saltstack 安装和基本配置使用
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了saltstack 安装和基本配置使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
环境: rhel6.5 server1master
server2 minion server3 minion
配置yum安装包:rhel6
[[email protected] ~]# yum install salt-master
[[email protected] ~]# /etc/init.d/salt-master start
[[email protected] ~]# yum install salt-minion
[roo[email protected] ~]# vim /etc/salt/minion
master: 172.25.135.1
[[email protected] ~]# /etc/init.d/salt-minion start
[[email protected] ~]# salt-key -A
The following keys are going to be accepted:
Unaccepted Keys:
server2
Proceed? [n/Y] y
Key for minion server2 accepted.
[[email protected] ~]# salt-key -L
Accepted Keys:
server2
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
Rejected Keys:
[[email protected] ~]# salt server2 test.ping
server2:
True
[[email protected] ~]# salt server2 cmd.run hostname
server2:
server2
[[email protected] ~]# salt server2 cmd.run df
server2:
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/vg_server0-lv_root 18102140 2078072 15104516 13% /
tmpfs 510200 16 510184 1% /dev/shm
/dev/vda1 495844 34532 435712 8% /boot
[[email protected] ~]# salt server2 cmd.run poweroff #测试关机
server2:
[[email protected] ~]# vim /etc/salt/master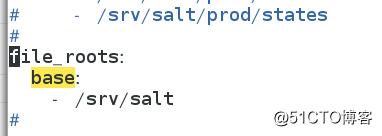
[[email protected] ~]# cd /srv/salt/
[[email protected] salt]# ls
[[email protected] salt]# mkdir apache
[[email protected] salt]# cd apache/
[[email protected] apache]# vim install.sls
httpd:
pkg.installed #写个简单的http安装
[[email protected] apache]# salt server2 state.sls apache.install
[[email protected] apache]# mkdir files
[[email protected] ~]# scp /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf server1:/srv/salt/apache/files
[[email protected] apache]# cd files/
[[email protected] files]# ls
httpd.conf
[[email protected] files]# vim httpd.conf #简单修改一下80端口为8080
[[email protected] apache]# ls
files install.sls
[[email protected] apache]# vim install.sls
apache-install:
pkg.installed:
-
pkgs:
file.managed:
- name: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
- source: salt://apache/files/httpd.conf
- mode: 644
- user: root
-
group: root
service.running:
- name: httpd
- enable: Ture
- watch:
- file: apache-install
[[email protected] apache]# salt server2 state.sls apache.install #server2上apache自动修改端口为8080
[[email protected] salt]# mkdir pkgs #自动推送源码nginx
[[email protected] salt]# cd pkgs
[[email protected] pkgs]# vim make.sls
gcc-make:
pkg.installed:
- file: apache-install
- pkgs:
- gcc
- pcre-devel
- openssl-devel
[[email protected] pkgs]# ls
make.sls
[[email protected] pkgs]# cd ..
