20172333 2018-2019-1 《程序设计与数据结构》第七周学习总结
Posted yanyujun527
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了20172333 2018-2019-1 《程序设计与数据结构》第七周学习总结相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
20172333 2018-2019-1 《程序设计与数据结构》第七周学习总结
教材学习内容总结
《Java软件结构与数据结构》第十一章-二叉查找树
一、二叉查找树的概念及相关方法
- ①思路:二叉查找树与普通的二叉树的区别类似于有序链表与无序链表的差别,二叉查找树因为实现了Comparable接口的类型的对象,所以该二叉树在添加数据到树中的时候就会自动排序,将大于根节点的数据放在右结点,反之则保存在左结点。这样排序好的二叉树方便查找所以叫二叉查找树。
- ②方法:
public interface BinarySearchTreeADT<T> extends BinaryTreeADT<T>
{
/**
* Adds the specified element to the proper location in this tree.
*
* @param element the element to be added to this tree
*/
public void addElement(T element);
/**
* Removes and returns the specified element from this tree.
*
* @param targetElement the element to be removed from the tree
* @return the element to be removed from the tree
*/
public T removeElement(T targetElement);
/**
* Removes all occurences of the specified element from this tree.
*
* @param targetElement the element to be removed from the tree
*/
public void removeAllOccurrences(T targetElement);
/**
* Removes and returns the smallest element from this tree.
*
* @return the smallest element from the tree.
*/
public T removeMin();
/**
* Removes and returns the largest element from this tree.
*
* @return the largest element from the tree
*/
public T removeMax();
/**
* Returns the smallest element in this tree without removing it.
*
