import operator def evaluate(parseTree): operators={‘+‘:operator.add,‘-‘:operator.sub,‘*‘:operator.mul,‘/‘:operator.div } rootval = parseTree.getRootVal() left = parseTree.getLeftChild() right = parseTree.getRightChild() if left and right: fn = operators[rootval] return fn(evaluate(left),evaluate(right)) else: return parseTree.getRootVal()
中序遍历解析树,可以将其还原为全括号数学表达式,python代码如下:

#解析树转换为全括号数学表达式 def printexp(tree): val = ‘‘ if tree: val = ‘(‘+printexp(tree.getLeftChild()) val = val +str(tree.getRootVal()) val = val +printexp(tree.getRightChild())+‘)‘ if tree.getLeftChild()==None and tree.getRightChild()==None: val = val.strip(‘()‘) return val t = buildParseTree("( ( 10 + 5 ) * 3 )") exp = printexp(t) print exp
3,树的遍历
树的遍历包括前序遍历(preorder),中序遍历(inorder)和后序遍历(postorder).
前序遍历:先访问根节点,再访问左子树,最后访问右子树(递归),python代码实现如下:

def preorder(tree): if tree: print tree.getRootVal() preorder(tree.getLeftChild()) preorder(tree.getRightChild()) #定义在类中的前序遍历 # def preorder(self): # print self.key # if self.leftChild: # self.leftChild.preorder() # if self.rightChild: # self.rightChild.preorder()
中序遍历:先访问左子树,再访问根节点,最后访问右子树(递归),python代码实现如下:

#中序遍历inorder def inorder(tree): if tree: preorder(tree.getLeftChild()) print tree.getRootVal() preorder(tree.getRightChild())
后续遍历:先访问左子树,再访问右子树,最后访问根节点,python代码实现如下:

def postorder(tree): if tree : postorder(tree.getLeftChild()) postorder(tree.getRightChild()) print(tree.getRootVal())
4,优先队列和二叉树(priority queue and binary heap)
优先队列:优先队列和队列类似,enqueue操作能加入元素到队列末尾,dequeue操作能移除队列首位元素,不同的是优先队列的元素具有优先级,首位元素具有最高或最小优先级,因此当进行enqueue操作时,还需要根据元素的优先级将其移动到适合的位置。优先队列一般利用二叉堆来实现,其enqueue和dequeue的复杂度都为O(logn)。(也可以用list来实现,但list的插入复杂度为O(n),再进行排序的复杂度为O(n logn))
二叉堆:二叉堆是一颗完全二叉树,当父节点的键值总是大于或等于任何一个子节点的键值时为最大堆,当父节点的键值总是小于或等于任何一个子节点的键值时为最小堆。(完全二叉树:除最后一层外,每一层上的节点数均达到最大值;在最后一层上只缺少右边的若干结点;满二叉树:除叶子结点外的所有结点均有两个子结点。节点数达到最大值。所有叶子结点必须在同一层上)
最小堆示例及操作如下:(父节点的值总是小于或等于子节点)

BinaryHeap() #创建空的二叉堆 insert(k) #插入新元素 findMin() #返回最小值,不删除 delMin() #返回最小值,并删除 isEmpty() size() buildHeap(list) #通过list创建二叉堆
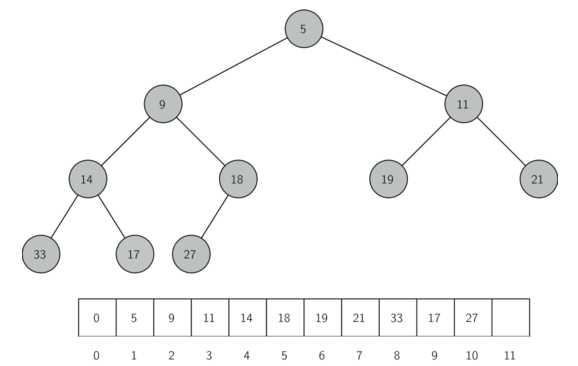
对于完全二叉树,若根节点的序号为p,则左右节点的序号应该为2p和2p+1,结合上图可以发现,可以用一个队列(首位元素为0)来表示二叉堆的结构。最小堆的python实现代码如下:(heaplist中第一个元素为0,不会用到,只是为了保证二叉堆的序列从1开始,方便进行除和乘2p,2p+1)

