201771010128王玉兰《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第十周学习总结
Posted wang963
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了201771010128王玉兰《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第十周学习总结相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
第一部分:理论知识部分总结:
(1) 定义简单泛型类:
A:泛型:也称参数化类型(parameterizedtype),就是在定义类、接口和方法时,通过类型参数指 示将要处理的对象类型。
B:泛型程序设计(Genericprogramming):编写 代码可以被很多不同类型的对象所重用。
C: 一个泛型类(genericclass)就是具有一个或多 个类型变量的类,即创建用类型作为参数的类。
(2)泛型方法(可以定义在普通类中,也可以定义在泛型类中)除了泛型类外,还可以只单独定义一个方法作 为泛型方法,用于指定方法参数或者返回值为 泛型类型,留待方法调用时确定。
(3):泛型变量的限定:定义泛型变量的上界用extends,下界用super.
A:上下界的说明:a: extends关键字所声明的上界既可以是一个类, 也可以是一个接口;b;一个类型变量或通配符可以有多个限定,限定类 型用“&”分割。
c: 通过使用super关键字可以固定泛型参数的类型为某种 类型或者其超类;
d: 当程序希望为一个方法的参数限定类型时,通常可以使 用下限通配符.
(4)通配符类型 :通配符 –“?”符号表明参数的类型可以是任何一种类 型,它和参数T的含义是有区别的。T表示一种 未知类型,而“?”表示任何一种类型。这种 通配符一般有以下三种用法:
–单独的?,用于表示任何类型。
–? extends type,表示带有上界。
–? super type,表示带有下界。
第二部分:实验
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 理解泛型概念;
(2) 掌握泛型类的定义与使用;
(3) 掌握泛型方法的声明与使用;
(4) 掌握泛型接口的定义与实现;
(5)了解泛型程序设计,理解其用途。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第8章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
l 编辑、调试、运行教材311、312页 代码,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在泛型类定义及使用代码处添加注释;
l 掌握泛型类的定义及使用。
package pair1;
/**
* @version 1.00 2004-05-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Pair<T> //Pair类引入一个类型变量T
{
private T first;//类定义中的类型变量指定方法的返回类型以及域和局部变量的类型
private T second;
public Pair() { first = null; second = null; }
public Pair(T first, T second) { this.first = first; this.second = second; }
public T getFirst() { return first; }
public T getSecond() { return second; }
public void setFirst(T newValue) { first = newValue; }
public void setSecond(T newValue) { second = newValue; }
}
package pair1;
/**
* @version 1.01 2012-01-26
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PairTest1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
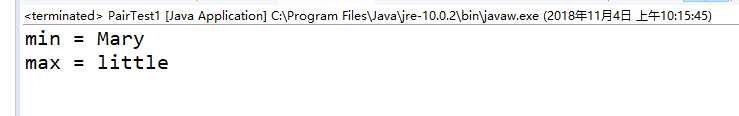
String[] words = { "Mary", "had", "a", "little", "lamb" };//初始化一个String对象数组
Pair<String> mm = ArrayAlg.minmax(words);//通过类名ArrayAlg调用minmax方法
System.out.println("min = " + mm.getFirst());
System.out.println("max = " + mm.getSecond());
}
}
class ArrayAlg//泛型类
{
/**
* Gets the minimum and maximum of an array of strings.
* @param a an array of strings
* @return a pair with the min and max value, or null if a is null or empty
*/
public static Pair<String> minmax(String[] a)//实例化以后的pair类对象
{
if (a == null || a.length == 0) return null;
String min = a[0];
String max = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
{
if (min.compareTo(a[i]) > 0) min = a[i];
if (max.compareTo(a[i]) < 0) max = a[i];
}
return new Pair<>(min, max);//带参数的构造器
}
}
测试程序2:
l 编辑、调试运行教材315页 PairTest2,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在泛型程序设计代码处添加相关注释;
l 掌握泛型方法、泛型变量限定的定义及用途。
package pair2;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import pair1.Pair;
/**
* @version 1.02 2015-06-21
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PairTest2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
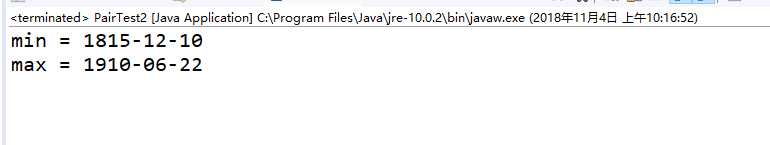
LocalDate[] birthdays =
{
LocalDate.of(1906, 12, 9), // G. Hopper
LocalDate.of(1815, 12, 10), // A. Lovelace
LocalDate.of(1903, 12, 3), // J. von Neumann
LocalDate.of(1910, 6, 22), // K. Zuse
};
Pair<LocalDate> mm = ArrayAlg.minmax(birthdays);//通过类名调用minmax 方法
System.out.println("min = " + mm.getFirst());
System.out.println("max = " + mm.getSecond());
}
}
class ArrayAlg
{
/**
Gets the minimum and maximum of an array of objects of type T.