* @return the smallest element in the tree
*/
public T findMin();
/**
* Returns the largest element in this tree without removing it.
*
* @return the largest element in the tree
*/
public T findMax();
}
| 操作 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| addElement | 从树中添加一个元素 |
| removeElement | 从树中删除一个元素 |
| removeAllOccurrences | 从树中删除所指定元素的人和存在 |
| removeMin | 删除树中最小元素 |
| removeMax | 删除树中最大元素 |
| findMin | 返回一个指向树中最小元素的索引 |
| findMax | 返回一个指向树中最大元素的索引 |
二、用链表实现二叉查找树
- ①二叉查找树的方法实现
- 书上实现了大部分的方法,只剩下findMax和findMin以及removeMax的方法尚未实现。
public T findMax() {
if ( isEmpty() ) {
throw new RuntimeException("树为空");
}
return findMax(root).element;
}
public T findMin()
{
if ( isEmpty() )
{
throw new RuntimeException("树为空");
}
return findMin(root).element;
}
public E removeMax()
{
E ret = maximum();
root = removeMax(root);
return ret;
}
private Node removeMax(Node node)
{
if(node.right == null)
{
Node leftNode = node.left;
node.left = null;
size --;
return leftNode;
}
node.right = removeMax(node.right);
return node;
}
- ②相关的方法的一些注意事项
- 1.构造函数一共有两个,一个负责创建一个空的LinkedBinarySearchTree,一个负责创建一颗根节点为特定元素的LinkedBinarySearchTree。
2.添加元素示意图
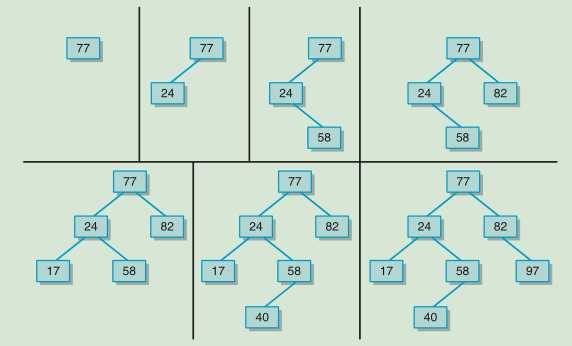
- 3.删除方法的实现与之前的线性研究结构不同,这里的删除不能直接将制定结点的相关引用结点给删除而是要用另外一个结点来替代该结点的位置。一共三种情况
- 如果被删除结点没有孩子,则replacement返回null
- 如果被删除结点有一个孩子,则返回这个孩子
- 如果被删除结点有两个孩子,则返回中序后继者(中序后继者指得是,使用中序遍历之后将目标元素删除后的下一位)删除方法示意图
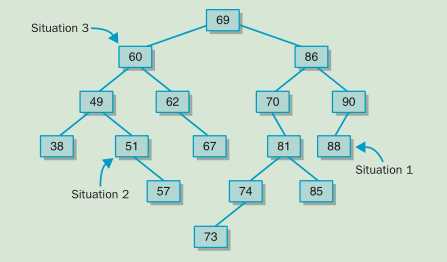
三、用有序列表实现二叉查找树
- ①方法
