循环链表的实现
Posted zhaobinyouth
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了循环链表的实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 什么是循环链表
1.1概念
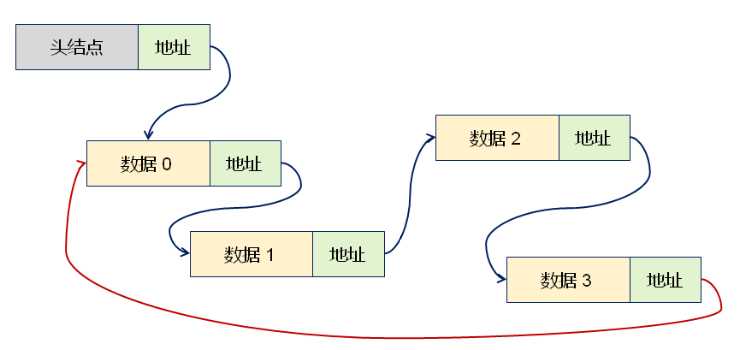
- 任意数据元素都有一个前驱(地址)和一个后继(地址)
- 所有的数据元素的关系构成一个逻辑上的环
1.2实现
- 循环链表是一种特殊的单链表
- 尾节点的指针保存了首节点的地址
2. 循环链表的逻辑构成
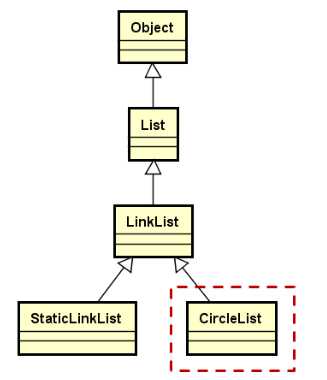
继承层次结构
3. 循环链表的实现思路
(1)通过模板定义CircleList类,继承自LinkList类
(2)定义内部函数makeCircle(),用于将单链表首尾相连
(3)特殊处理:首元素的插入操作和删除操作
①插入位置为0时:头结点和尾结点均指向新结点;新结点成为首结点。
②删除位置为0时:头结点和尾结点指向位置为1的结点;安全销毁首结点。
(4)重新实现:清空操作和遍历操作
【编程实验】循环链表的实现
//LinkList.h
1 #ifndef LINKLIST_H 2 #define LINKLIST_H 3 #include "List.h" 4 namespace DataStructureLib 5 { 6 template <typename T> 7 8 class LinkList:public List<T> 9 { 10 protected: 11 struct Node{ 12 T value; 13 Node* next; 14 }; 15 16 mutable Node m_header;//头结点 、mutable为了让get函数中的const属性导致的&m_header(编译器认为是要修改成员变量)mutable就允许const成员函数取地址 17 int m_length;//链表的长度 18 19 Node* position(int i) const//返回第i和元素的指针 20 { 21 Node* ret=&m_header; 22 23 for(int p=0;p<i;p++) 24 { 25 ret=ret->next; 26 } 27 28 return ret;//元素地址保存在该节点的next指针域中 29 } 30 31 //游标 32 int m_step; 33 Node* m_current ; 34 public: 35 LinkList() 36 { 37 m_header.next=NULL; 38 m_length=0; 39 m_step=1; 40 m_current=NULL; 41 } 42 bool insert(const T &elem) //O(n) 43 { 44 return insert(m_length, elem); 45 } 46 47 bool insert(int index, const T& elem)//思路:1.找到index位置处的元素;2.在该元素尾部insert新元素 48 { 49 bool ret=(index<=m_length)&&(index>=0); 50 51 if (ret) 52 { 53 Node* NewNode=createNode() ; 54 55 if (NULL!=NewNode) 56 { 57 NewNode->value=elem; 58 59 Node* currentNode=position(index); 60 NewNode->next=currentNode->next; 61 currentNode->next=NewNode; 62 63 m_length++; 64 } 65 else{ 66 throw("has Not enougth memory to insert new element ..."); 67 } 68 69 } 70 return ret; 71 } 72 73 bool remove(int index) 74 { 75 bool ret=((index<=m_length)&&(index>=0)); 76 77 if (ret) 78 { 79 Node* CurrentNode=position(index); 80 Node* toDelNode=CurrentNode->next; 81 if(this->m_current==toDelNode) 82 { 83 this->m_current=toDelNode->next; 84 } 85 CurrentNode->next=toDelNode->next; 86 87 delete toDelNode ; 88 m_length--; 89 } 90 91 return ret; 92 } 93 94 bool set(int index,const T& e) 95 { 96 bool ret=((0<=index)&&(index<=m_length)); 97 98 if (ret) 99 { 100 Node* CurrentNode=position(index); 101 CurrentNode->next->value=e; 102 } 103 104 return ret; 105 } 106 107 bool get(int index, T& elem) const 108 { 109 bool ret=((index<=m_length)&&(index>=0)); 110 111 if (ret) 112 { 113 Node* CurrentNode=position(index); 114 elem= CurrentNode->next->value; 115 } 116 117 return ret; 118 } 119 120 T get(int index) 121 { 122 T ret; 123 if((index<m_length)&&(0<=index)) 124 { 125 Node* CurrentNode=position(index); 126 ret= CurrentNode->next->value; 127 } 128 129 return ret; 