使用MATLAB分析风险之下的投资分配方案
Posted hanani
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了使用MATLAB分析风险之下的投资分配方案相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. discrete returns
讨论收益回报的离散性(例如,每天每周等)

gross return:总收益,指的是(不计成本的)所有的收益
net return通常称为净回报,指的是扣除所有成本的真正收益
annualized gross return 年化总收益
annualized net return 年化净收益
为方便计算,通常

事实上,虽然是取极限等于,其实在n=10时约等号两边就以及很接近啦.
2.continuously compounded return (log return)
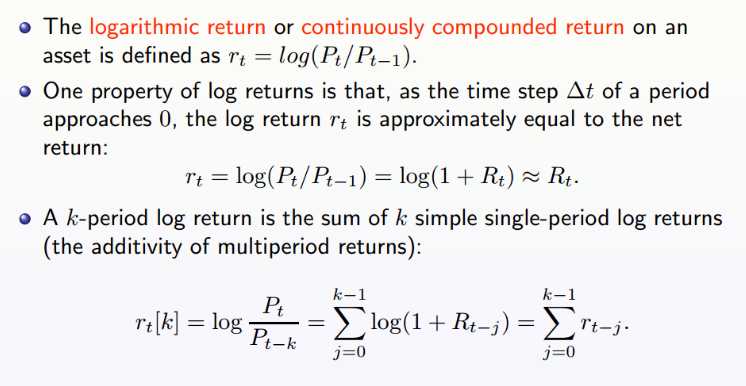
实际问题中可能直接将continuously compounded return称为continuous return.
第二点的解释:取的时间间隔很小时,log return和net return(净收益)几乎相等
NOTE:第三点中虽然k时间段内的log return是期间所有的log return求和,但未指明针对整段时间的情况下,这个continuous return会是一个list,从t0-t1一直到tn-1 - tn
3.Adjusted closed price (调整后的收盘价)
(约定俗成!!)通常使用Adjusted closed price来计算上述的各个return
4.计算股票年收益时
mean and covariance matrix for the yearly returns of the stocks = mean and covariance matrix for the weekly returns of the stocks * 52
本年度最难知识点了..对不起小学老师,可我真的忘记一年有52周了...一副扑克牌有多少张我也不知道/(ㄒoㄒ)/~~
5.案例
Consider the portfolios each having a different choice over the assets such that we cover all the following possibilities
[0, 0, 1]
[0, 0.1, 0.9]
[0.1, 0.1, 0.8]
.
.
[0.9, 0.1, 0]
[1, 0, 0]
三只股票分别是McDonald,Coca Cola和Microsoft, 时间为1991年1月1日到2001年1月1日
通过使用之前随笔中介绍的hist_stock_data获取.
if ~exist(‘stocks‘, ‘var‘)
stocks=hist_stock_data(‘01011991‘,‘01012001‘,‘KO‘,‘MCD‘,‘MSFT‘,‘frequency‘,‘wk‘);
CocaCola = stocks(1);
McDonalds = stocks(2);
Microsoft = stocks(3);
end
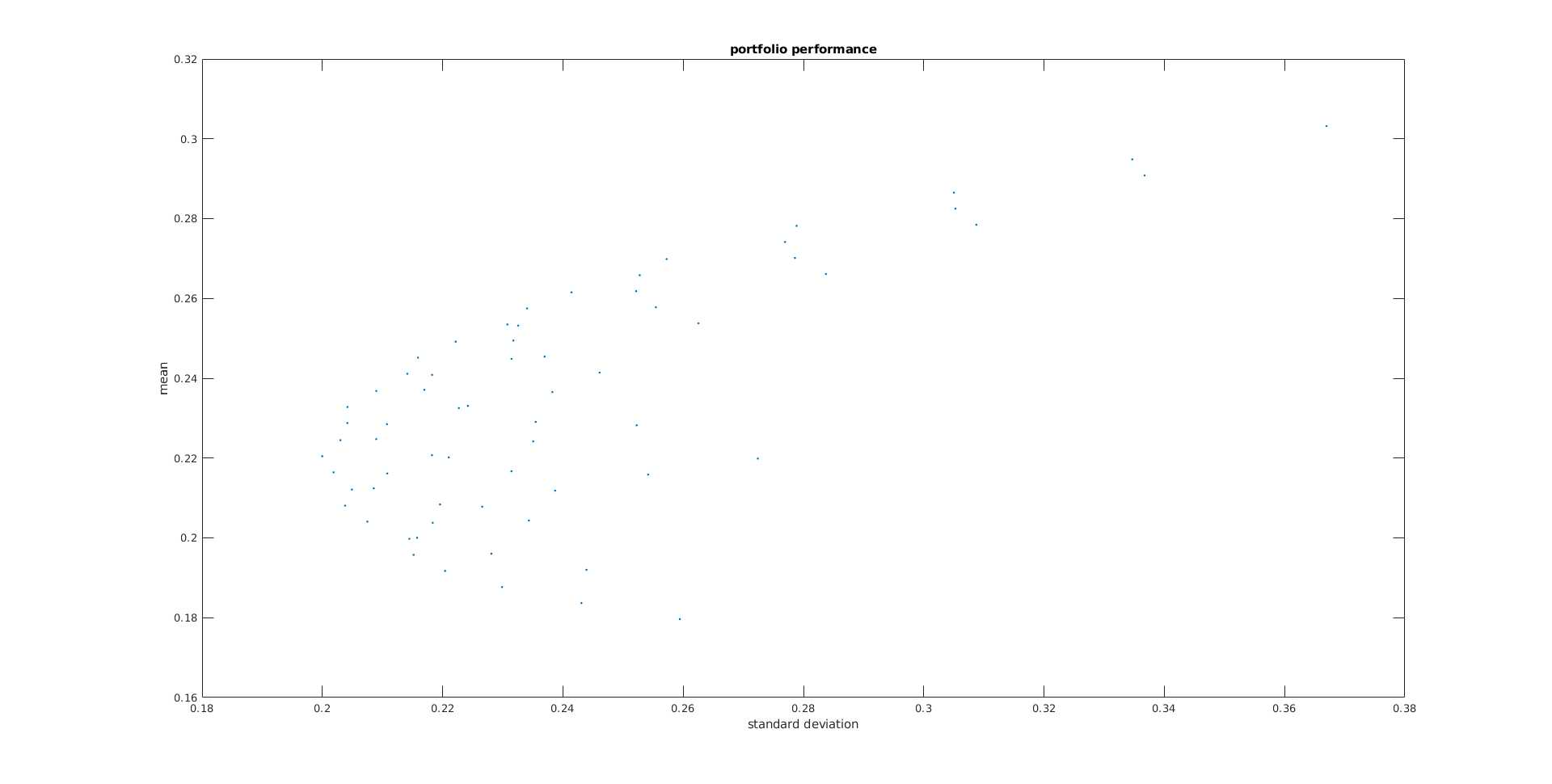
5.1 For each of the portfolios calculate the yearly mean and yearly standard deviation. Create a similar graph of mean against standard deviation.