| 操作 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| removefirst | 删除列表的首元素 |
| removelast | 删除列表的尾元素 |
| remove | 删除列表中的一个特定元素 |
| first | 考察列表前端的那个元素 |
| last | 考察列表末端的那个元素 |
| contains | 判定列表是否含有一个特定的元素 |
| is Empty | 判定列表是否为空 |
| size | 判定列表中的元素数目 |
public class BinarySearchTreeList<T> extends LinkedBinarySearchTree<T>
implements ListADT<T>, OrderedListADT<T>, Iterable<T>
{
/**
* Creates an empty BinarySearchTreeList.
*/
public BinarySearchTreeList()
{
super();
}
/**
* Adds the given element to this list.
*
* @param element the element to be added to the list
*/
public void add(T element)
{
addElement(element);
}
/**
* Removes and returns the first element from this list.
*
* @return the first element in the list
*/
public T removeFirst()
{
return removeMin();
}
/**
* Removes and returns the last element from this list.
*
* @return the last element from the list
*/
public T removeLast()
{
return removeMax();
}
/**
* Removes and returns the specified element from this list.
*
* @param element the element being sought in the list
* @return the element from the list that matches the target
*/
public T remove(T element)
{
return removeElement(element);
}
/**
* Returns a reference to the first element on this list.
*
* @return a reference to the first element in the list
*/
public T first()
{
return findMin();
}
/**
* Returns a reference to the last element on this list.
*
* @return a reference to the last element in the list
