自制有声书阅读器:用PaddleSpeech打开读书新方式
Posted 百度大脑
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了自制有声书阅读器:用PaddleSpeech打开读书新方式相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。


吕声辉,飞桨开发者技术专家(PPDE),某网络科技公司研发工程师。主要研究方向为图像识别,自然语言处理等。
• AI Studio主页
https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/personalcenter/thirdview/227158

项目背景
随着互联网的发展,普通用户对于书籍展示形式的需求已由纯文字变成了图文、语音、视频等多种形式,因此将文本书籍转换为有声读物具有很大的市场需求。本文以飞桨语音模型库PaddleSpeech提供的语音合成技术为核心,通过音色克隆、语速设置、音量调整等附加功能,展示有声书籍的技术可行方案。
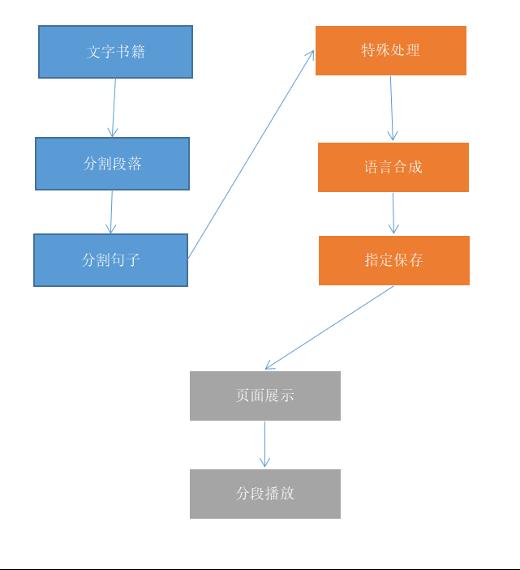
最终呈现效果如
player.bilibili.com/player.html?bvid=BV1x84y1V7SR
网页体验访问地址
https://book.weixin12306.com/

环境准备
PaddleSpeech 是基于飞桨的语音方向开源模型库,用于语音和音频中的各种关键任务的开发,包含大量基于深度学习的前沿和有影响力的模型。首先进行PaddleSpeech安装环境的配置,配置如下:
# 注意如果之前运行过这步 下次就不用再运行了,这个目录重启项目也不会清空的
# 下载解压说话人编码器
!wget -P data https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlespeech/Parakeet/released_models/ge2e/ge2e_ckpt_0.3.zip
!unzip -o -d work data/ge2e_ckpt_0.3.zip
# 下载解压声码器
!wget -P data https://paddlespeech.bj.bcebos.com/Parakeet/released_models/pwgan/pwg_aishell3_ckpt_0.5.zip
!unzip -o -d work data/pwg_aishell3_ckpt_0.5.zip
# 下载解压声学模型
!wget -P data https://paddlespeech.bj.bcebos.com/Parakeet/released_models/fastspeech2/fastspeech2_nosil_aishell3_vc1_ckpt_0.5.zip
!unzip -o -d work data/fastspeech2_nosil_aishell3_vc1_ckpt_0.5.zip
# 下载解压nltk包
!wget -P data https://paddlespeech.bj.bcebos.com/Parakeet/tools/nltk_data.tar.gz
!tar zxvf data/nltk_data.tar.gz
# 安装PaddleSpeech
!pip install pytest-runner
!pip install paddlespeech
# 将nltk_data 拷贝到 /home/aistudio 目录
!cp -r /home/aistudio/work/nltk_data /home/aistudio
# 安装moviepy
!pip install moviepy==1.0.3
数据处理每本书的内容均以json格式存放在txt文本中,路径为
/work/books/inputs/bookname.txt。为方便演示,这里以三国演义为例。
“name”: “三国演义”,
“lists”: [
“title”: “第一回 宴桃园豪杰三结义 斩黄巾英雄首立功”
“content”: “滚滚长江东逝水,浪花淘尽英雄。是非成败转头空。青山依
,
“title”: “第二回 张翼德怒鞭督邮 何国舅谋诛宦竖”,
“content”: “且说董卓字仲颖,陇西临洮人也,官拜河东太守,自来骄傲
]

