list源码2(参考STL源码--侯捷):constructorpush_backinsert
Posted ybf-yyj
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了list源码2(参考STL源码--侯捷):constructorpush_backinsert相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
list的push_back、insert的使用如下:

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int i;
list<int> l;
cout<<l.size()<<endl; //0
l.push_back(1);
l.push_back(3);
l.push_back(5);
l.push_back(7);
l.push_back(9);
cout<<l.size()<<endl; //5
list<int>::iterator it;
for(it=l.begin();it!=l.end();++it){
cout<<*it<<‘ ‘; //1 3 5 7 9
}
cout<<endl;
it=find(l.begin(),l.end(),5);
if(*it==5)
l.insert(it,99);
for(auto i:l) cout<<i<<‘ ‘; //1 3 99 5 7 9
cout<<endl;
it=find(l.begin(),l.end(),55);
if(*it==55)
l.insert(it,20);
for(auto i:l) cout<<i<<‘ ‘; //1 3 99 5 7 9
cout<<endl;
it=find(l.begin(),l.end(),55);
l.insert(it,20);
for(auto i:l) cout<<i<<‘ ‘; //1 3 99 5 7 9 20
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
list缺省使用alloc作为空间适配器,并据此另外定义了一个list_node_allocator,为的是更方便地以节点大小为配置单位:
template <class T,class Alloc=alloc>
class list{
protected:
typedef __list_node<T> list_node;
//专属之空间适配器,每次配置一个节点大小
typedef simple_alloc<list_node,Alloc> list_node_allocator;
...
};
于是list_node_allocator(n)表示配置n个节点空间,以下4个函数,分别来配置、释放、构造、销毁一个节点:
protected:
//配置一个节点并传回
link_type get_node(){return list_node_allocator::allocate();}
//释放一个节点
void put_node(link_type p){list_node_allocator::deallocate(p);}
//产生(配置并构造)一个节点,带有元素值
link_type create_node(const T& x){
linke_type p=get_node();
construct(&p->data,x);//全局函数,构造/析构基本工具
return p;
}
//销毁(析构并释放)一个节点
void destory_node(link_type p){
destory(&p->data);
put_node(p);//全局函数,构造/析构基本工具
}
list提供有许多constructors,其中一个是default constructor,允许我们不指定任何参数做出一个空的list出来:
public:
list(){empty_initialize();} //产生一个空链表
protected:
void empty_initialize(){
node=get_node(); //配置一个节点空间,令node指向它
node->next=node; //令node的头尾指向自己,不设元素值
node->prev=node;
}
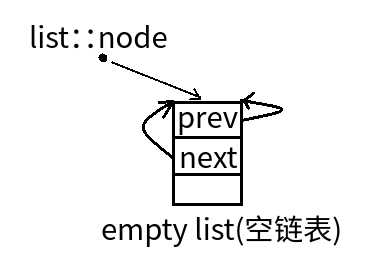
当我们以push_back()将新元素插入list尾端时,此函数内部调用insert():
void push_back(const T& x) {insert(end(),x);}
insert()是一个重载函数,有多种形式,其中最简单的一种如下,符合以上所需,首先配置并构造一个节点,然后在尾端进行适当的指针操作,将新节点插入进去:
//函数的目的:在迭代器position所指位置插入一个节点,内容为x
iterator insert(iterator position,const T& x){
link_type temp=create_node(x);//产生一个节点
//调整双向指针,使temp插入进去
temp->next=position.node;
temp->prev=position.node->prev;
(link_type(position.node->prev))->next=temp;
position.node->prev=temp;
return temp;
}
由于list不像vector那样有可能在空间不足时做重新配置,数据移动的操作,所以插入之前的迭代器仍然有效。
以上是关于list源码2(参考STL源码--侯捷):constructorpush_backinsert的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