*/
public T last()
{
return findMax();
}
/**
* Returns an iterator for the list.
*
* @return an iterator over the elements in the list
*/
public Iterator<T> iterator()
{
return iteratorInOrder();
}
}
四、平衡二叉查找树
- ①蜕化树
- 数根为最小元素,此时的二叉树为蜕化树,蜕化树的效率比线性结构还要低。
- ②右旋
- 1.使根的左子结点变为新的根。
- 2.原根节点变为新根的右节点。
- 3.原根节点的左子结点的右子结点变为原根结点的新的左子结点。图右旋示意图
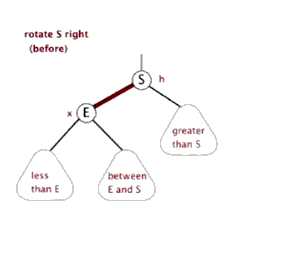
- ③左旋
- 1.使根的右子结点变为新的根。
- 2.原根节点变为新根的右节点。
- 3.原根节点的右子结点的左子结点变为原根结点的新的右子结点。图左旋示意图
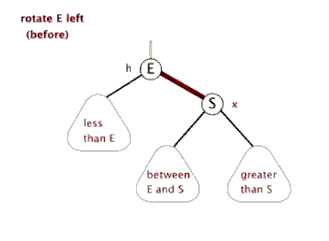
- ④右左旋(内部)
- 1.先右旋后左旋。图右左旋示意图
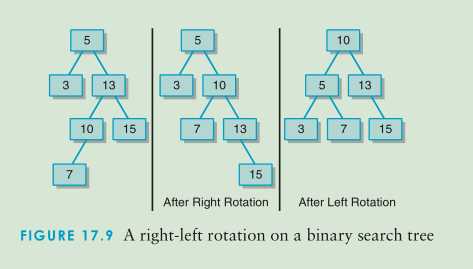
- 1.先右旋后左旋。图右左旋示意图
- ⑤左右旋(内部)
- 1.先左旋后右旋。图左右旋示意图
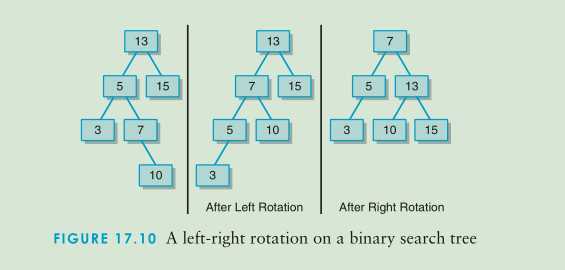
- 1.先左旋后右旋。图左右旋示意图
五、实现二叉查找树AVL树
- ①AVL树
- AVL树相较于普通的二叉搜索树,自主要的就是做了平衡化处理,使得二叉树变的平衡,高度降低。
- 平衡因子就是左右子树的高度差(用右子树的高度减去左子树的高度)。
- 当平衡因子大于1或者小于-1则该结点为树根的子树需要平衡。
- 一个平衡树的不平衡的方法只有两种:插入结点或者删除结点。
- ②AVL树的右旋
- 当某结点的平衡因子<-1时,则证明该结点的左孩子过长,在该结点的左孩子的平衡因子也是<-1则此时需要使用右旋。
- ③AVL树的左旋
- 当某结点的平衡因子>1时,则证明该结点的右孩子过长,在该结点的右孩子的平衡因子也是>1的时候,则此时需要使用左旋。
- ④AVL树的左右旋
- 当某结点的平衡因子<-1时,则证明该结点的左孩子过长,在该结点的左孩子的平衡因子却>1则此时需要使用右左旋。
⑤AVL树的右左旋
-- 当某结点的平衡因子>1时,则证明该结点的右孩子过长,在该结点的右孩子的平衡因子却<-1的时候,则此时需要右左旋。六、实现二叉查找树:红黑树
- ①红黑树
- 根节点为黑色
- 红色结点的所有孩子都是黑色
- 从数根到树叶的每条路径都包含同样数目的黑色结点。
- ②红黑树的元素插入
- 图红黑树元素插入及调整
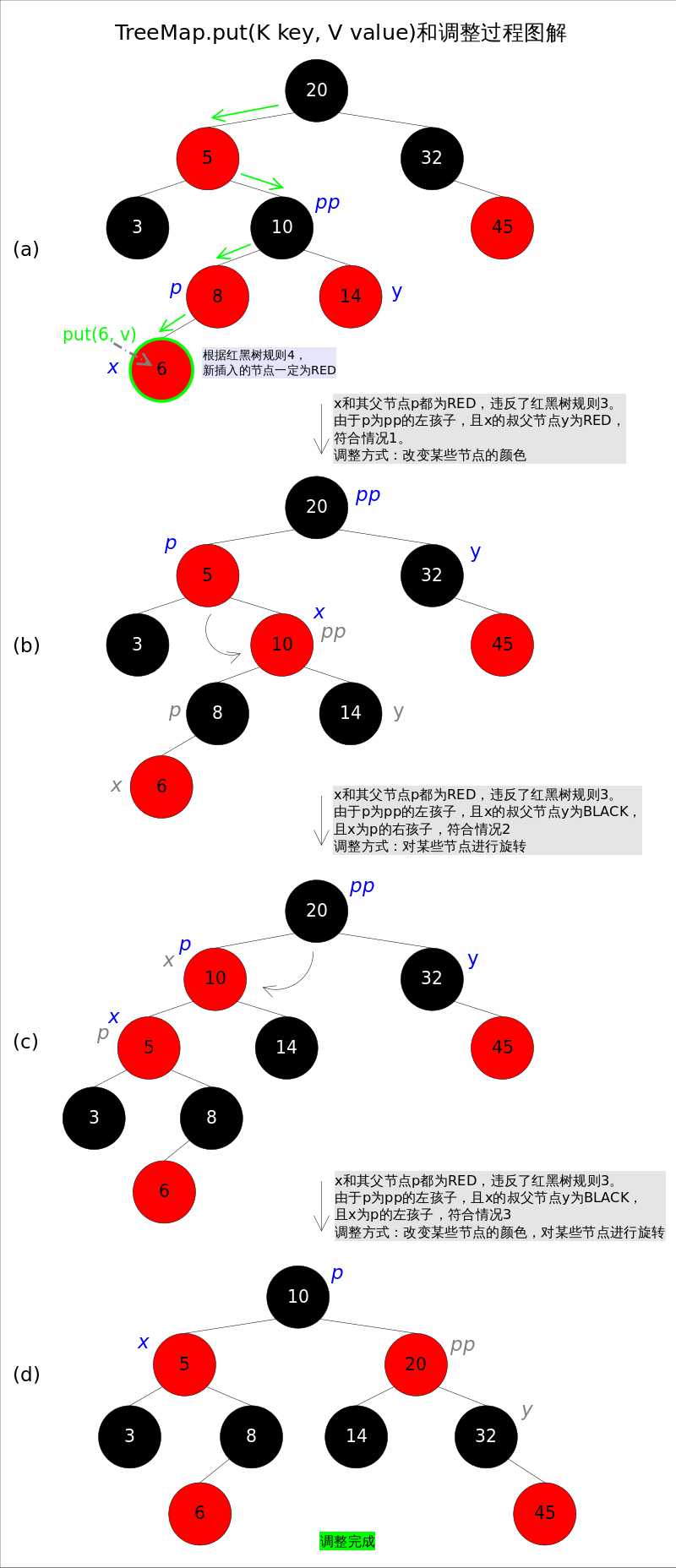
- 图红黑树元素插入及调整
- ③红黑树的元素删除
图红黑树元素删除及调整
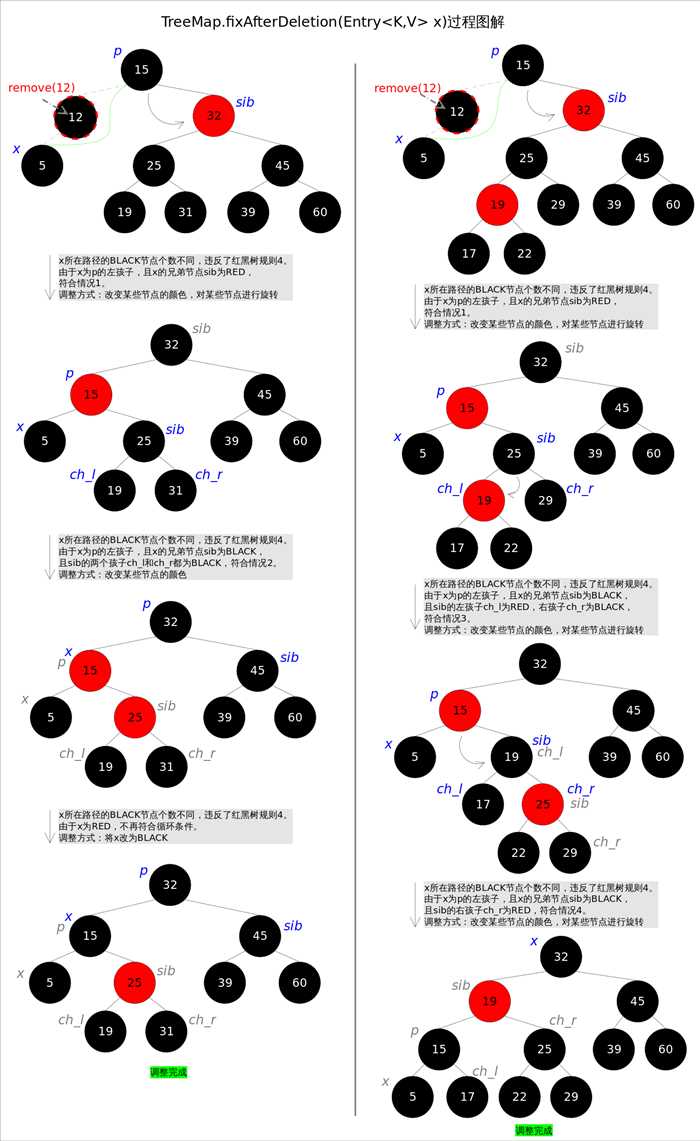
在进行删除之前需要找到该结点的后继结点来替代图红黑树替代
教材学习中的问题和解决过程
- 问题1:书上解释蜕化树的效率比链表还要低下为什么?