@param a an array of objects of type T
@return a pair with the min and max value, or null if a is
null or empty
*/
public static <T extends Comparable> Pair<T> minmax(T[] a) //extends表示上界约束的泛型方法
{
if (a == null || a.length == 0) return null;//a.length 是数组的一个属性
T min = a[0];
T max = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
{
if (min.compareTo(a[i]) > 0) min = a[i];
if (max.compareTo(a[i]) < 0) max = a[i];
}
return new Pair<>(min, max);
}
}
测试程序3:
l 用调试运行教材335页 PairTest3,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 了解通配符类型的定义及用途。
package pair3;
import pair1.Pair;
/**
* @version 1.01 2012-01-26
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PairTest3
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Manager ceo = new Manager("Gus Greedy", 800000, 2003, 12, 15);//创建了Manager对象
Manager cfo = new Manager("Sid Sneaky", 600000, 2003, 12, 15);
Pair<Manager> buddies = new Pair<Manager>(ceo, cfo); //实例化pair对象
printBuddies(buddies);
ceo.setBonus(1000000);//更改器
cfo.setBonus(500000);
Manager[] managers = { ceo, cfo };
Pair<Employee> result = new Pair<Employee>();//尖括号里既可以用Manager,也可以用Employee
minmaxBonus(managers, result);
System.out.println("first: " + result.getFirst().getName()
+ ", second: " + result.getSecond().getName());
maxminBonus(managers, result);
System.out.println("first: " + result.getFirst().getName()
+ ", second: " + result.getSecond().getName());
}
public static void printBuddies(Pair<? extends Employee> p)//?是通配符,extends表示带有上界
{
Employee first = p.getFirst();//访问器方法
Employee second = p.getSecond();
System.out.println(first.getName() + " and " + second.getName() + " are buddies.");
}
public static void minmaxBonus(Manager[] a, Pair<? super Manager> result)
{
if (a.length == 0) return;
Manager min = a[0];
Manager max = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
{
if (min.getBonus() > a[i].getBonus()) min = a[i];//访问器方法
if (max.getBonus() < a[i].getBonus()) max = a[i];
}
result.setFirst(min);
result.setSecond(max);
}
public static void maxminBonus(Manager[] a, Pair<? super Manager> result)//super表示带有下界的泛型方法
{
minmaxBonus(a, result);
PairAlg.swapHelper(result); // OK--swapHelper captures wildcard type
}
// Can‘t write public static <T super manager> . . .
}
class PairAlg//泛型类
{
public static boolean hasNulls(Pair<?> p)
{
return p.getFirst() == null || p.getSecond() == null;
}
public static void swap(Pair<?> p) { swapHelper(p); }
public static <T> void swapHelper(Pair<T> p)
//限定泛型类Pair类型变量的下界为p;
{ T t = p.getFirst();
p.setFirst(p.getSecond());
p.setSecond(t); } }

实验2:编程练习:
编程练习1:实验九编程题总结
l 实验九编程练习1总结(从程序总体结构说明、模块说明,目前程序设计存在的困难与问题三个方面阐述)。
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Collections;//对集合进行排序、查找、修改等;
public class Test {
private static ArrayList<Citizen> citizenlist;
public static void main(String[] args) {
citizenlist = new ArrayList<>();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
File file = new File("E:/java/身份证号.txt");
//异常捕获
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis));
String temp = null;
while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) {
Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp);
linescanner.useDelimiter(" ");
String name = linescanner.next();
String id = linescanner.next();
String sex = linescanner.next();
String age = linescanner.next();
String birthplace = linescanner.nextLine();
Citizen citizen = new Citizen();
citizen.setName(name);
citizen.setId(id);
citizen.setSex(sex);
// 将字符串转换成10进制数
int ag = Integer.parseInt(age);
citizen.setage(ag);
citizen.setBirthplace(birthplace);
citizenlist.add(citizen);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("信息文件找不到");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("信息文件读取错误");
e.printStackTrace();
}
boolean isTrue = true;
while (isTrue) {
System.out.println("1.按姓名字典序输出人员信息");
System.out.println("2.查询最大年龄的人员信息、查询最小年龄人员信息");
System.out.println("3.查询人员中是否查询人员中是否有你的同乡");