[[email protected] salt]# ls
apache nginx pkgs
[[email protected] salt]# cd nginx/
[[email protected] nginx]# ls
files install.sls
[[email protected] nginx]# vim install.sls
include:
- pkgs.make
nginx-install:
file.managed:
- name: /mnt/nginx-1.14.0.tar.gz
-
source: salt://nginx/files/nginx-1.14.0.tar.gz
cmd.run:
- name: cd /mnt && tar zxf nginx-1.14.0.tar.gz && cd nginx-1.14.0 && sed -i.bak ‘s/#define NGINX_VER "nginx/" NGINX_VERSION/#define NGINX_VER "nginx"/g‘ src/core/nginx.h && sed -i.bak ‘s/CFLAGS="$CFLAGS -g"/#CCFLAGS="$CFLAGS -g"/g‘ auto/cc/gcc && ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-threads --with-file-aio &>/dev/null && make &>/dev/null && make install &>/dev/null && cd .. && rm -fr nginx-1.14.0
- creates: /usr/local/nginx
[[email protected] nginx]# salt server3 state.sls nginx.install
写启动脚本修改一些
[[email protected] nginx]# vim service.sls
include:- nginx.install
/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf:
file.managed:
- source: salt://nginx/files/nginx.conf
/etc/init.d/nginx:
file.managed:
- source: salt://nginx/files/nginx
- mode: 755
nginx:
service.running:
- reload: True
- watch:
- file: /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
[[email protected] files]# ls
nginx nginx-1.14.0.tar.gz nginx.conf #将启动脚步和配置文件放到nginx中的files文件夹内
[[email protected] salt]# vim top.sls
base:
"server2":- apache.service
"server3": - nginx.service
[[email protected] salt]# salt ‘*‘ state.highstate
负载均衡haproxy
[[email protected] salt]# yum install salt-minion
[[email protected] salt]# vim /etc/salt/minion #修改master端口
[[email protected] salt]# /etc/init.d/salt-minion start
[[email protected] salt]# salt-key -a server1
[[email protected] salt]# mkdir haproxy
[[email protected] salt]# cd haproxy/
[[email protected] haproxy]# mkdir files
[[email protected] haproxy]# cd files/
[[email protected] files]# ls #包和配置文件拷贝过来
haproxy-1.6.11.tar.gz haproxy.cfg haproxy.init
[[email protected] haproxy]# vim install.sls
include: - pkgs.make
- apache.service
- file: /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
haproxy-install:
file.managed:
- name: /mnt/haproxy-1.6.11.tar.gz
- source: salt://haproxy/files/haproxy-1.6.11.tar.gz
cmd.run: - name: cd /mnt && tar zxf haproxy-1.6.11.tar.gz && cd haproxy-1.6.11 && make TARGET=linux2628 USE_PCRE=1 USE_OPENSSL=1 USE_ZLIB=1 PREFIX=/usr/local/haproxy &> /dev/null && make TARGET=linux2628 USE_PCRE=1 USE_OPENSSL=1 USE_ZLIB=1 PREFIX=/usr/local/haproxy install
- creates: /usr/local/haproxy
/etc/haproxy:
file.directory:
- mode: 755
/usr/sbin/haproxy:
file.symlink:
- target: /usr/local/haproxy/sbin/haproxy
[[email protected] haproxy]# vim service.sls
include:- haproxy.install
- users.haproxy
/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg:
file.managed:
- source: salt://haproxy/files/haproxy.cfg
haproxy-service:
file.managed:
- name: /etc/init.d/haproxy
- source: salt://haproxy/files/haproxy.init
- mode: 755
service.running: - name: haproxy
- relpad: True
- watch:
- file: /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
[[email protected] salt]# mkdir users
[[email protected] users]# vim haproxy.sls
haproxy-group:
group.present:
- name: haproxy
- gid: 200
haproxy-user:
user.present:
- name: haproxy
- uid: 200
- gid: 200
- shell: /sbin/nologin
- home: /usr/local/haproxy
- createhome: False
[[email protected] salt]# vim top.sls
base:
"server1":- haproxy.service
"server2": - apache.service
"server3": -
nginx.service