#coding:utf-8 class BinaryHeap(object): def __init__(self): self.heapList=[0] self.size = 0 #将元素加到完全二叉树末尾,然后再根据其大小调整其位置 def insert(self,k): self.heapList.append(k) self.size = self.size+1 self._percUp(self.size) # 如果当前节点比父节点小,和父节点交换位置,一直向上重复该过程 def _percUp(self,size): i = size while i>0: if self.heapList[i]<self.heapList[i//2]: temp = self.heapList[i] self.heapList[i] = self.heapList[i//2] self.heapList[i//2] = temp i=i//2 # 将根元素返回,并将最末尾元素移动到根元素保持完全二叉树结构不变,再根据大小,将新的根元素向下移动到合适的位置 def delMin(self): temp = self.heapList[1] self.heapList[1]=self.heapList[self.size] self.size = self.size-1 self.heapList.pop() self._percDown(1) return temp # 如果当前节点比最小子节点大,和该子节点交换位置,一直向下重复该过程 def _percDown(self,i): while (2*i)<=self.size: mc = self._minChild(i) if self.heapList[i]>self.heapList[mc]: temp = self.heapList[i] self.heapList[i]=self.heapList[mc] self.heapList[mc] =temp i = mc #返回左右子节点中较小子节点的位置 def _minChild(self,i): if (2*i+1)>self.size: return 2*i else: if self.heapList[2*i] < self.heapList[2*i+1]: return 2*i else: return 2*i+1 #通过一个list建立二叉堆 def buildHeap(self,list): i = len(list)//2 self.heapList = [0]+list[:] self.size = len(list) while i>0: self._percDown(i) i = i-1
insert()插入过程示例图如下:将元素加到完全二叉树末尾,然后再根据其大小调整其位置
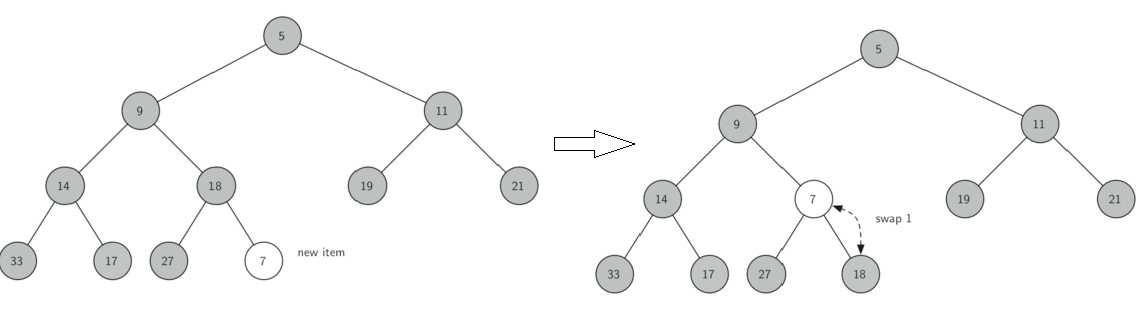
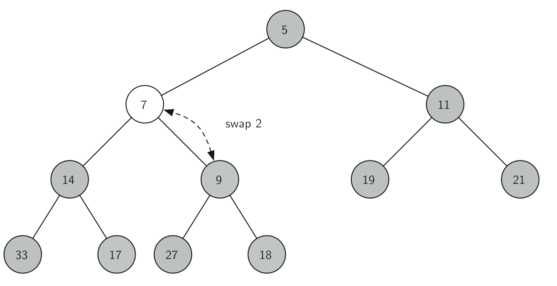
delMin()操作过程示例如下:将根元素返回,并将最末尾元素移动到根元素保持完全二叉树结构不变,再根据大小,将新的根元素向下移动到合适的位置
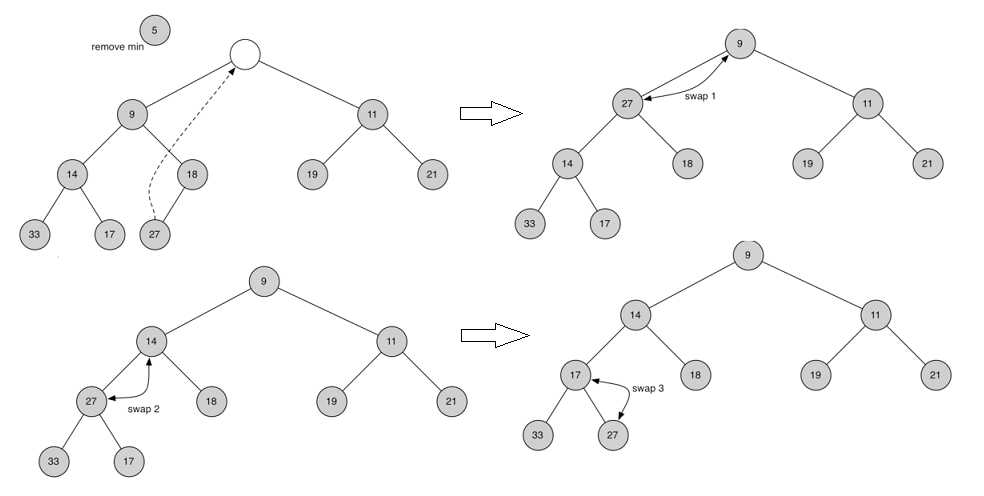
insert和delMin的复杂度都为O(log n), buildHeap的复杂度为O(n),利用二叉堆对list进行排序,复杂度为O(n log n),代码如下:

#通过list构造二叉堆,然后不断将堆顶元素返回,就得到排序好的list alist = [54,26,93,17,98,77,31,44,55,20] h = BinaryHeap() h.buildHeap(alist) s=[] while h.size>0: s.append(h.delMin()) print s
5,二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree, bst)
二叉搜索树:左节点的值,总是小于其父节点的值,右节点的值总是大于其父节点的值(bst property)。如下图所示:
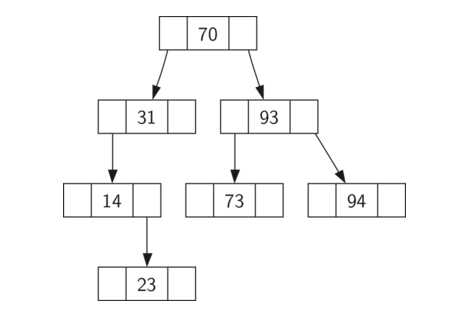
利用二叉搜索树实现map(字典),常用操作如下:

Map() # 创建字典 put(key,val) # 字典中插入数据 get(key) # 取键值 del # 删除 len() # 求长度 in # 是否存在
python实现map代码如下:

