RabbitMQ队列
Posted sui776265233
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了RabbitMQ队列相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1、为啥要使用MQ
以常见的订单系统为例,用户点击【下单】按钮之后的业务逻辑可能包括:扣减库存、生成相应单据、发红包、发短信通知。在业务发展初期这些逻辑可能放在一起同步执行,随着业务的发展订单量增长,需要提升系统服务的性能,这时可以将一些不需要立即生效的操作拆分出来异步执行,比如发放红包、发短信通知等。这种场景下就可以用 MQ ,在下单的主流程(比如扣减库存、生成相应单据)完成之后发送一条消息到 MQ 让主流程快速完结,而由另外的单独线程拉取MQ的消息(或者由 MQ 推送消息),当发现 MQ 中有发红包或发短信之类的消息时,执行相应的业务逻辑。
2、MQ的介绍
MQ全称为Message Queue, 消息队列(MQ)是一种应用程序对应用程序的通信方法。MQ是消费-生产者模型的一个典型的代表,一端往消息队列中不断写入消息,而另一端则可以读取队列中的消息。消息发布者只管把消息发布到 MQ 中而不用管谁来取,消息使用者只管从 MQ 中取消息而不管是谁发布的。这样发布者和使用者都不用知道对方的存在。你可以想想在生活中的一种场景:当你把信件的投进邮筒,邮递员肯定最终会将信件送给收件人。我们可以把MQ比作 邮局和邮递员。
MQ和邮局的主要区别是,它不处理消息,但是,它会接受数据、存储消息数据、转发消息
3、队列,生产者,消费者
队列是RabbitMQ的内部对象,用于存储消息。生产者(下图中的P)生产消息并投递到队列中,消费者(下图中的C)可以从队列中获取消息并消费。

多个消费者可以订阅同一个队列,这时队列中的消息会被平均分摊给多个消费者进行处理,而不是每个消费者都收到所有的消息并处理。

队列的作用:
- 存储消息、数据
- 保证消息的顺序
- 保证数据的正确交付
为啥不直接使用Queue而是RabbitMQ?
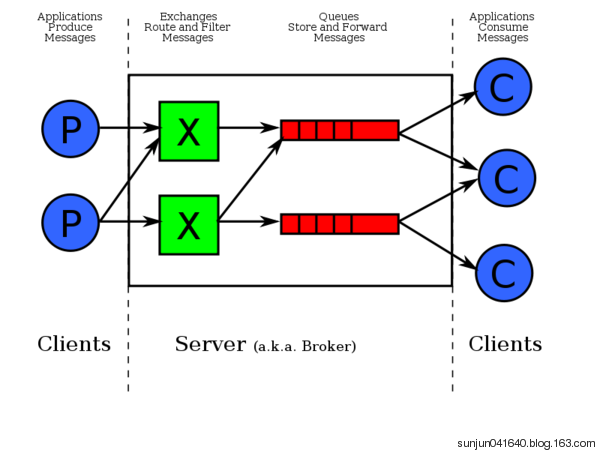
4、RabbitMQ架构介绍
-
Publisher
消息的生产者,也是一个向交换器发布消息的客户端应用程序。
-
Exchange
交换器,用来接收生产者发送的消息并将这些消息路由给服务器中的队列。
-
Queue
消息队列,用来保存消息直到发送给消费者。它是消息的容器,也是消息的终点。一个消息可投入一个或多个队列。消息一直在队列里面,等待消费者连接到这个队列将其取走。
-
Channel
信道,多路复用连接中的一条独立的双向数据流通道
-
Consumer
消息的消费者,表示一个从消息队列中取得消息的客户端应用程序
5、RabbitMQ安装
- server端的安装
|
1
|
安装 http://www.rabbitmq.com/install-standalone-mac.html
|
- API的安装
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
pip install pika
or
easy_install pika
or
源码
https://pypi.python.org/pypi/pika
|
生产者
import pika credentials = pika.PlainCredentials(‘lisi‘,‘123456‘) connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host="localhost", credentials=credentials)) channel = connection.channel() channel.queue_declare(‘test‘) channel.basic_publish(exchange=‘‘, routing_key=‘test‘, body=‘hello test‘) print(‘publish done‘) connection.close()
消费者
import pika credentials = pika.PlainCredentials(‘lisi‘,‘123456‘) connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host="localhost", credentials=credentials)) channel = connection.channel() channel.queue_declare(queue=‘test‘) def callback(ch, method, properties, body): print("consume done", ch, method, properties,body) channel.basic_consume(callback, queue="test", no_ack=True) channel.start_consuming()
远程连接rabbitmq server的话,需要配置权限
首先在rabbitmq server上创建一个用户
|
1
|
sudo rabbitmqctl add_user zhangsan 123456
|
同时还要配置权限,允许从外面访问
|
1
2
3
4
|