[[email protected] haproxy]# ls
files install.sls service.sls
[[email protected] haproxy]# cd files/
[[email protected] files]# ls
haproxy-1.6.11.tar.gz haproxy.cfg haproxy.init
[[email protected] files]# vim haproxy.cfg #修改配置文件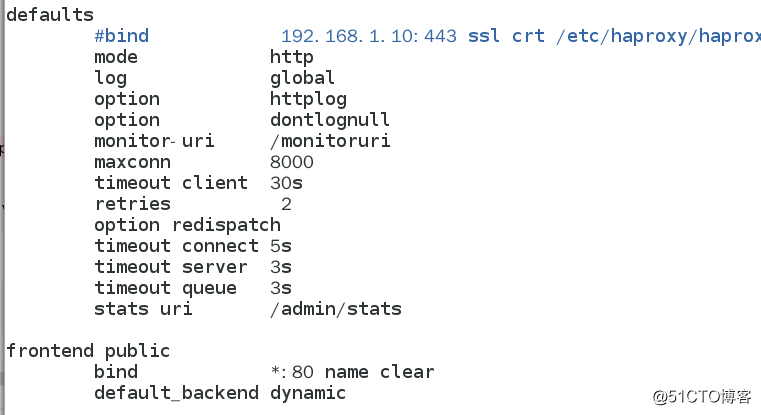
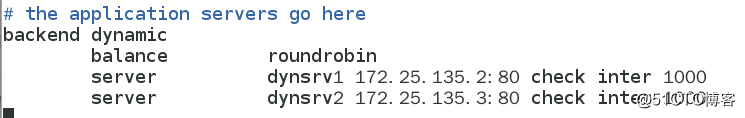
[[email protected] files]# salt ‘*‘ state.highstate #推送完毕,给server2
和server3发布目录写个测试页面
[[email protected] files]# for i in {1..6}; do curl 172.25.135.1; done #测试
nginx
apache
nginx
apache
nginx
apache
批量主机定义:
[[email protected] salt]# salt server3 grains.item os
server3:os:
RedHat
[[email protected] salt]# salt server2 grains.item os
server2:os:
RedHat
[[email protected] salt]# salt -G ‘os:redhat‘ cmd.run hostname
server2:
server2
server1:
server1
server3:
server3
[[email protected] ~]# vim /etc/salt/minion
grains:
roles:
- haproxy.service
- apache
[[email protected] ~]# /etc/init.d/salt-minion restart
[[email protected] ~]# cd /etc/salt/
[[email protected] salt]# vim grains
roles: nginx
[[email protected] salt]# salt server2 grains.item roles
server2:
roles:
- apache[[email protected] salt]# salt server3 grains.item roles
server3:
roles:
nginx[[email protected] salt]# vim top.sls
base:
"server1":
- haproxy.service
"roles:apache": - match: grain
- apache.service
"roles:nginx": - match: grain
- nginx.service
[[email protected] salt]# salt ‘*‘ state.highstate
[[email protected] salt]# mkdir _grains
[[email protected] salt]# cd _grains/
[[email protected] _grains]# vim my_grains.py
#! /usr/bin/env python
def my_grains():
grains = {};
grains[‘hello‘] = ‘world‘
grains[‘salt‘] = ‘stack‘
return grains
[[email protected] _grains]# salt server2 saltutil.sync_grains
[[email protected] _grains]# salt server2 grains.item hello
server2:
hello:
world[[email protected] salt]# cd /etc/salt
[[email protected] salt]# mkdir /srv/pillar/
[[email protected] pillar]# /etc/init.d/salt-master restart
[[email protected] pillar]# mkdir web
[[email protected] pillar]# cd web/
[[email protected] web]# ls
[[email protected] web]# vim install.sls
{% if grains[‘fqdn‘] == ‘server2‘ %}
webserver: httpd
{% elif grains[‘fqdn‘] == ‘server3‘%}
webserver: nginx
{% endif %}
[[email protected] web]# cd ..
[[email protected] pillar]# ls
web
[[email protected] pillar]# vim top.sls
base:
‘*‘:
-
web.install
[[email protected] pillar]# salt ‘*‘ pillar.items
server2:webserver:
httpd
server1:server3:
webserver:
nginx
[[email protected] pillar]# salt ‘‘ saltutil.refresh_pillar
server2:
True
server3:
True
server1:
True
[[email protected] pillar]# salt ‘‘ pillar.items webserver
server3:webserver:
nginx
server1:webserver:
server2:webserver:
httpd
[[email protected] pillar]# salt -I ‘webserver:nginx‘ test.ping
server3:
True
[[email protected] pillar]# salt -S 172.25.135.0/24 test.ping
server3:
True
server2:
True
server1:
True
金佳模版:
[[email protected] salt]# cd apache/
[[email protected] apache]# vim install.sls
apache-install:
pkg.installed: -
pkgs:
- httpd
- php
- php-mysql
file.managed:
- name: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
- source: salt://apache/files/httpd.conf
- mode: 644
- user: root
- group: root
- template: jinja
- context:
port: 80
bind: {{ grains[‘ipv4‘][1] }}
[[email protected] apache]# vim files/httpd.conf #修改监听端口
Listen {{ bind }}:{{ port }}
[[email protected] apache]# salt server2 state.sls apache.install
以上是关于saltstack 安装和基本配置使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章