#coding:utf-8 class TreeNode(object): def __init__(self,key, value, leftChild=None,rightChild=None,parent=None): self.key = key self.value = value self.leftChild = leftChild self.rightChild = rightChild self.parent = parent self.balanceFactor =0 def hasLeftChild(self): return self.leftChild def hasRightChild(self): return self.rightChild def isLeftChild(self): return self.parent and self.parent.leftChild==self def isRightChild(self): return self.parent and self.parent.rightChild==self def isRoot(self): return not self.parent def isLeaf(self): return not (self.leftChild or self.rightChild) def hasAnyChildren(self): return self.leftChild or self.rightChild def hasBothChildren(self): return self.leftChild and self.rightChild def replaceNodeData(self,key,value,lc=None,rc=None): self.key=key self.value = value self.leftChild = lc self.rightChild = rc if self.hasLeftChild(): self.leftChild.parent = self if self.hasRightChild(): self.rightChild = self def __iter__(self): if self: if self.hasLeftChild(): for elem in self.leftChild: #调用self.leftChiLd.__iter__(),所以此处是递归的 yield elem yield self.key, self.value, self.balanceFactor if self.hasRightChild(): for elem in self.rightChild: #调用self.rightChiLd.__iter__() yield elem def findSuccessor(self): #寻找继承 succ = None if self.hasRightChild(): succ = self.rightChild._findMin() else: if self.parent: if self.isLeftChild(): succ = self.parent else: self.parent.rightChild = None succ = self.parent.findSuccessor() self.parent.rightChild = self return succ def _findMin(self): current = self while current.hasLeftChild(): current = current.leftChild return current def spliceOut(self): if self.isLeaf(): if self.isLeftChild(): self.parent.leftChild=None else: self.parent.rightChild=None elif self.hasAnyChildren(): if self.hasLeftChild(): if self.isLeftChild(): self.parent.leftChild = self.leftChild else: self.parent.rightChild = self.leftChild self.leftChild.parent = self.parent else: if self.isLeftChild(): self.parent.leftChild = self.rightChild else: self.parent.rightChild = self.rightChild self.rightChild.parent = self.parent class BinarySearchTree(object): def __init__(self): self.root = None self.size = 0 def length(self): return self.size def __len__(self): return self.size def __iter__(self): return self.root.