如何实现同等间隙的卡片布局
Posted imwtr
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了如何实现同等间隙的卡片布局相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在列表展示中,经常会使用卡片的内容展示形式,为了美观,常常要求各卡片间的间隙是一致的。
卡片内容不一样可能高度不等,但一般来说为了整体的一致性,会限制每个卡片的宽高都相等。
本文就基于宽高一致的多个卡片,在不同屏幕大小下,每行卡片数量可能有调整,考量如何实现等间隙的布局。
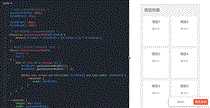
放置一张张卡片项,为了设置间距,最常见的就是直接使用一个特定的margin值了,这种方式虽然可以(通过精确计算后确实也可以)
直接设置一个间距,比如统一 margin-left 和 margin-bottom都为 20px ,并不能保证每行最后一个卡片之后的间距是20px
关于如何定这个 margin的值,需要通过一个规则来计算,这个后文再说明
设置同等间距,常用的还有 flex布局中的 justify-content: space-between,可以定义各子项目以相同间距布局,但不好处理左右子项目与边框的间距。 space-around这个就更用不得了,会使得左右子项目右margin == 左margin * 2
所以最终还是回到使用margin值来设置,通过一个可用的规则,来保证间距是一致的。
先把基本结构搭上
<div class="container"> <h2>项目列表</h2> <ul class="proj-items"></ul> </div> <!-- 模板结构 --> <script type="text/template" id="proj-item-tpl"> <li class="proj-item"> <a href="#/p/{{projectID}}"> <h3 class="proj-item__title">{{projectName}}</h3> <p class="proj-item__author">{{author}}</p> </a> </li> </script>
JS生成N个项目
function addEvent(elem, type, handler) { elem.addEventListener(type, handler, false); } function qs(selector) { return document.querySelector(selector); } function qsa(selectors) { return document.querySelectorAll(selectors); } var mockData = (function(num) { var data = []; for (var i = 1; i <= num; ++i) { data.push({ projectID: i, projectName: ‘项目‘ + i, author: ‘张大大‘ }); } return data; })(8); var itemTpl = qs(‘#proj-item-tpl‘).innerhtml; var itemsDOM = qs(‘.proj-items‘); /** * 渲染数据 * @param {[type]} data [description] * @return {[type]} [description] */ function renderList(data) { var html = ‘‘; var fragment = document.createDocumentFragment(); data.forEach(function(item) { var divTemp = document.createElement(‘div‘); // 模板替换 divTemp.innerHTML = itemTpl.replace(/{{(w+)}}/g, function(input, match) { return match ? item[match] || ‘‘ : ‘‘; }); fragment.appendChild(divTemp.firstElementChild); }); // 渲染 itemsDOM.appendChild(fragment); } renderList(mockData);
把基础样式放上,这里我们先指定一个特定的itemMargin值为20px
$itemMargin: 20px; $itemWidth: 130px; $itemHeight: 150px; .container { margin: 20px auto; width: 450px; background-color: #f2f2f2; color: #666; h2 { margin: 20px; padding-top: 20px; font-size: 20px; } } .proj-items { display: flex; flex-wrap: wrap; /* justify-content: space-between; */ padding: 0; list-style: none; &:after { content: ""; display: block; flex-grow: 99999; } } .proj-item { margin-left: $itemMargin; margin-bottom: $itemMargin; width: $itemWidth; height: $itemHeight; background-color: #fff; border-radius: 3px; text-align: center; &:hover { box-shadow: 0 0 20px #ddd; } a { display: block; padding: 15px; height: 100%; color: #666; text-decoration: none; } &__title { margin-top: 0; font-size: 16px; } &__author { font-size: 12px; } }