System.out.println("4.输入你的年龄,查询文件中年龄与你最近人的姓名、身份证号、年龄、性别和出生地");
System.out.println("5.退出");
int nextInt = scanner.nextInt();
switch (nextInt) {
case 1:
Collections.sort(citizenlist);
System.out.println(citizenlist.toString());
break;
case 2:
int max = 0, min = 100;
int m, k1 = 0, k2 = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < citizenlist.size(); i++) {
m = citizenlist.get(i).getage();
if (m > max) {
max = m;
k1 = i;
}
if (m < min) {
min = m;
k2 = i;
}
}
System.out.println("年龄最大:" + citizenlist.get(k1));
System.out.println("年龄最小:" + citizenlist.get(k2));
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("出生地:");
String find = scanner.next();
String place = find.substring(0, 3);
for (int i = 0; i < citizenlist.size(); i++) {
if (citizenlist.get(i).getBirthplace().substring(1, 4).equals(place))
System.out.println("出生地" + citizenlist.get(i));
}
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("年龄:");
int yourage = scanner.nextInt();
int near = peer(yourage);
int j = yourage - citizenlist.get(near).getage();
System.out.println("" + citizenlist.get(near));
break;
case 5:
isTrue = false;
System.out.println("程序已退出!");
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入有误");
}
}
}
public static int peer(int age) {
int flag = 0;
int min = 53, j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < citizenlist.size(); i++) {
j = citizenlist.get(i).getage() - age;
if (j < 0)
j = -j;
if (j < min) {
min = j;
flag = i;
}
}
return flag;
}
}
public class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
private String name;
private String number ;
private String sex ;
private int age;
private String province;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getnumber() {
return number;
}
public void setnumber(String number) {
this.number = number;
}
public String getsex() {
return sex ;
}
public void setsex(String sex ) {
this.sex =sex ;
}
public int getage() {
return age;
}
public void setage(int age) {
// int a = Integer.parseInt(age);
this.age= age;
}
public String getprovince() {
return province;
}
public void setprovince(String province) {
this.province=province ;
}
public int compareTo(Student o) {
return this.name.compareTo(o.getName());
}
public String toString() {
return name+" "+sex+" "+age+" "+number+" "+province+"
";
}
}
程序总体说明:由主类Test和子类Student组成
模块说明:main方法的使用
A: 确定主函数,实现题目所要求的功能
B::将文件信息导入进去,保存到相应的包下
C:进行编辑,运行结果,完成程序
目前程序设计存在的困难与问题:
A:读取文件的位置,即路径是否准确
B:实现的功能要求比较复杂,掌握的知识过少,解决代码错误时消耗时间过长,基础知识不牢固
l 实验九编程练习2总结(从程序总体结构说明、模块说明,目前程序设计存在的困难与问题三个方面阐述)。
import java.io
.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io
.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class jisuan{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in
);
Caculator1 computing=new Caculator1();
PrintWriter output = null;
try {
output = new PrintWriter("Caculator.txt");
} catch (Exception e) {
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < 11; i++) {
int a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
int b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
int s = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 3);
switch(s)
{
case 1:
System.out.println(i+": "+a+"/"+b+"=");
while(b==0){
b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
}
double c = in.nextDouble();
output.println(a+"/"+b+"="+c);
if (c == (double)computing.division(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("正确");
}
else {
System.out.println("错误");
}
break;
case 2:
System.out.println(i+": "+a+"*"+b+"=");
int c1 = in.nextInt();
output.println(a+"*"+b+"="+c1);
if (c1 == computing.multiplication(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("正确");
}
else {
System.out.println("错误");
}
break;
case 3:
System.out.println(i+": "+a+"+"+b+"=");
int c2 = in.nextInt();
output.println(a+"+"+b+"="+c2);
if (c2 == computing.addition(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("正确");
}
else {
System.out.println("错误");