__iter__() #加入元素 def put(self,key,value): if self.root: self._put(key,value,self.root) else: self.root = TreeNode(key,value) self.size = self.size+1 def _put(self,key,value,currentNode): if currentNode.key<key: if currentNode.hasRightChild(): self._put(key,value,currentNode.rightChild) else: currentNode.rightChild=TreeNode(key,value,parent=currentNode) elif currentNode.key>key: if currentNode.hasLeftChild(): self._put(key,value,currentNode.leftChild) else: currentNode.leftChild=TreeNode(key,value,parent=currentNode) else: currentNode.replaceNodeData(key,value) def __setitem__(self, key, value): self.put(key,value) #获取元素值 def get(self,key): if self.root: node = self._get(key,self.root) if node: return node.value else: return None else: return None def _get(self,key,currentNode): if not currentNode: return None if currentNode.key==key: return currentNode elif currentNode.key<key: return self._get(key,currentNode.rightChild) #rightChild可能不存在 else: return self._get(key,currentNode.leftChild) #leftChild可能不存在 # def _get(self,key,currentNode): # if currentNode.key == key: # return currentNode # elif currentNode.key<key: # if currentNode.hasRightChild(): # return self._get(key,currentNode.rightChild) # else: # return None # else: # if currentNode.hasLeftChild(): # return self._get(key,currentNode.leftChild) # else: # return None def __getitem__(self, key): return self.get(key) def __contains__(self, key): #实现 in 操作 if self._get(key,self.root): return True else: return False def delete(self,key): if self.size>1: node = self._get(key,self.root) if node: self._del(node) self.size = self.size - 1 else: raise KeyError(‘Error, key not in tree‘) elif self.size==1 and self.root.key==key: self.root = None self.size = self.size - 1 else: raise KeyError(‘Error, key not in tree‘) def _del(self,currentNode): if currentNode.isLeaf(): if currentNode.isLeftChild(): currentNode.parent.leftChild = None elif currentNode.isRightChild(): currentNode.parent.rightChild = None elif currentNode.hasBothChildren(): successor = currentNode.findSuccessor() #此处successor为其右子树的最小值,即最左边的值 successor.spliceOut() currentNode.key = successor.key