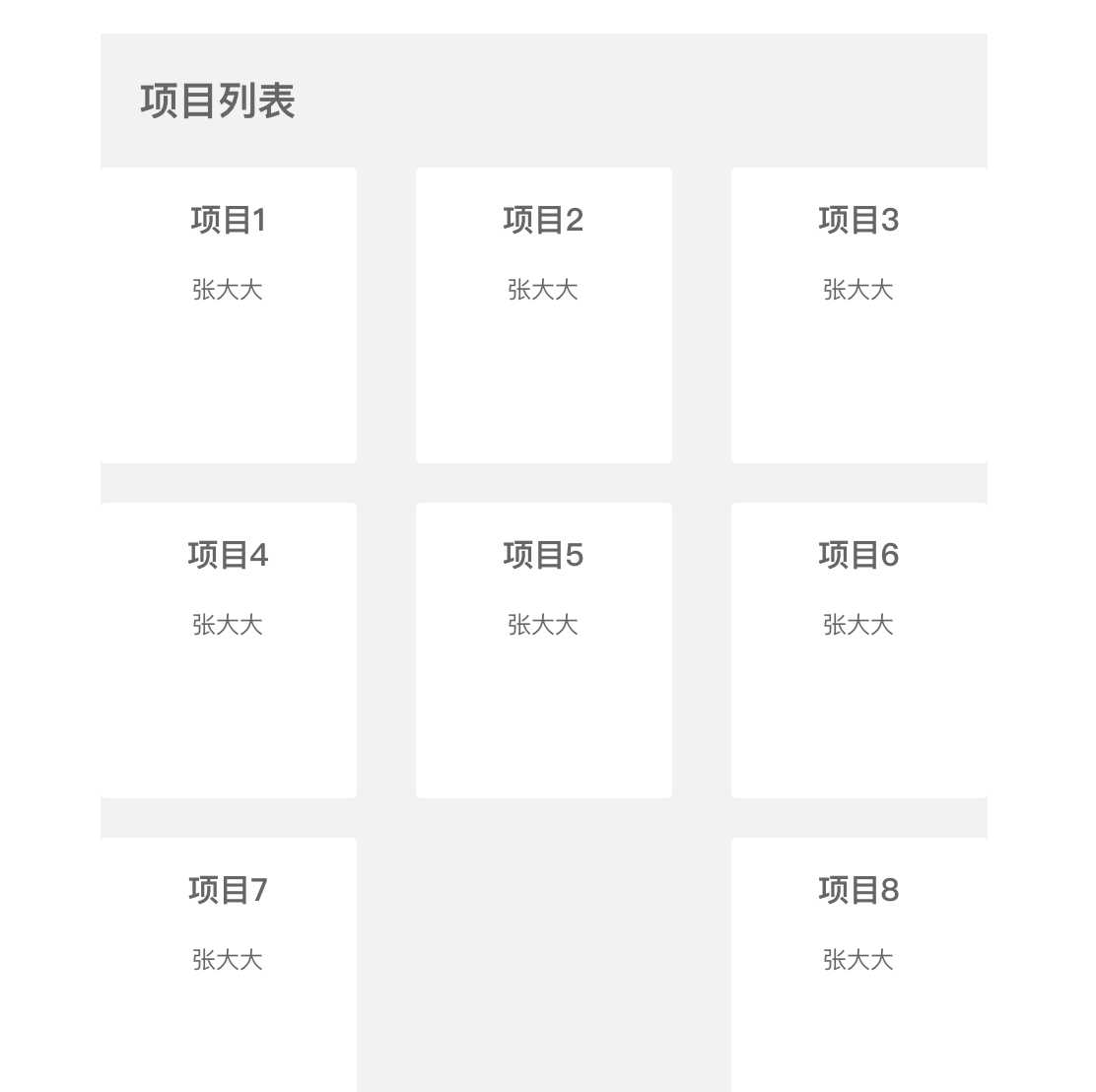
可以看到,每行最后一个间距不一致了,所以不能简单的写个margin值
再来看看设置 space-between的时候
.proj-items { justify-content: space-between; ... } .proj-item { /* margin-left: $itemMargin; */ margin-bottom: $itemMargin; ... }

看来并不够强大
如果看得仔细,应该能看到项目7和8是挨在一起的,为何没有间距呢
其一是因为没有margin-left值,其二是在项目列表后放了一个坑来占位,防止最后一行项目过少时 space-between的值太大了
把这个撤掉看看这个影响
&:after { content: ""; display: block; flex-grow: 99999; }
还是把目光投向margin值的设定规则吧
在设计一个页面布局时,至少已经确定了XX页面大小的情况下,容器宽度应该设置为多少(比如为1200px),每行放n个项目,项目的宽高是多少
有了这些指标(也必须有这些指标),我们就可以用来计算margin值了
containerWidth == n * itemWidth + (n + 1) * itemMargin
得出
itemMargin = (containerWidth - n * itemWidth) / (n + 1)
代入这里的情况,containerWidth 450px,itemWidth 130px,每行 3个,即可得出 itemMargin 正好为 15px

