平时二十四测
Posted edsheeran
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了平时二十四测相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
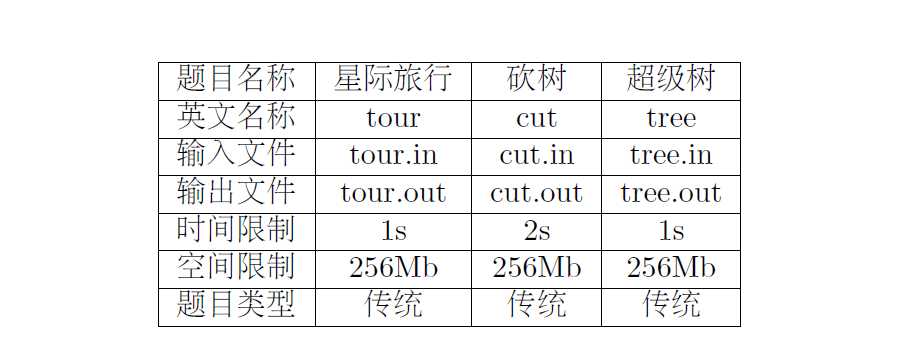

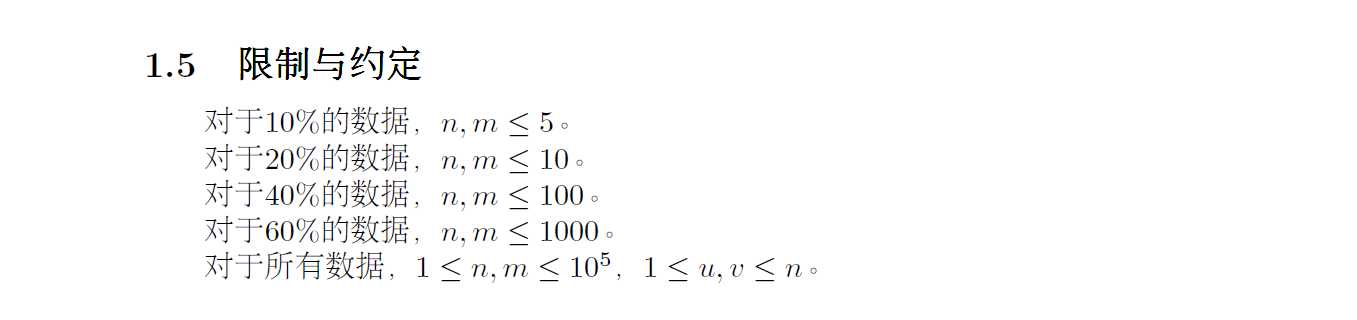

今天都是思维题
题解:
第一题:https://www.cnblogs.com/mlystdcall/p/6645725.html
首先图不连通的时候肯定答案是0,我们下面讨论图联通的情况
首先考虑,如果我们每条边都经过两边,那么肯定是可行的
因为这样相当于把每条边复制一遍,然后问图中是否存在欧拉路径
既然每条边都出现了两遍,那么所有点的度数一定都是偶数,所以肯定有欧拉路径
现在考虑将某两条边变成出现一遍,这样的话可能会有一些点的度数变成奇数
如果我们把两条非自环的边变成出现一遍,并且这两条边不交于同一个点,那么就会有四个度数为奇数的点,则图中不存在欧拉路径
如果我们把两条非自环的边变成出现一遍,并且这两条边交于同一个点,那么就会有两个度数为奇数的点,存在欧拉路径
如果我们把两条自环边变成出现一遍,所有点的度数仍然为偶数,存在欧拉路径
如果我们把一条自环,一条非自环的边变成出现一遍,那么就会有两个度数为奇数的点,存在欧拉路径
所以一共就几种情况,除去判联通的部分,我们只要记录每个点的度数(不含自环)和自环的数量就好了
因为题目中保证一条边不会出现两遍,所以我们的方法才是可行的
维护联通性是边联通,不是点联通