currentNode.value = successor.value elif currentNode.hasAnyChildren(): if currentNode.hasLeftChild(): if currentNode.isLeftChild(): currentNode.parent.leftChild = currentNode.leftChild currentNode.leftChild.parent = currentNode.parent elif currentNode.isRightChild(): currentNode.parent.rightChild = currentNode.leftChild currentNode.leftChild.parent = currentNode.parent else: # currentNode has no parent (is root) currentNode.replaceNodeData(currentNode.leftChild.key, currentNode.leftChild.value, currentNode.leftChild.leftChild, currentNode.leftChild.rightChild) elif currentNode.hasRightChild(): if currentNode.isLeftChild(): currentNode.parent.leftChild = currentNode.rightChild currentNode.rightChild.parent = currentNode.parent elif currentNode.isRightChild(): currentNode.parent.rightChild = currentNode.rightChild currentNode.rightChild.parent = currentNode.parent else: # currentNode has no parent (is root) currentNode.replaceNodeData(currentNode.rightChild.key, currentNode.rightChild.value, currentNode.rightChild.leftChild, currentNode.rightChild.rightChild) def __delitem__(self, key): self.delete(key) if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: mytree = BinarySearchTree() mytree[8]="red" mytree[4]="blue" mytree[6]="yellow" mytree[5]="at" mytree[9]="cat" mytree[11]="mat" print(mytree[6]) print(mytree[5]) for x in mytree: print x del mytree[6] print ‘-‘*12 for x in mytree: print x
在上述代码中最复杂的为删除操作,删除节点时有三种情况:节点为叶子节点,节点有两个子节点,节点有一个子节点。当节点有两个子节点时,对其删除时,应该用其右子树的最小值来代替其位置(即右子树中最左边的值)。
对于map进行复杂度分析,可以发现put,get取决于tree的高度,当节点随机分配时复杂度为O(log n),但当节点分布不平衡时,复杂度会变成O(n),如下图所示:
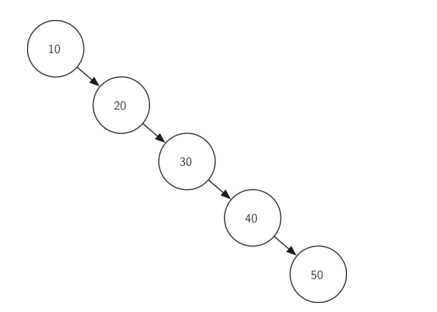
6, 平衡二叉搜索树 (Balanced binary search tree, AVL tree)
平衡二叉搜索树:又称为AVL Tree,取名于发明者G.M. Adelson-Velskii 和E.M. Landis,在二叉搜索树的基础上引入平衡因子(balance factor),每次插入和删除节点时都保持树平衡,从而避免上面出现的搜索二叉树复杂度会变成O(n)。一个节点的balance factor的计算公式如下,即该节点的左子树高度减去右子树高度。
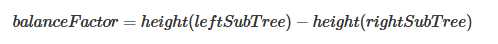
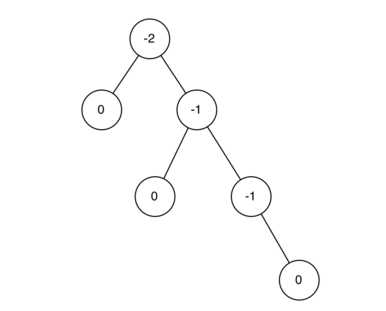
当树所有节点的平衡因子为-1,0,1时,该树为平衡树,平衡因子大于1或小于-1时,树不平衡需要调整,下图为一颗树的各个节点的平衡因子。(1时树left-heavy,0时完全平衡,-1时right-heavy)
相比于二叉搜索树,AVL树的put和delete操作后,需要对节点的平衡因子进行更新,如果某个节点不平衡时,需要进行平衡处理,主要分为左旋转和右旋转。