130 } 131 int getlength() const 132 { 133 return m_length; 134 135 } 136 137 void clear() 138 { 139 140 while (m_header.next) 141 { 142 Node* toDelNode=m_header.next; 143 m_header.next=toDelNode->next; 144 delete toDelNode; 145 } 146 m_length=0; 147 } 148 149 //寻找e元素所在的位置, 150 //返回值 失败:-1 成功:e元素所在的位置的id 151 int find(T& e) 152 { 153 int ret = -1; 154 for (int i=0;i<m_length;i++) 155 { 156 if (e==get(i)) 157 { 158 ret=i; 159 } 160 } 161 162 return ret; 163 } 164 165 bool move(int i,int step=1)//将游标定位到目标位置,//i代表目标位置 step游标每次移动的节点的数目 166 { 167 bool ret= (0<=i)&&(i<m_length)&&(step>0); 168 169 if (ret) 170 { 171 m_current=position(i)->next; 172 m_step=step; 173 } 174 175 return ret; 176 177 } 178 179 bool end()//游标有无到达链表尾部 180 { 181 return (m_current==NULL); 182 } 183 184 T current()//获取游标所指向的数据元素 185 { 186 if(!end()) 187 { 188 return m_current->value ; 189 } 190 else 191 { 192 throw("No Value at current position..."); 193 } 194 } 195 196 //移动游标 相当于每次移动的大小m_step 197 bool next() 198 { 199 200 int i=0; 201 202 while ((m_step>i)&&(!end())) 203 { 204 m_current=m_current->next; 205 i++; 206 } 207 208 return (i==m_step); 209 } 210 211 //封装节点创建和销毁函数,以便子类可以重载这个函数。 212 virtual Node* createNode() 213 { 214 return new Node(); 215 } 216 217 virtual void destroyNode(Node* pn) 218 { 219 delete pn; 220 } 221 222 ~LinkList() 223 { 224 clear(); 225 } 226 }; 227 } 228 #endif
//CircleList.h
1 #ifndef CIRCLELIST_H 2 #define CIRCLELIST_H 3 4 #include "LinkList.h" 5 6 namespace DataStructureLib 7 { 8 template <typename T> 9 10 class CircleList:public LinkList<T> 11 { 12 protected: 13 typedef typename LinkList<T>::Node Node ;//这种情况下要加上typename,因为不加编译器有可能将LinkList<T>::Node Node 试图 14 //解释为变量,你在typedef 就会有语法错误。加上以后就是让编译器认为LinkList<T>::Node Node 它是一个类型 15 16 Node* last() const // 17 { 18 return this->position(m_length-1)->next;////返回指向尾结点指针 19 } 20 21 void makeCircleList() const {//尾节点的指针指向第一个节点(即首节点的指针域) 22 if(this->m_header.next) 23 last()->next=this->m_header.next; 24 } 25 26 int mod(int i)//判断循环链表中的第i个元素在链表的位置 27 { 28 return (this->m_length==0)?0:(i %this->m_length); 29 } 30 31 public: 32 bool insert(int index, const T& elem) 33 { 34 bool ret=true; 35 36 index=index%(this->m_length+1); 37 38 ret=LinkList<T>::insert(index,elem); 39 if (ret && (index==0)) 40 { 41 makeCircleList(); //首尾相连 42 } 43 44 return ret; 45 } 46 47 bool insert(const T& elem) 48 { 49 return insert(this->m_length,elem); 50 51 } 52 53 bool remove(int index) 54 { 55 bool ret = true; 56 index=mod(index); 57 58 if (index==0) //删除0位置时 59 { 60 Node* toDel=this->m_header.next; 61 if (toDel!