有了某种特定情况下的布局规则之后,接下来还要考虑不同屏幕大小的情况下,怎么调整这个margin值
这个需要结合媒体查询来设定,同时相应的计算规则也可以通过scss来处理
第一种情况是每行3个,n只可能为整数,即可推算出需要处理的临界值为1 2 3 4 5 6 ... 这些整数值
加入n为4,如果要保证 itemMargin值15px在各种情况下都相等,计算可得 容器宽度containerWidth值 为 595px
同理求得 n是5时为 740px ,n是2时为 305px
当然,如果觉得这个containerWidth值不太好看,也可以自己定义,比如 n是4的时候设置为 600px,代入公式那么 itemMargin值为16px。
为了保证各种请下间距都相等,我个人就不推荐这么干了


通过上述的规则计算,我们可以得出每行项目数量递增时的容器宽度临界值。把这些临界值放在媒体查询里面配置,即可方便地实现这种布局的自适应。
/* 这两个为初始就确定的基准值 */ $containerWidth: 305px; $itemMargin: 15px; $itemWidth: 130px; $itemHeight: 150px; /* 每行项目数量为itemNum时的容器宽度 */ @function getContainerWidth($itemNum) { @return $itemNum * $itemWidth + ($itemNum + 1) * $itemMargin; } /* 配置各个页面宽度下的容器宽度(应用) */ @mixin adjustContainerWidth( $from: 2, $to: 5 ) { @for $i from $from through $to { $minWidth: getContainerWidth($i); $maxWidth: getContainerWidth($i + 1); @media only screen and (min-width: $minWidth) and (max-width: $maxWidth) { .container { width: $minWidth; } } } } .container { margin: 20px auto; width: $containerWidth; background-color: #f2f2f2; color: #666; h2 { margin: 20px; padding-top: 20px; font-size: 20px; } } @include adjustContainerWidth( $from: 1, $to: 7 );
即可实现各个页面大小下的自适应效果
完整的CSS部分

1 /* 这两个为初始就确定的基准值 */ 2 $containerWidth: 305px; 3 $itemMargin: 15px; 4 5 $itemWidth: 130px; 6 $itemHeight: 150px; 7 8 /* 每行项目数量为itemNum时的容器宽度 */ 9 @function getContainerWidth($itemNum) { 10 @return $itemNum * $itemWidth + ($itemNum + 1) * $itemMargin; 11 } 12 13 /* 配置各个页面宽度下的容器宽度(应用) */ 14 @mixin adjustContainerWidth( 15 $from: 2, 16 $to: 5 17 ) { 18 @for $i from $from through $to { 19 $minWidth: getContainerWidth($i); 20 $maxWidth: getContainerWidth($i + 1); 21 22 @media only screen and (min-width: $minWidth) and (max-width: $maxWidth) { 23 .container { 24 width: $minWidth; 25 } 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 30 .container { 31 margin: 20px auto; 32 width: $containerWidth; 33 background-color: #f2f2f2; 34 color: #666; 35 36 h2 { 37 margin: 20px; 38 padding-top: 20px; 39 font-size: 20px; 40 } 41 } 42 43 @include adjustContainerWidth( 44 $from: 1, 45 $to: 7 46 ); 47 48 .proj-items { 49 display: flex; 50 flex-wrap: wrap; 51 padding: 0; 52 list-style: none; 53 } 54 55 .proj-item { 56 margin-left: $itemMargin; 57 margin-bottom: $itemMargin; 58 width: $itemWidth; 59 height: $itemHeight; 60 background-color: #fff; 61 border-radius: 3px; 62 text-align: center; 63 64 &:hover { 65 box-shadow: 0 0 20px #ddd; 66 } 67 68 a { 69 display: block; 70 padding: 15px; 71 height: 100%; 72 color: #666; 73 text-decoration: none; 74 } 75 76 &__title { 77 margin-top: 0; 78 font-size: 16px; 79 } 80 81 &__author { 82 font-size: 12px; 83 } 84 }
以上是关于如何实现同等间隙的卡片布局的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