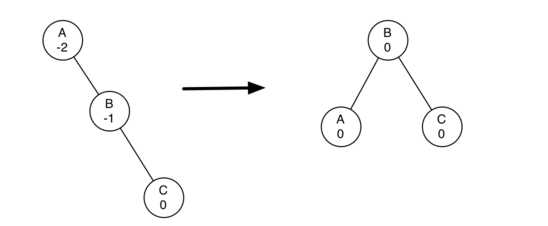
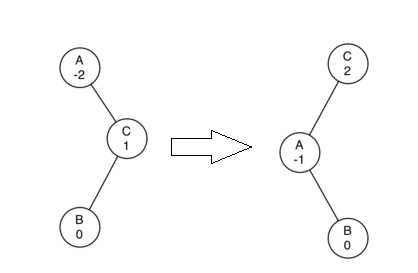
左旋转:如图,节点A的平衡因子为-2(right heavy),不平衡,对其进行左旋转,即以A为旋转点,AB边逆时针旋转。
详细操作为:1,A的右节点B作为新的子树根节点
2,A成为B的左节点,如果B有左节点时,将其左节点变为A的右节点(A的右节点原来为B,所以A的右节点现在为空)
右旋转:如图,节点E的平衡因子为2(left heavy),不平衡,对其进行右旋转,即以E为旋转点,EC边顺时针旋转。
详细操作为:1,E的左节点C作为新的子树根节点
2,E成为C的右节点,如果C有右节点时,将其右节点变为E的左节点(E的左节点原来为C,所以E的左节点现在为空)
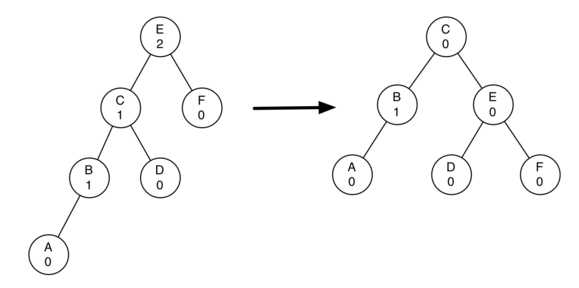
特殊情况:当出现下面的情况时,如图所示,A依旧为right heavy,但若进行左旋转,又会出现left heavy,无法完成平衡操作。 所以在进行左旋转和右旋转前需要进行一步判断,具体操作如下:
1,如果某节点需要进行左旋转平衡时(right heavy),检查其右子节点的平衡因子,若右子节点为left heavy,先对右子节点右旋转,然后对该节点左旋转
2,如果某节点需要进行右旋转平衡时(left heavy),检查其左子节点的平衡因子,若左子节点为right heavy,先对左子节点左旋转,然后对该节点右旋转
AVL tree用python实现的代码如下:

#coding:utf-8 from binarySearchTree import TreeNode, BinarySearchTree # class AVLTreeNode(TreeNode): # # def __init__(self,*args,**kwargs): # self.balanceFactor = 0 # super(AVLTreeNode,self).__init__(*args,**kwargs) class AVLTree(BinarySearchTree): def _put(self,key,value,currentNode): if currentNode.key<key: if currentNode.hasRightChild(): self._put(key,value,currentNode.rightChild) else: currentNode.rightChild=TreeNode(key,value,parent=currentNode) self.updateBalance(currentNode.rightChild) elif currentNode.key>key: if currentNode.hasLeftChild(): self._put(key,value,currentNode.leftChild) else: currentNode.leftChild=TreeNode(key,value,parent=currentNode) self.updateBalance(currentNode.leftChild) else: currentNode.replaceNodeData(key,value) def _del(self,currentNode): if currentNode.isLeaf(): if currentNode.isLeftChild(): currentNode.parent.leftChild = None currentNode.parent.balanceFactor -=1 elif currentNode.isRightChild(): currentNode.parent.rightChild = None currentNode.parent.balanceFactor += 1 if currentNode.parent.balanceFactor>1 or currentNode.parent.balanceFactor<-1: self.reblance(currentNode.parent) elif currentNode.hasBothChildren(): successor = currentNode.findSuccessor() #此处successor为其右子树的最小值,即最左边的值 # 先更新parent的balanceFactor if successor.isLeftChild(): successor.parent.balanceFactor -= 1 elif successor.isRightChild(): successor.parent.balanceFactor += 1 successor.spliceOut() currentNode.key = successor.key