- 回答1:最后在书上找到与我相同的问题,这个问题是说每个结点都有相应的两个子节点树的存储空间,而很多方法都有对于null的检测过程,就会浪费很多时间,效率必然比链表还要低
- 问题2:红黑树插入原理解释不清楚。
- 回答2:插入一个元素到红黑树中,需要沿着插入点到根节点的路径上移动(遍历),在每一个经过的结点有三个操作:如果右子节点是红色的而左子节点也是红色的,进行右旋转。
如果左子节点是红色的且它的左子节点也是红色的,进行右旋转
如果左右子节点均为红色,进行颜色转换。本质上就是正常的二叉树插入,而将红黑进行转化, - 问题3:红黑树相对于AVL的优点在哪里?
回答3:1.红黑树的平衡是局部平衡所以平衡时旋转次数要通常比AVL少。2.红黑树在插入失衡最多两次平衡,删除失衡最多三次平衡,效率更高。3.读取比AVL树慢,但是维护更加容易与稳定。
代码调试中的问题和解决过程
问题1:在编写ppAVL的实现的时候,在关于左旋代码的实现过程中出现空指针问题图
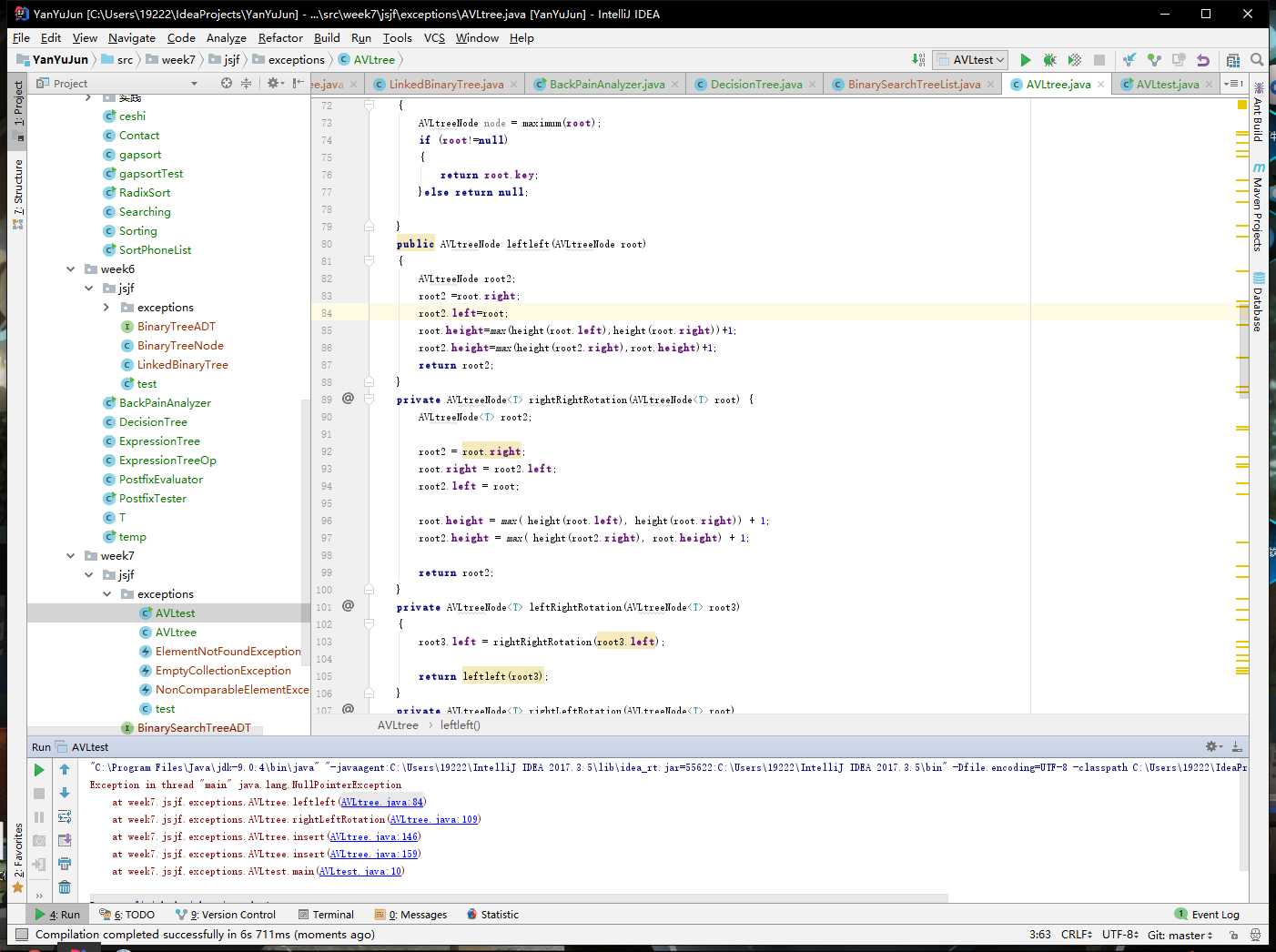
解答1:在进行debug的时候,脑阔疼,实在是看不懂debug的流程,按照书上的意思画了个草图,一步一步对照,后来发现指针的位置由于自己的疏忽给错对象了。改正后图
代码托管
-图代码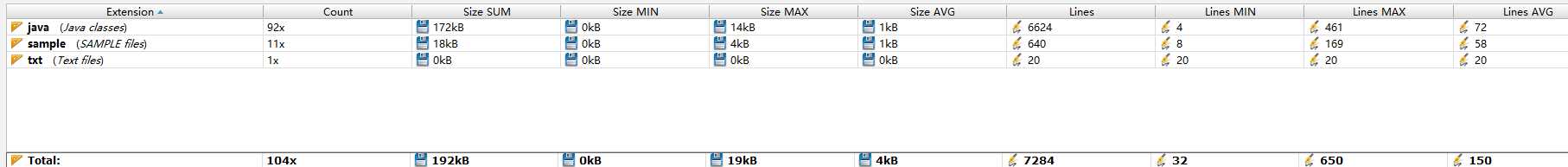
上周考试错题总结
- 有但是不知道错在哪里因为结果还没出来。
结对及互评
基于评分标准,我给李楠的博客打分:7分。得分情况如下:
正确使用Markdown语法(加1分)
模板中的要素齐全(加1分)
教材学习中的问题和解决过程, (加3分)
代码调试中的问题和解决过程, 无问题
感想,体会真切的(加1分)
点评认真,能指出博客和代码中的问题的(加1分)
点评过的同学博客和代码
- 本周结对学习情况
- 20172330李楠
- 结对照片
- 结对学习内容
- 二叉查找树
其他(感悟、思考等,可选)
看不懂。
学习进度条
| 代码行数(新增/累积) | 博客量(新增/累积) | 学习时间(新增/累积) | 重要成长 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目标 | 5000行 | 30篇 | 400小时 | |
| 第一周 | 0/0 | 1/1 | 10/10 | |
| 第二周 | 0/0 | 1/2 | 10/20 | |
| 第三周 | 1500/1500 | 1/3 | 10/30 | |
| 第四周 | 2761/4261 | 2/5 | 25/55 | |
| 第五周 | 814/5075 | 1/6 | 15/70 | |
| 第六周 | 1091/6166 | 1/7 | 15/85 | |
| 第七周 | 1118/7284 | 1/8 | 15/100 |
以上是关于20172333 2018-2019-1 《程序设计与数据结构》第七周学习总结的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章