% Caclualte log returns CCLR = log(CocaCola.AdjClose(2:end)./CocaCola.AdjClose(1:end-1) ); McLR = log(McDonalds.AdjClose(2:end)./McDonalds.AdjClose(1:end-1) ); MicLR = log(Microsoft.AdjClose(2:end)./Microsoft.AdjClose(1:end-1) ); LogReturns = [ CCLR, McLR, MicLR ]; yearlymean = 52 * mean(LogReturns)‘; yearlycov = 52 * cov(LogReturns)‘;
S = yearlycov;
% Now think about the portfolio
% p is such that in total p_1 + p_2 + p_3 = 1 and we look at the following
% combinations of the form (0.1, 0.1, 0.8), (0.1, 0.2, 0.7) and so forth
x = zeros(67,0);
portfolios = [];
count = 1;
for i = 0:10
for j = 0:10-i
k = 10 - i - j;
% assume the portfolio weights as x
x = [i; j; k] / 10;
portfolios = [ portfolios; x‘];
port_mean(count) = x‘ * yearlymean;
port_var(count) = x‘ * S * x;
port_std(count) = sqrt(port_var(count));
count = count+1;
end
end
np = count -1;
% Plot portfolios
plot(port_std, port_mean, ‘.‘);
title (‘portfolio performance‘);
xlabel(‘standard deviation‘);
ylabel(‘mean‘);
得到的Plot:
5.2 Which of the portfolios has the maximal mean
% highest expected return max_r = find (port_mean == max(port_mean)); portfolios(max_r, :) %pause; hold on; plot(port_std(max_r),port_mean(max_r), ‘rx‘);
就是mean最高的点,(Y轴最高)
5.3 Which of the portfolios has the lowest standard deviation
% Lowest standatd deviation min_std = find (port_std == min(port_std)); portfolios(min_std, :) %pause; hold on; plot(port_std(min_std),port_mean(min_std), ‘rx‘);
类似上步, x轴最小
5.4
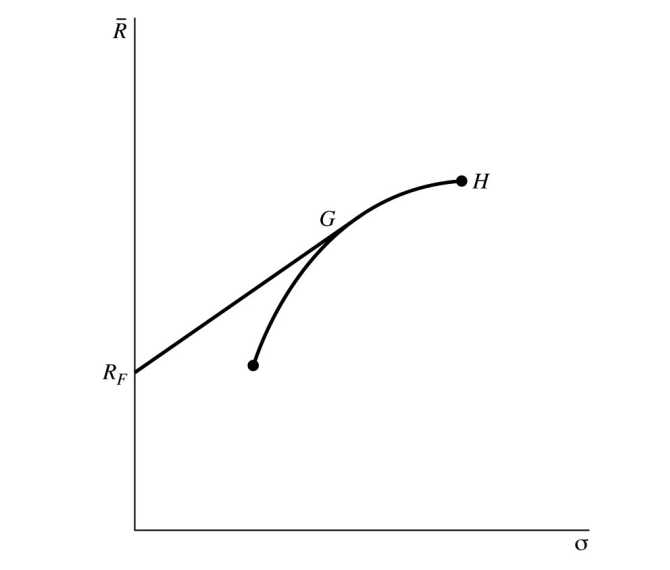
Which of the portfolios has the highest ratio of mean to stdev ( μx/σx )? why is this portfolio interesting?