currentNode.value = successor.value # 删除后,再判断是否需要再平衡,然后进行再平衡操作 if successor.parent.balanceFactor>1 or successor.parent.balanceFactor<-1: self.reblance(successor.parent) elif currentNode.hasAnyChildren(): #先更新parent的balanceFactor if currentNode.isLeftChild(): currentNode.parent.balanceFactor -= 1 elif currentNode.isRightChild(): currentNode.parent.balanceFactor += 1 if currentNode.hasLeftChild(): if currentNode.isLeftChild(): currentNode.parent.leftChild = currentNode.leftChild currentNode.leftChild.parent = currentNode.parent elif currentNode.isRightChild(): currentNode.parent.rightChild = currentNode.leftChild currentNode.leftChild.parent = currentNode.parent else: # currentNode has no parent (is root) currentNode.replaceNodeData(currentNode.leftChild.key, currentNode.leftChild.value, currentNode.leftChild.leftChild, currentNode.leftChild.rightChild) elif currentNode.hasRightChild(): if currentNode.isLeftChild(): currentNode.parent.leftChild = currentNode.rightChild currentNode.rightChild.parent = currentNode.parent elif currentNode.isRightChild(): currentNode.parent.rightChild = currentNode.rightChild currentNode.rightChild.parent = currentNode.parent else: # currentNode has no parent (is root) currentNode.replaceNodeData(currentNode.rightChild.key, currentNode.rightChild.value, currentNode.rightChild.leftChild, currentNode.rightChild.rightChild) #删除后,再判断是否需要再平衡,然后进行再平衡操作 if currentNode.parent!=None: #不是根节点 if currentNode.parent.balanceFactor>1 or currentNode.parent.balanceFactor<-1: self.reblance(currentNode.parent) def updateBalance(self,node): if node.balanceFactor>1 or node.balanceFactor<-1: self.reblance(node) return if node.parent!=None: if node.isLeftChild(): node.parent.balanceFactor +=1 elif node.isRightChild(): node.parent.balanceFactor -=1 if node.parent.balanceFactor!=0: self.updateBalance(node.parent) def reblance(self,node): if node.balanceFactor>1: if node.leftChild.balanceFactor<0: self.rotateLeft(node.leftChild) self.rotateRight(node) elif node.balanceFactor<-1: if node.rightChild.balanceFactor>0: self.rotateRight(node.rightChild) self.rotateLeft(node) def rotateLeft(self,node): newroot = node.rightChild node.rightChild = newroot.leftChild if newroot.hasLeftChild(): newroot.leftChild.parent = node newroot.parent = node.parent if node.parent!