react-router的简单使用
Posted mrfanl
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了react-router的简单使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
React Router是一个基于React之上的强大路由库,可以让你向应用中快速的添加视图和数据流,同时保持页面与URL间的同步。
1.安装:
npm install --save react-router
2.问题说明:
刚开始的时候由于没有注意到版本信息,导致出现了一些错误,现在记录如下:
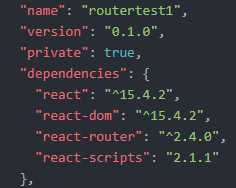
这是我package.js中的版本信息,
说明1:react-router的2.x版本和4.x版本不兼容,默认下载的4.x的版本,我这里选择的是2.x版本不然会报 “
TypeError: Cannot read property ‘location‘ of undefined”
说明2:react 16和react-router2.x的版本不兼容,会报“TypeError: Cannot read property ‘func‘ of undefined”,我这里讲react降级到了15
3.路由配置:
(1)路由配置是一组指令,用来告诉router如何匹配URL
React.render((
<Router>
<Route path="/" component={App}>
<Route path="about" component={About}>
<Route path="inbox" component={Message}>
</Route >
</Router>
),doucument.body);
其中<Route>中指定路径path 和 需要显示的组件component相匹配,并且Route之间允许嵌套,如上:About组件的路径就是“/about”。
(2)<IndexRoute>组件放在可以添加首页效果 ,在还未点击about,或者inbox时,自动显示在页面上,即类似在当请求的的URL匹配某个目录时,允许你指定一个类似index.html的入口文件。
ReactDOM.render(
<Router>
<Route path="/" component={App}>
<IndexRoute component={DashBoard}/>
<Route path="about" component={About}/>
<Route path="inbox" component={Inbox}>
<Route path="message/:id" component={Message}/>
</Route>
</Route>
</Router>
, document.getElementById(‘root‘));
显示效果如下:

URL路径与组件的联系如下:

如果在<Route>中将Message的路径改为绝对路径,如“/messages/:id”,
则最后一个URL与路径的匹配改为:/messages/:id-》app->Inbox->Message
(3)上面一条的最后我们改了URL,这使得旧的URL会出现错误界面,这时,我们可以通过<Redirect>这个组件使得原来的URL也可以正常工作。
ReactDOM.render(
<Router>
<Route path="/" component={App}>
<IndexRoute component={DashBoard}/>
<Route path="about" component={About}/>
<Route path="inbox" component={Inbox}>
<Route path="/message/:id" component={Message}/>
<Redirect from="message/:id" to="/message/:id"/>
</Route>
</Route>
</Router>
, document.getElementById(‘root‘));
(4)路由匹配的原理
三个属性来决定是否匹配一个URL:
- 嵌套关系
嵌套路由被描述成一个树形结构,并且通过深度优先遍历寻找一个与给定URL相匹配的路由。
- 路径语法
路由路径是匹配一个(或一部分)URL 的 一个字符模式串。大部分的路由路径都可以直接按照字面量理解,除了几个特殊的符号:
:paramName – 匹配一段位于 /、? 或 # 之后的 URL。 命中的部分将被作为一个参数
() – 在它内部的内容被认为是可选的
* – 匹配任意字符(非贪婪的)直到命中下一个字符或者整个 URL 的末尾,并创建一 个 splat参数
- 优先级
路由算法会根据定义的顺序自顶向下匹配路由。因此,当你拥有两个兄弟路由节点配置时,你必须确认前一个路由不会匹配后一个路由中的路径
4.Histories
React Router 是建立在 还是history之上的。 简而言之,一个 history 知道如何去监听浏览器地址栏的变化, 并解析这个 URL 转化为 location 对象, 然后 router 使用它匹配到路由,最后正确地渲染对应的组件。
(下面介绍一下history)
----------------------------------------分割线---------------------------------
history是一个javascript库,它允许您在JavaScript运行的任何地方轻松管理会话历史。history抽象了不同环境中的差异,并提供了一个最小的API,允许您管理历史堆栈、导航、确认导航和会话之间的持久状态。
history提供三种不同的方法去创建一个history对象,这取决于你的环境
createBrowserHistory,createMemoryHistory,createHashHistory
我们主要运用到createBrowserHistory,下面以这个为例子:
const history = createBrowserHistory(); const location = history.location; const unlisten = history.listen((location, action) => { console.log(location); }); history.push("/about",{some:"state"}); unlisten();
输出的location对象为:
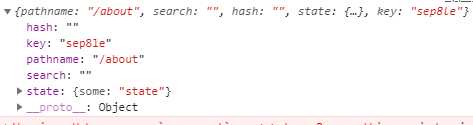
其中的pathname项就是当前url的地址。
有关history更多的信息,可以参考:https://github.com/ReactTraining/history
-----------------------------又是一条分割线--------------------------------------------------------
在React Router中可以引入browserHistory
import { browserHistory } from ‘react-router‘;
ReactDOM.render(
<Router history={browserHistory}>
<Route path="/" component={App}>
<IndexRoute component={DashBoard}/>
<Route path="about" component={About}/>
<Route path="inbox" component={Inbox}>
<Route path="/message/:id" component={Message}/>
<Redirect from="message/:id" to="/message/:id"/>
</Route>
</Route>
</Router>
, document.getElementById(‘root‘));
这样地址栏的地址会变为:
没有了奇怪的/#/
以上是关于react-router的简单使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章