sudo rabbitmqctl set_permissions -p / zhangsan ".*" ".*" ".*"
# 命令讲解
set_permissions [-p vhost] {user} {conf} {write} {read}
|
1、单条消息丢失
在生产者端,需要加上一个属性
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
channel.basic_publish(exchange=‘mydirect‘,
routing_key=‘task_queue‘,
body=message,
properties=pika.BasicProperties(
delivery_mode=2, # make message persistent
)
)
|
在消费者端,需要加上确认消息代码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] Received %r" % body)
time.sleep(10)
print(" [x] Done")
print("method.delivery_tag",method.delivery_tag)
ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag=method.delivery_tag)
|
并且,我们需要去掉no_ack=true这段代码
2、消息队列宕机
如果你的服务器宕机了,所有的消息都会丢失,咋办?
channel.queue_declare(queue=’test’, durable=True)
注意:队列必须在第一次声明的时候,就必须要持久化,途中设置回报错
3、消息的能者多劳
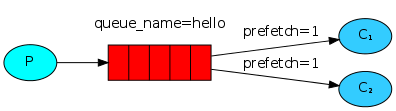
服务器的性能大小不一,有的服务器处理的快,有的服务器处理的慢,因此默认的轮询方式不能够满足我们的需求,我们要的是 能者多劳,最大限度的发挥我们机器的性能. 为解决此问题,可以在各个消费者端,配置perfetch=1,意思就是告诉RabbitMQ在我这个消费者当前消息还没处理完的时候就不要再给我发新消息了。
|
1
2
3
4
|
channel.basic_qos(prefetch_count=1)
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue=‘task_queue‘)
|
7、Exchange类型
Exchange分发消息时根据类型的不同分发策略有区别,目前共四种类型:direct、fanout、topic、headers 。headers 匹配消息的 header头部字节 而不是路由键,此外 headers 交换器和 direct 交换器完全一致,但性能差很多,目前几乎用不到了,所以直接看另外三种类型:
1、direct
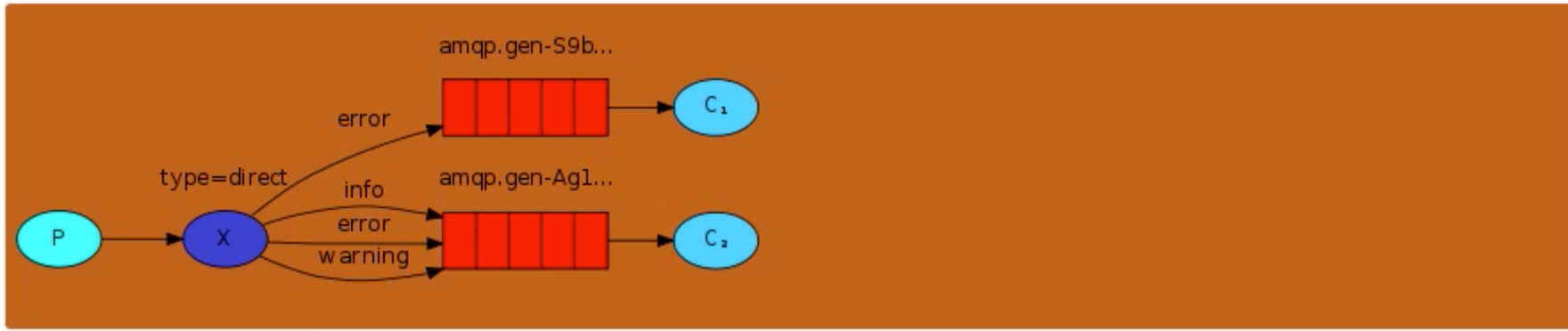
消息中的路由键(routing key)如果和 Binding 中的 binding key 一致, 交换器就将消息发到对应的队列中。路由键与队列名完全匹配,如果一个队列绑定到交换机要求路由键为“dog”,则只转发 routing key 标记为“dog”的消息,不会转发“dog.puppy”,也不会转发“dog.guard”等等。它是完全匹配、单播的模式
生产者
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
#author:shangzekai
import pika,sys
credentials = pika.PlainCredentials(‘lisi‘,‘123456‘)
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host="localhost", credentials=credentials))
channel = connection.channel()
# 开始连接exchange
channel.exchange_declare(exchange=‘mydirect‘,type=‘direct‘)
log_level = sys.argv[1] if len(sys.argv) > 1 else "info"
message = ‘ ‘.join(sys.argv[1:]) or "info:helloworld!"
channel.basic_publish(exchange=‘mydirect‘,
routing_key=log_level,
body=message)
print("publish %s to %s" % (message,log_level))
connection.close()
|
消费者
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
import pika,sys
credentials = pika.PlainCredentials(‘lisi‘,‘123456‘)
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host="localhost", credentials=credentials))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange=‘mydirect‘, type=‘direct‘)