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int M = 1e6 + 5; int deg[M], loop, fa[M], l[M]; int find(int x){return fa[x] == x ? x : fa[x] = find(fa[x]);} int main(){ freopen("tour.in","r",stdin); freopen("tour.out","w",stdout); int n, m; scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) fa[i]=i; for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ int v; scanf("%d%d",&l[i],&v); fa[find(l[i])]=find(v); if(l[i]==v)loop++; else deg[l[i]]++,deg[v]++; } int lst=find(l[1]); for(int i=2;i<=m;i++) if(find(l[i]) != lst) return !puts("0"); long long ans=1LL*loop*(loop-1)/2 + 1LL*(m-loop)*loop; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ ans+=1LL*deg[i]*(deg[i]-1)/2; } printf("%lld ",ans); }
第二题:原题,见:https://www.cnblogs.com/EdSheeran/p/9530002.html

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define ll long long const int M = 1e7; int a[105], tot, n; ll yz[M], k; bool vis[M]; void chai(int x){ for(int d = x; d > 0; ){ int fm = (x + d - 1) / d; int nw = (x + fm - 1) / fm; if(fm < 1e6 && !vis[fm]){ yz[++tot] = fm; vis[fm]=1; } else yz[++tot] = fm; d = nw - 1; } } bool check(ll now){ ll ans = 0; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) ans = ans + 1LL*(a[i] + now - 1)/now * now - a[i]; return ans <= k; } int main(){ freopen("cut.in","r",stdin); freopen("cut.out","w",stdout); scanf("%d%lld", &n, &k); for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ scanf("%d", &a[i]); chai(a[i]); k += a[i]; } ll ans = -1; yz[++tot] = 1e12; sort(yz + 1, yz + 1 + tot); tot = unique(yz + 1, yz + 1 + tot) - yz - 1; for(int i = 1; i <= tot; i++){ ll cur = 0; for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) cur = cur + 1LL*(a[j] + yz[i] - 1)/yz[i]; ll mx = k/cur; if(mx>=yz[i]) ans = max(ans, mx); } printf("%lld ", ans); }
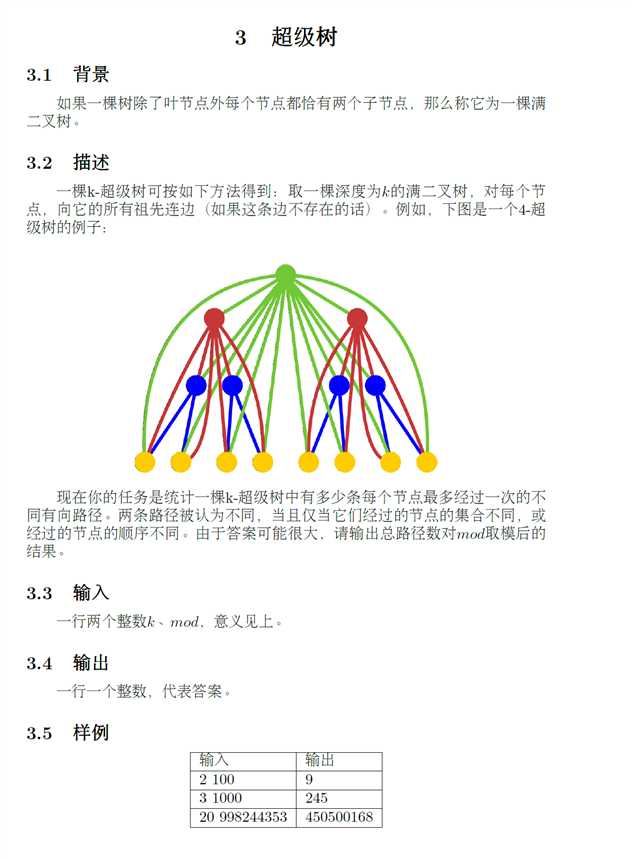
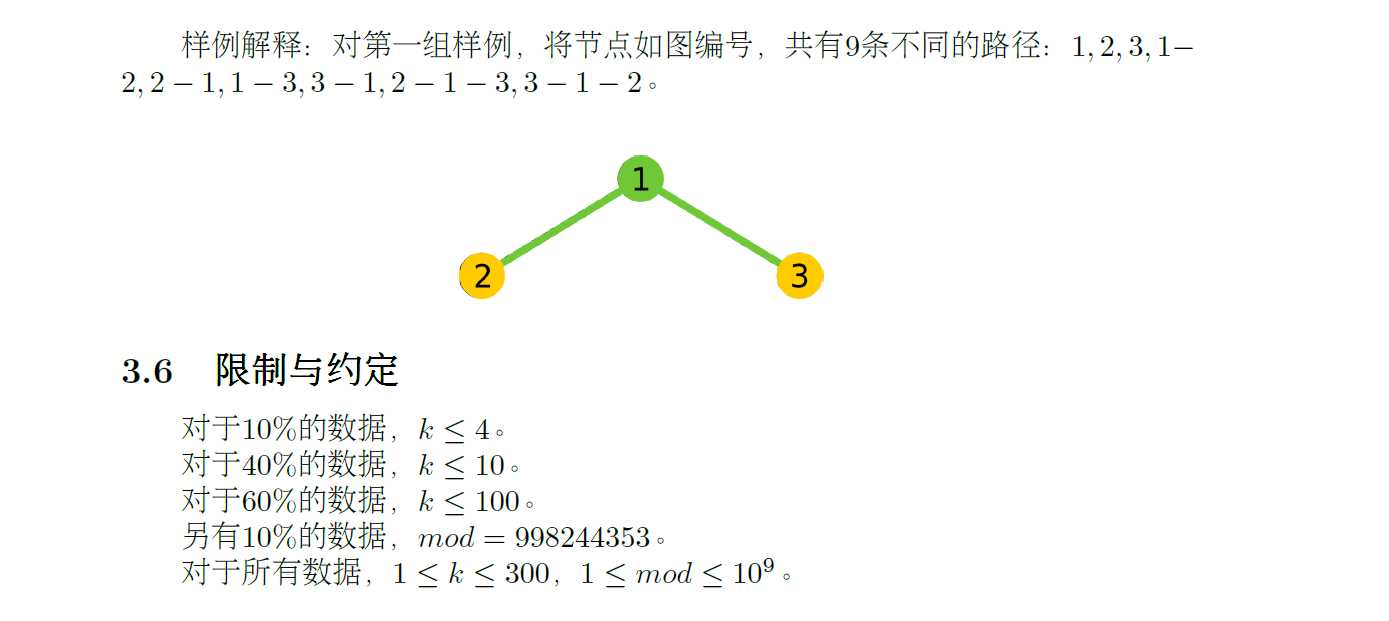
第三题:


这题*2是因为新加的点可以作为起点或者终点,所以图中的边记录的都是有向的

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define ll long long ll dp[305][305], mod; inline void up(ll &a, ll b){ a += b; if(a >= mod) a -= mod; } int main(){ freopen("tree.in","r",stdin); freopen("tree.out","w",stdout); int n; cin>>n>>mod; dp[1][0] = dp[1][1] = 1; for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){ int lim=n-i+2; for(int l=0;l<=lim;l++) for(int r=0;r+l-1<=lim;r++){ ll num=dp[i-1][l]*dp[i-1][r]%mod; up(dp[i][l+r], num); up(dp[i][l+r+1], num); up(dp[i][l+r], num*(l+r)*2%mod); if(l+r){ up(dp[i][l+r-1], num*l*r*2%mod); up(dp[i][l+r-1], num*(l*(l-1)+r*(r-1))%mod); } } } printf("%lld ", dp[n][1]%mod); }
以上是关于平时二十四测的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