=NULL) 62 { 63 this->m_header.next=toDel->next; 64 this->m_length--; 65 66 if(this->m_length>0) 67 { 68 makeCircleList(); 69 if(this->m_current==toDel) 70 { 71 this->m_current=toDel->next; 72 } 73 } 74 else 75 { 76 this->m_header.next=NULL; 77 78 this->m_current=NULL; 79 } 80 81 this->destroyNode(toDel); 82 } 83 else 84 { 85 ret=false; 86 } 87 } 88 89 else 90 { 91 LinkList<T>::remove(index); 92 } 93 94 95 96 return ret; 97 } 98 99 bool set(int index, const T& elem) 100 { 101 return LinkList<T>::set(mod(index), elem); 102 } 103 104 T get(int index) const 105 { 106 return LinkList<T>::get(mod(index)); 107 } 108 109 bool get(int index, const T& elem) const 110 { 111 return LinkList<T>::get(mod(index), elem); 112 } 113 114 int find(const T& elem) const 115 { 116 int ret = -1; 117 Node* slider = this->m_header.next; 118 119 for(int i=0; i<this->m_length; i++){ 120 if(slider->value == elem){ 121 ret = i; 122 break; 123 } 124 125 slider = slider->next; 126 } 127 128 return ret; 129 } 130 131 void clear() 132 { 133 if (this->m_length>1) 134 { 135 //remove(1)而不remove(0)是因为避开删除首结点 136 //而导致效率低下的问题。 137 remove(1); 138 } 139 if (this->m_length==1) 140 { 141 Node* toDel = this->m_header.next; 142 this->m_header.next = NULL; 143 this->m_length = 0; 144 this->m_current=NULL; 145 this->destroyNode(toDel); 146 } 147 148 } 149 150 bool move(int i,int step) //O(n) 151 { 152 return LinkList<T>::move(mod(i),step); 153 } 154 155 bool end() //O(1) 156 { 157 return ( (this->m_length == 0) || (this->m_current == NULL) ); 158 } 159 160 ~CircleList() 161 { 162 clear(); 163 } 164 165 }; 166 167 } 168 #endif
约瑟夫环问题
小故事
在罗马人占领乔塔帕特后,39个犹太人与Josephus及他的朋友躲到一个洞中,39个犹太人决定宁愿死也不要被敌人抓到,于是决定了一个自杀方式,41个人排成一个圆圈,由第1个人开始报数,每报到第3人该人就必须自杀,然后再由下一个重新报数,直到所有人都自杀身亡为止。然而Josephus和他的朋友并不想遵从。那么,一开始要站在什么地方才能避免被处决?
约瑟夫环
己知n个人(以编号0,1,2,3,…,n-1分别表示)围坐在一张圆桌周围。从编号为k的人开始报数,数到m的那个人出列;他的下一个人又从1开始报数,数到m的那个人又出列;依此规律重复下去,直到圆桌周围的人全部出列。
【编程实验】约瑟夫问题
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "CircleList.h" 3 4 using namespace std; 5 using namespace DataStructureLib; 6 7 void josephus(int n, int s, int m) 8 { 9 CircleList<int> cl; 10 11 for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) 12 { 13 cl.insert(i); 14 } 15 16 cl.move(s-1,m-1); //游标指向0处,步长2 17 18 int i=0; 19 20 while( cl.getlength() > 0 ) 21 { 22 cl.next(); 23 24 if (i%8==0) 25 { 26 cout<<‘ ‘; 27 } 28 29 cout <<"("<<++i<<")"<< cl.current() << " "; //当前要自杀的 30 31 int index=cl.find(cl.current()); 32 cl.remove(index); 33 } 34 } 35 36 int main() 37 { 38 josephus(41,1,3); //41个人,从1号开始数,数到第三个人开始自杀 39 40 return 0; 41 }
(1)3 (2)6 (3)9 (4)12 (5)15 (6)18 (7)21 (8)24 (9)27 (10)30 (11)33 (12)36 (13)39 (14)1 (15)5 (16)10 (17)14 (18)19 (19)23 (20)28 (21)32 (22)37 (23)41 (24)7 (25)13 (26)20 (27)26 (28)34 (29)40 (30)8 (31)17 (32)29 (33)38 (34)11 (35)25 (36)2 (37)22 (38)4 (39)35 (40)16 (41)31
4. 小结
(1)循环链表是一种特殊的单链表
(2)尾结点的指针域保存了首结点的地址
(3)特殊处理首元素的插入操作和删除操作
(4)重新实现清空操作和遍历操作
以上是关于循环链表的实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章