音频合成

段落句子分割
以换行符"\\n"分割为段落,以"。"分割为句子。
# 段落和句子分割
def lists(self, lists):
results = []
for i in range(len(lists)):
item = lists[i]
title = item['title']
content = item['content']
sections = []
sentences = []
contents = content.split('\\n')
for citem in contents:
if len(citem) > 1:
sections.append(citem)
sentenceIndex = 0
for sitems in sections:
sitems_ = []
for tmp in sitems.split('。'):
if len(tmp) > 1:
sitems_.append(tmp)
for j in range(len(sitems_)):
sentence =
'id':sentenceIndex,
'sentence': sitems_[j],
'end': 0 if j < len(sitems_) - 1 else 1
sentences.append(sentence)
sentenceIndex += 1
result =
'id':i,
'title':title,
'sentences':sentences
results.append(result)
return results
特殊字符处理
在国学书籍中,有可能出现很多生僻字或者特殊符号,这里需要做针对性的替换。
# 特殊处理示例,工程化最好用字典自动判断替换
def dealText(self, text):
text = text.replace('-','')
text = text.replace(' ', '')
text = text.replace('’','')
text = text.replace('﨑','崎')
text = text.replace("[",' ')
text = text.replace("]",' ')
text = text.replace(' ',' ')
text = text.replace(",]","")
text = text.replace("1","1")
text = text.replace("2",'2')
text = text.replace("6","6")
text = text.replace("〔","")
text = text.replace("─","")
text = text.replace("┬","")
text = text.replace("┼","")
text = text.replace("┴","")
text = text.replace("〖"," ")
text = text.replace("〗"," ")
text = text.replace("礻殳","祋")
return text
音频合成
根据分割的ID,保存到对应位置。
# 音频合成
def audio(self, contents):
self.tts = TTSExecutor()
for i in range(len(contents['lists'])):
item = contents['lists'][i]
basePath = self.bookPathOutput+'/'+self.bookname+'/'+str(i)
if os.path.exists(basePath) is False:
os.makedirs(r''+basePath)
# 生成每回标题音频
self.text2audio(item['title'], basePath+'/title.wav')
# 生成每句内容音频
for j in range(len(item['sentences'])):
sitem = item['sentences'][j]
self.text2audio(sitem['sentence'], basePath+'/'+str(sitem['id'])+'.wav')
def text2audio(self, text, path):
text = self.dealText(text)
self.voice_cloning(text, path)
#self.tts(text=text, output=path)
音色克隆
可以事先将不同音色音频放置在 /work/sounds 目录下。此处音色克隆部分的功能主要参考自PaddleSpeech语音克隆项目。
项目链接
https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4265795?channelType=0&channel=0
def clone_pre(self):
# Init body.
with open(self.am_config) as f:
am_config = CfgNode(yaml.safe_load(f))
self.am_config_ = am_config
with open(self.voc_config) as f:
voc_config = CfgNode(yaml.safe_load(f))
# speaker encoder
p = SpeakerVerificationPreprocessor(
sampling_rate=16000,
audio_norm_target_dBFS=-30,
vad_window_length=30,
vad_moving_average_width=8,
vad_max_silence_length=6,
mel_window_length=25,
mel_window_step=10,
n_mels=40,
partial_n_frames=160,
min_pad_coverage=0.75,
partial_overlap_ratio=0.5)
print("Audio Processor Done!")
self.p = p
speaker_encoder = LSTMSpeakerEncoder(
n_mels=40, num_layers=3, hidden_size=256, output_size=256)
speaker_encoder.set_state_dict(paddle.load(self.ge2e_params_path))
speaker_encoder.eval()
self.speaker_encoder = speaker_encoder
print("GE2E Done!")
with open(self.phones_dict, "r") as f:
phn_id = [line.strip().split() for line in f.readlines()]
vocab_size = len(phn_id)
print("vocab_size:", vocab_size)
# acoustic model
odim = am_config.n_mels
# model: model_name_dataset
am_name = self.am[:self.am.rindex('_')]
am_dataset = self.am[self.am.rindex('_') + 1:]
am_class = dynamic_import(am_name, self.model_alias)
am_inference_class = dynamic_import(
am_name + '_inference', self.model_alias)
if am_name == 'fastspeech2':
am = am_class(
idim=vocab_size, odim=odim, spk_num=None, **am_config["model"])
elif am_name == 'tacotron2':
am = am_class(idim=vocab_size, odim=odim, **am_config["model"])