queue_obj = channel.queue_declare(exclusive=True) #不指定queue名字,rabbit会随机分配一个名字,exclusive=True会在使用此queue的消费者断开后,自动将queue删除
queue_name = queue_obj.method.queue
print(‘queue name‘,queue_name,queue_obj)
log_levels = sys.argv[1:]
if not log_levels:
sys.stderr.write("Usage: %s [info] [warning] [error]
" % sys.argv[0])
sys.exit(1)
for level in log_levels:
channel.queue_bind(exchange=‘mydirect‘,queue=queue_name,routing_key=level) #绑定队列到Exchange
print(‘ [*] Waiting for logs. To exit press CTRL+C‘)
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] %r" % body)
channel.basic_consume(callback,queue=queue_name, no_ack=True)
channel.start_consuming()
|
2、fanout
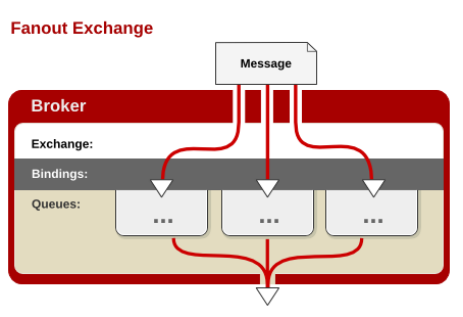
每个发到 fanout 类型交换器的消息都会分到所有绑定的队列上去。fanout 交换器不处理路由键,只是简单的将队列绑定到交换器上,每个发送到交换器的消息都会被转发到与该交换器绑定的所有队列上。很像子网广播,每台子网内的主机都获得了一份复制的消息。fanout 类型转发消息是最快的。
生产者代码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
import pika
credentials = pika.PlainCredentials(‘用户名‘, ‘密码‘)
parameters = pika.ConnectionParameters(host=‘localhost‘,credentials=credentials)
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(parameters)
channel = connection.channel()
# 开始连接exchange
channel.exchange_declare(exchange=‘myfanout‘,type=‘fanout‘)
message = sys.argv[1] if(len(sys.argv[1])>1) else "info"
channel.basic_publish(exchange=‘myfanout‘,
routing_key=‘‘,
body=message)
print("publish done %s" % message)
connection.close()
|
消费者代码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
import pika
credentials = pika.PlainCredentials(‘用户名‘, ‘密码‘)
parameters = pika.ConnectionParameters(host=‘localhost‘,credentials=credentials)
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(parameters)
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange=‘myfanout‘, type=‘fanout‘)
queue_obj = channel.queue_declare(exclusive=True) #不指定queue名字,rabbit会随机分配一个名字,exclusive=True会在使用此queue的消费者断开后,自动将queue删除
queue_name = queue_obj.method.queue
print(‘queue name‘,queue_name,queue_obj)
channel.queue_bind(exchange=‘myfanout‘,queue=queue_name) #绑定队列到Exchange
print(‘ [*] Waiting for logs. To exit press CTRL+C‘)
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] %r" % body)
channel.basic_consume(callback,queue=queue_name, no_ack=True)
channel.start_consuming()
|
3、topic
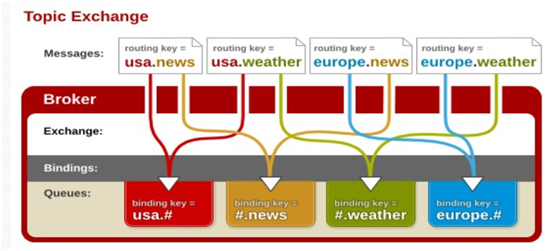