% Max slope (sharpe ratio) max_slope = find (port_mean ./ port_std == max(port_mean ./ port_std)); %pause; hold on; plot(port_std(max_slope),port_mean(max_slope), ‘rx‘); portfolios(max_slope, :) % Which portfolios dominate other portfolios
这个点对应的最佳投资, 为从mean轴对应var最小的点向曲线引出的切线与斜线的交点. 投资此处可以兼顾利润和风险
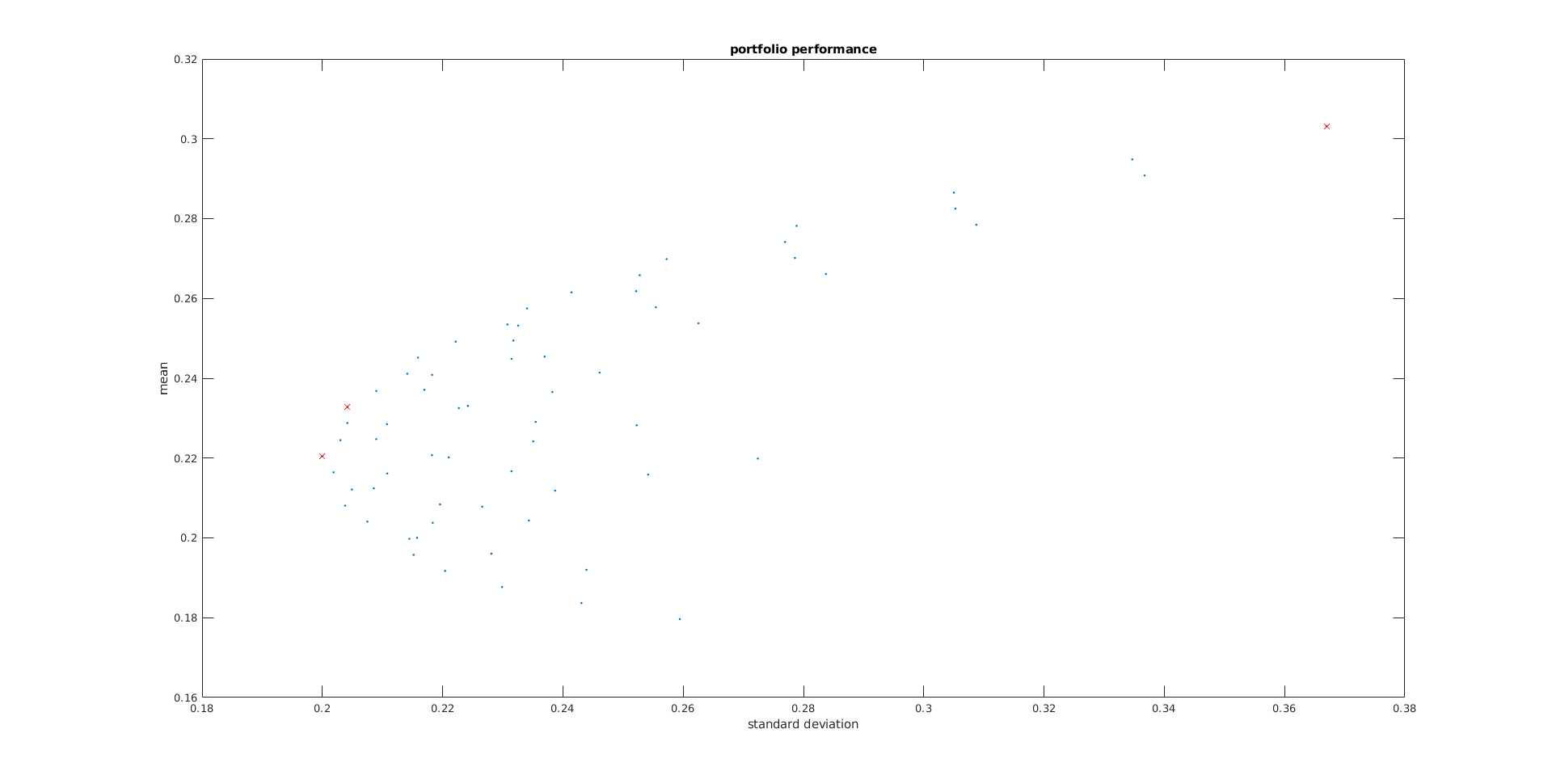
对应的最佳投资点:
以上是关于使用MATLAB分析风险之下的投资分配方案的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章