am.set_state_dict(paddle.load(self.am_ckpt)["main_params"])
am.eval()
am_mu, am_std = np.load(self.am_stat)
am_mu = paddle.to_tensor(am_mu)
am_std = paddle.to_tensor(am_std)
am_normalizer = ZScore(am_mu, am_std)
am_inference = am_inference_class(am_normalizer, am)
am_inference.eval()
self.am_inference = am_inference
print("acoustic model done!")
# vocoder
# model: model_name_dataset
voc_name = self.voc[:self.voc.rindex('_')]
voc_class = dynamic_import(voc_name, self.model_alias)
voc_inference_class = dynamic_import(
voc_name + '_inference', self.model_alias)
voc = voc_class(**voc_config["generator_params"])
voc.set_state_dict(paddle.load(self.voc_ckpt)["generator_params"])
voc.remove_weight_norm()
voc.eval()
voc_mu, voc_std = np.load(self.voc_stat)
voc_mu = paddle.to_tensor(voc_mu)
voc_std = paddle.to_tensor(voc_std)
voc_normalizer = ZScore(voc_mu, voc_std)
voc_inference = voc_inference_class(voc_normalizer, voc)
voc_inference.eval()
self.voc_inference = voc_inference
print("voc done!")
self.frontend = Frontend(phone_vocab_path=self.phones_dict)
print("frontend done!")
# 获取音色
ref_audio_path = self.soundsInput+'/'+str(self.sound)+'.mp3'
mel_sequences = self.p.extract_mel_partials(self.p.preprocess_wav(ref_audio_path))
# print("mel_sequences: ", mel_sequences.shape)
with paddle.no_grad():
spk_emb = self.speaker_encoder.embed_utterance(paddle.to_tensor(mel_sequences))
# print("spk_emb shape: ", spk_emb.shape)
self.spk_emb = spk_emb
def voice_cloning(self, text, path):
input_ids = self.frontend.get_input_ids(text, merge_sentences=True)
phone_ids = input_ids["phone_ids"][0]
with paddle.no_grad():
wav = self.voc_inference(self.am_inference(phone_ids, spk_emb=self.spk_emb))
sf.write(path, wav.numpy(), samplerate=self.am_config_.fs)
self.post_del(path)
语速和音量调整
def post_del(self, path):
old_au = AudioFileClip(path)
new_au = old_au.fl_time(lambda t: self.speed*t, apply_to=['mask', 'audio'])
new_au = new_au.set_duration(old_au.duration/self.speed)
new_au = (new_au.fx(afx.volumex, self.volumex))
final_path = path.replace('outputs','final')
print(path, final_path)
new_au.write_audiofile(final_path)
print('^^^^^^')音色、语速和音量需要在 main.py 的头部中设置。
class Main(object):
def __init__(self):
self.bookPathInput = './books/inputs' # 书籍输入目录
self.bookPathOutput = './books/outputs' # 常规输出目录
self.bookPathFinal = './books/final' # 最终输出目录
self.bookname = 'sanguoyanyi'
self.tts = None
self.soundsInput = './sounds' # 音色文件存放目录
self.sound = '001' # 音色编号
self.speed = 1.0 # 语速
self.volumex = 1.1 # 音量
# 音频合成,一键命令
%cd /home/aistudio/work/
!python main.py
查看生成结果
最终切分好的数据在
/work/outputs/sanguoyanyi目录下,原始语速和音量音频在outputs目录下,指定语速和音量音频在final目录下。其中的outputs.txt为切分内容,而音频会按照每个章节以及每个章节的句子索引排序好。
以下为outputs.txt 内容:
“name”: “三国演义”,
“lists”: [
“id”: 0,
“title”: “第一回 宴桃园豪杰三结义 斩黄巾英雄首立功”,
“sentence”: [
“id”: 0
“sentence”: “滚滚长江东逝水,浪花淘尽英雄”,
“end”: 0
,
“id”: 1,
“sentence”: “是否成败转头空”,
“end”: 0
,
“id”: 2,
“sentence”: “青山依旧在,几度夕阳红”,
“end”: 0
,
“id”: 3,
“sentence”: “白发渔樵江渚上,惯看秋月春风”,
“end”: 0
,
“id”: 4,
“sentence”: “一壶浊酒喜相逢”,
“end”: 0
, 以下为第一回的每个句子wav格式音频。

客户端展示
输出第三部分生成好的内容和音频。这里用H5页面简单展示一下有声书阅读的效果,包括内容展示和逐句朗读高亮两种功能。
H5的具体代码已放在GitHub 上,大家可在下方链接中查看
https://github.com/lvsh2012/book2audio
手机或者PC也可直接体验
https://book.weixin12306.com/

总结
通过PaddleSpeech可以简单快速地实现语音合成功能,轻松实现书籍有声化。使用者在这里需要关注下,当以H5展示播放效果时,需要注意内容和音频的对应关系。除了语音合成功能外,PaddleSpeech还提供了包括语音识别、声纹提取、标点恢复等其他功能。相信大家基于PaddleSpeech可以在该领域挖掘出更多的可能性!

关注【飞桨PaddlePaddle】公众号
获取更多技术内容~
以上是关于自制有声书阅读器:用PaddleSpeech打开读书新方式的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章