平时二十五测
Posted edsheeran
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了平时二十五测相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
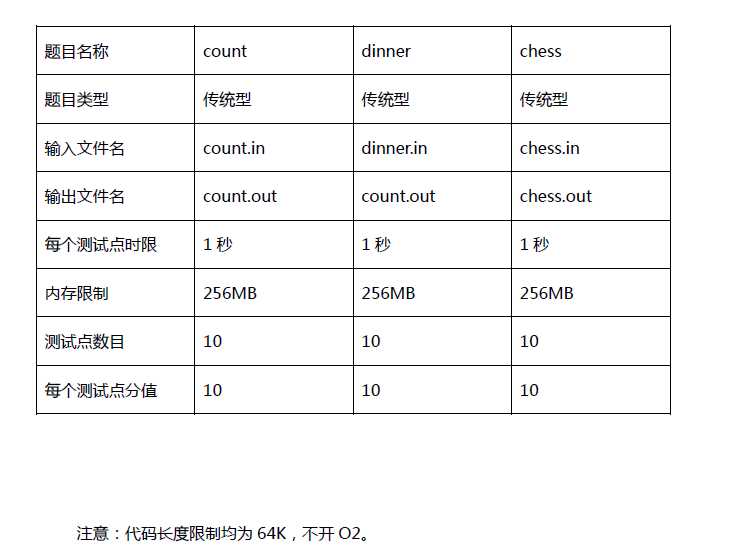





今天翻盘了,没有上两次的傻逼错误;
题解:

其实O(N)check不会T,不是严格的,而且1e6里面的约数很少,从重心跑很快;

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define ex(i, u) for(int i = h[u]; i; i = G[i].nxt) const int M = 1e6 + 5; int h[M], fg ,tot, siz[M], f[M], tmp[M], n, root, vis[M]; struct edge{int v, nxt;}G[M<<1]; void add(int u, int v){G[++tot].v = v, G[tot].nxt = h[u], h[u] = tot;} void getroot(int u, int fa){ siz[u] = 1; ex(i, u){ int v = G[i].v; if(v == fa) continue; getroot(v, u); siz[u] += siz[v]; f[u] = max(f[u], siz[v]); } f[u] = max(f[u], n - siz[u]); if(f[u] < f[root]) root = u; } int dfs(int u, int fa, int k){ if(siz[u] == k) return 0; tmp[u] = 1; ex(i, u){ if(!fg) return 0; int v = G[i].v; if(v == fa)continue; if(siz[v] < k) tmp[u] += siz[v]; else { tmp[u] += dfs(v, u, k); } } if(tmp[u] > k) fg = 0; if(tmp[u] == k) return 0; return tmp[u]; } int read(){ int x=0,f=1;char c=getchar(); while(c<‘0‘||c>‘9‘){if(c==‘-‘)f=-1;c=getchar();} while(c>=‘0‘&&c<=‘9‘){x=x*10+c-‘0‘;c=getchar();} return x*f; } int main(){ freopen("count.in","r",stdin); freopen("count.out","w",stdout); int cnt = 0; n = read(); for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){ int u = read(), v = read(); add(u, v), add(v, u); } f[root] = 2e9; getroot(1, 0); for(int i = 2; i * i <= n; i++){ if(n % i == 0){ fg = 1; dfs(root, 0, i); cnt += fg; if(i * i != n){ fg = 1; dfs(root, 0, n/i); cnt += fg; } } } printf("%d ",cnt+2); }

这道题还有一个巧妙的剪枝,不用O(N)枚举起点,对于一个点,他在传递过程的位置是1——最后,我们把1当起点,做一遍不行,就把他当第二个,当他作为最后一个后就可以停了,实测跑得飞快(这样不倍增都有60分)

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int M = 1e5 + 5; int n, a[M], m, s[M]; bool check(int k){ int up = n, tot = 0, lst = 0; while(1){ int cnt = 1; for(int i = 1; i <= up; i++){ if(tot + a[i] <= k) tot += a[i]; else tot = a[i], cnt++; } if(cnt <= m) return 1; tot = lst + a[up]; lst += a[up]; up--; if(tot + a[1] > k) return 0; } } int read(){ int x=0,f=1;char c=getchar(); while(c<‘0‘||c>‘9‘){if(c==‘-‘)f=-1;c=getchar();} while(c>=‘0‘&&c<=‘9‘){x=x*10+c-‘0‘;c=getchar();} return x*f; } bool check2(int k){ int up = n, tot = 0, lst = 0; while(1){ int cnt = 1; for(int i = 1; i <= up; ){ int lf = i, rg = up, rec = -1; while(lf <= rg){ int mid = (lf + rg) >> 1; if(s[mid] - s[i - 1] + tot <= k) rec = mid, lf = mid + 1; else rg = mid - 1; } tot = 0; i = rec + 1; if(i == up + 1)break; cnt++; } if(cnt <= m) return 1; tot = lst + a[up]; lst += a[up]; up--; if(tot + a[1] > k) return 0; } } int main(){ freopen("dinner.in","r",stdin); freopen("dinner.out","w",stdout); n = read(); m = read(); int ans = -1, Mx = 0, sum = 0; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) { a[i] = read(), sum += a[i], Mx = max(Mx, a[i]); s[i] = s[i - 1] + a[i]; } int lf = Mx, rg = sum; if(n <= 5000){ while(lf <= rg){ int mid = (lf + rg) >> 1; if(check(mid)) ans = mid, rg = mid - 1; else lf = mid + 1; } } else { while(lf <= rg){ int mid = (lf + rg) >> 1; if(check2(mid)) ans = mid, rg = mid - 1; else lf = mid + 1; } } printf("%d ", ans); }