}
break ;
case 4:
System.out.println(i+": "+a+"-"+b+"=");
int c3 = in.nextInt();
output.println(a+"-"+b+"="+c3);
if (c3 == computing.subtraction(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("正确");
}
else {
System.out.println("错误");
}
break ;
}
}
System.out.println("scores:"+sum);
output.println("scores:"+sum);
output.close();
}
}
public class jiusuan_class
{
private int a;
private int b;
public int addition(int a,int b)
{
return a+b;
}
public int subtraction(int a,int b)
{
if((a-b)<0)
return 0;
else
return a-b;
}
public int multiplication(int a,int b)
{
return a*b;
}
public int division(int a,int b)
{
if(b!=0)
return a/b;
else
return 0;
}
}
程序总体结构说明:由主类jisuan和子类jiusuan组成
模块说明:文件输出和四则运算计算器的生成
目前程序设计的存在的困难和问题:
A:只能实现简单的 四则运算档,而且只要数比较打,就算结果正确也显示不足;
B:出现异常要进行处理;单独解决除数为0;
C :在编写程序时将算法和结构体还不能正确使用。
编程练习2:采用泛型程序设计技术改进实验九编程练习2,使之可处理实数四则运算,其他要求不变。
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Suanshu {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
Suanshu ss = new Suanshu();
PrintWriter out = null;
try {
out = new PrintWriter("test.txt");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("文件夹输出失败");
e.printStackTrace();
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
int a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
int b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
int m;
Random rand = new Random();
m = (int) rand.nextInt(4) + 1;
System.out.println("随机生成的四则运算类型:" + m);
switch (m) {
case 1:
a = b + (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
while(b == 0){
b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
}
while(a % b != 0){
a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
}
System.out.println(i + " " + a + "/" + b + "=");
int c0 = in.nextInt();
out.println(a + "/" + b + "=" + c0);
if (c0 == ss.chufa(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("right!");
} else {
System.out.println("error!");
}
break;
case 2:
System.out.println(i + " " + a + "*" + b + "=");
int c = in.nextInt();
out.println(a + "*" + b + "=" + c);
if (c == ss.chengfa(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("回答正确!");
} else {
System.out.println("回答错误!");
}
break;
case 3:
System.out.println(i + " " + a + "+" + b + "=");
int c1 = in.nextInt();
out.println(a + "+" + b + "=" + c1);
if (c1 == ss.jiafa(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("回答正确!");
} else {
System.out.println("回答错误!");
}
break;
case 4:
while (a < b) {
b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
}
System.out.println(i + " " + a + "-" + b + "=");
int c2 = in.nextInt();
out.println(a + "-" + b + "=" + c2);
if (c2 == ss.jiafa(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("回答正确!");
} else {
System.out.println("回答错误!");
}
break;
}
}
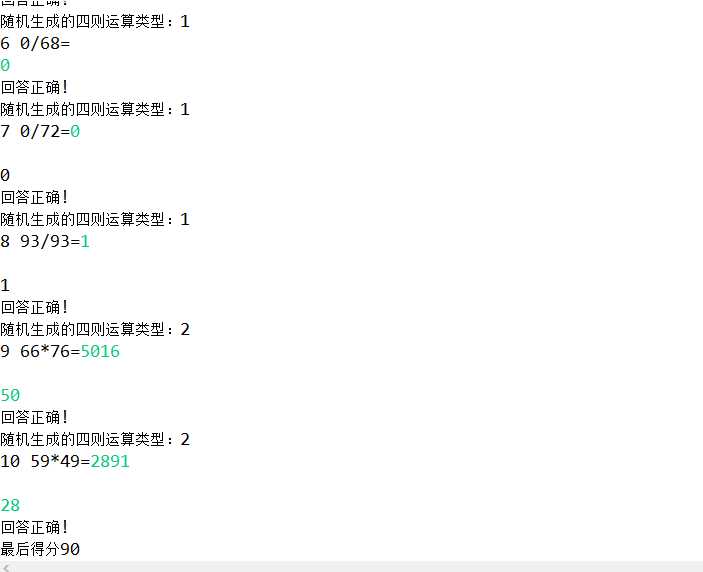
System.out.println("最后得分" + sum);
out.println("最后得分" + sum);
out.close();
}
private int jiafa(int a, int b) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
private int chengfa(int a, int b) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
private int chufa(int a, int b) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
}
public class Suanshu<T> {
private T a;
private T b;
public Suanshu() {
a = null;
b = null;
}
public Suanshu(T a, T b) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
public int jiafa(int a,int b) {
return a + b;
}
public int jianfa(int a, int b) {
return a - b;
}
public int chengfa(int a, int b) {
return a * b;
}
public int chufa(int a, int b) {
if (b != 0 && a%b==0)
return a / b;
else
return 0;
}
}
运行结果:

实验总结:这一章学习第九章类泛型程序设计,主要学习了如何定义简单泛型类,是用Pair类引入一个类型变量T,用<>,放在类名的后面,泛型类可以有多个泛型变量以及通配符胡类型,有带有上界和下界,分别是?extends type,?super type等基础知识,学习泛型程序设计是编写的代码可以被很多不同的对象所重用,程序员必掌握的技术,因此,之前也接触到了ArrayList类,泛型程序设计是用继承实现的,总而言之,将这几周学过的知识相结合运用到编写代码才是一种提升能力,自己还需要不断练习。
以上是关于201771010128王玉兰《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第十周学习总结的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章