=None: if node.isLeftChild(): node.parent.leftChild = newroot elif node.isRightChild(): node.parent.rightChild = newroot else: self.root = newroot newroot.leftChild = node node.parent = newroot node.balanceFactor = node.balanceFactor+1-min(newroot.balanceFactor,0) newroot.balanceFactor = newroot.balanceFactor+1+max(node.balanceFactor,0) def rotateRight(self,node): newroot = node.leftChild node.leftChild = newroot.rightChild if newroot.rightChild!=None: newroot.rightChild.parent = node newroot.parent = node.parent if node.parent!=None: if node.isLeftChild(): node.parent.leftChild = newroot elif node.isRightChild(): node.parent.rightChild = newroot else: self.root = newroot newroot.rightChild = node node.parent = newroot node.balanceFactor = node.balanceFactor-1-max(newroot.balanceFactor,0) newroot.balanceFactor = newroot.balanceFactor-1+min(node.balanceFactor,0) if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: mytree = AVLTree() mytree[8]="red" mytree[4]="blue" mytree[6]="yellow" mytree[5]="at" mytree[9]="cat" mytree[11]="mat" print(mytree[6]) print(mytree[5]) print ‘-‘*12 print (‘key‘,‘value‘,‘balanceFactor‘) for x in mytree: print x print ‘root:‘,mytree.root.key del mytree[6] print ‘-‘*12 print (‘key‘,‘value‘,‘balanceFactor‘) for x in mytree: print x print ‘root:‘,mytree.root.key
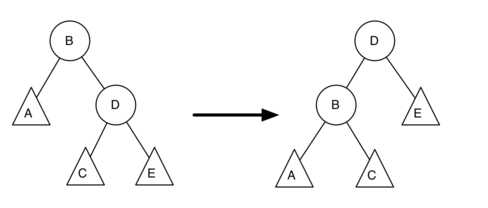
AVL Tree继承了二叉搜索树,对其插入和删除方法进行了重写,另外对TreeNode增加了balanceFactor属性。再进行左旋转和右旋转时,对于balanceFactor的需要计算一下,如图的左旋转过程中,D成为了新的根节点,只有B和D的平衡因子发生了变化,需要对其进行更新。(右旋转和左旋转类似)
B的平衡因子计算过程如下:(newBal(B)为左旋转后B的平衡因子,oldBal(B)为原来的节点B的平衡因子,h为节点的高度)
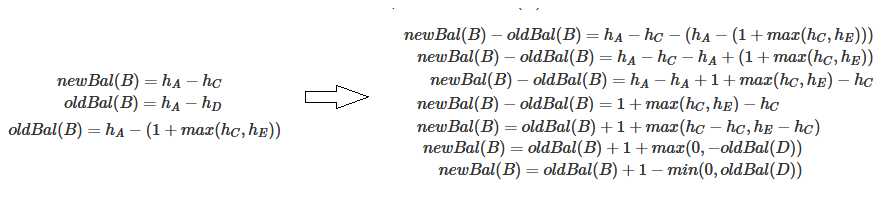
D的平衡因子计算过程如下:
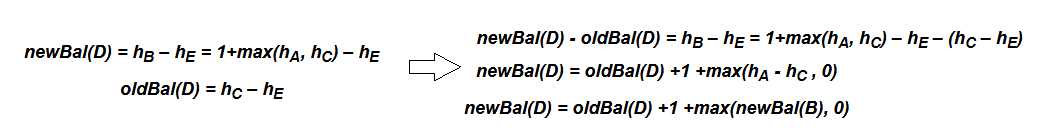
由于AVL Tree总是保持平衡,其put和get操作的复杂度能保持为O(log n)
7.总结
到目前为止,对于map(字典)数据结构,用二叉搜索树和AVL树实现了,也用有序列表和哈希表实现过,对应操作的复杂度如下:
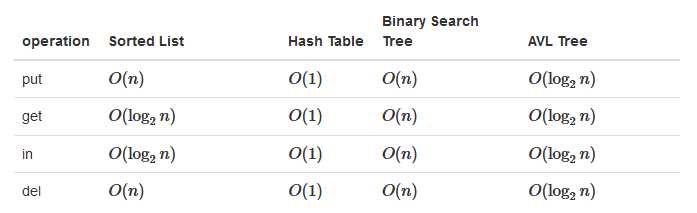
参考:http://interactivepython.org/runestone/static/pythonds/Trees/toctree.html
以上是关于树及其衍生算法(Trees and tree algorithms)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