一句话:最短路+缩边

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define ll long long const int M = 55, N = 3000; int a[M][M], tot, ans, inf = 2e9, cnt, n, m, tmp[N], dis[N], h[N], stx, sty, edx, edy; bool vis[M][M], inq[N], vis2[M][M], has[N][N]; ll fx[N]; int zl[8][2] = {{1, 2}, {1, -2}, {-1, 2}, {-1, -2}, {2, 1}, {2, -1}, {-2, 1}, {-2, -1}}; struct edge{int v,u, nxt;}G[100005]; void add(int u, int v){ G[++tot].v = v,G[tot].u=u, G[tot].nxt = h[u], h[u] = tot; } inline int id(int x,int y){return x * m + y;} inline bool check(int x, int y){ if(x > 0 && x <= n && y > 0 && y <= m && a[x][y] != 2) return 1; return 0; } void dfs(int x, int y){ for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++){ int nx = x + zl[i][0], ny = y + zl[i][1]; if(!check(nx, ny)) continue; if(a[nx][ny]==0 && !vis2[nx][ny]){ vis2[nx][ny] = 1; tmp[++cnt] = id(nx, ny); } else if(a[nx][ny]==1 && !vis[nx][ny]){ vis[nx][ny] = 1; dfs(nx, ny); } } } bool SPFA(){ queue <int> q; memset(dis, 127, sizeof(dis)); int S = id(stx, sty), T = id(edx, edy); dis[S] = 0, inq[S] = 1, fx[S] = 1; q.push(S); while(!q.empty()){ int u=q.front();q.pop();inq[u]=0; for(int i = h[u]; i; i = G[i].nxt){ int v = G[i].v; if(dis[v] > dis[u] + 1){ dis[v] = dis[u] + 1; fx[v] = fx[u]; //printf("%d %d %d ", u, v, dis[v]); if(!inq[v] && v != T){ q.push(v), inq[v] = 1; } } else if(dis[v] == dis[u] + 1){ fx[v] += fx[u]; if(!inq[v] && v != T){ q.push(v), inq[v] = 1; } } } } return 0; } int read(){ int x=0,f=1;char c=getchar(); while(c<‘0‘||c>‘9‘){if(c==‘-‘)f=-1;c=getchar();} while(c>=‘0‘&&c<=‘9‘){x=x*10+c-‘0‘;c=getchar();} return x*f; } //0表示格子为空,1表示格子上有敌军,2表示格子上有友军,3表示马的位置,4表示敌方的帅。 int main(){ freopen("chess.in","r",stdin); freopen("chess.out","w",stdout); n = read(), m = read(); for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++){ a[i][j] = read(); if(a[i][j] == 3) stx = i, sty = j, a[i][j] = 0; if(a[i][j] == 4) edx = i, edy = j, a[i][j] = 0; } for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++) if(!a[i][j]){ for(int k = 0; k < 8; k++){ int nx = i + zl[k][0], ny = j + zl[k][1]; if(check(nx, ny) && !a[nx][ny]) add(id(i, j), id(nx, ny)); } } for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++) if(!vis[i][j] && a[i][j] == 1){ memset(vis2, 0, sizeof(vis2)); cnt = 0; vis[i][j] = 1; dfs(i, j); for(int k = 1; k <= cnt; k++) for(int z = k + 1; z <= cnt; z++){ if(has[tmp[k]][tmp[z]]) continue; has[tmp[k]][tmp[z]] = has[tmp[z]][tmp[k]] = 1; add(tmp[k], tmp[z]); add(tmp[z], tmp[k]); } } /*for(int i = 1; i <= tot; i+=2){ printf("%d %d ", G[i].u, G[i].v); }*/ SPFA(); dis[id(edx, edy)] < inf ? printf("%d %lld ", dis[id(edx, edy)] - 1, fx[id(edx, edy)]) : printf("-1 "); }
以上是关于平时二十五测的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