topic 交换器通过模式匹配分配消息的路由键属性,将路由键和某个模式进行匹配,此时队列需要绑定到一个模式上。它将路由键和绑定键的字符串切分成单词,这些单词之间用点隔开
To receive all the logs run:
python receive_logs_topic.py “#”
To receive all logs from the facility “kern”:
python receive_logs_topic.py “kern.*”
Or if you want to hear only about “critical” logs:
python receive_logs_topic.py “*.critical”
You can create multiple bindings:
python receive_logs_topic.py “kern.“ “.critical”
And to emit a log with a routing key “kern.critical” type:
python emit_log_topic.py “kern.critical” “A critical kernel error”
生产者代码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
import pika
import sys
credentials = pika.PlainCredentials(‘用户名‘, ‘密码‘)
parameters = pika.ConnectionParameters(host=‘localhost‘,credentials=credentials)
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(parameters)
channel = connection.channel() #队列连接通道
channel.exchange_declare(exchange=‘mytopic‘,type=‘topic‘)
log_level = sys.argv[1] if len(sys.argv) > 1 else ‘all.info‘
message = ‘ ‘.join(sys.argv[1:]) or "all.info: Hello World!"
channel.basic_publish(exchange=‘topic_log‘,
routing_key=log_level,
body=message)
print(" [x] Sent %r" % message)
connection.close()
|
消费者
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
import pika,sys
credentials = pika.PlainCredentials(‘用户名‘, ‘密码‘)
parameters = pika.ConnectionParameters(host=‘localhost‘,credentials=credentials)
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(parameters)
channel = connection.channel()
queue_obj = channel.queue_declare(exclusive=True) #不指定queue名字,rabbit会随机分配一个名字,exclusive=True会在使用此queue的消费者断开后,自动将queue删除
queue_name = queue_obj.method.queue
log_levels = sys.argv[1:] # info warning errr
if not log_levels:
sys.stderr.write("Usage: %s [info] [warning] [error]
" % sys.argv[0])
sys.exit(1)
for level in log_levels:
channel.queue_bind(exchange=‘topic_log‘,
queue=queue_name,
routing_key=level)
print(‘ [*] Waiting for logs. To exit press CTRL+C‘)
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] %r" % body)
channel.basic_consume(callback,queue=queue_name, no_ack=True)
channel.start_consuming()
|
8、RabbitMQ服务器的管理
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
./sbin/rabbitmq-server -detached # 后台启动
./sbin/rabbitmqctl status # 查看状态
./sbin/rabbitmqctl stop # 关闭
./sbin/rabbitmqctl list_queues # 查看queue
|
以上是关于RabbitMQ队列的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章