[OI - 模拟考] LYOI2018模拟考N
Posted aiyi2000
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了[OI - 模拟考] LYOI2018模拟考N相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
博客背景
在很久之前LYOI就开始了停课集训的生活
当然集训的日子里少不了模拟考
之所以标题叫模拟考N
因为我也不知道这是第几次模拟考了啊
qwq
博客正文
T1
小豪的花园
2s 256MB
【题目描述】
小豪有一个花园,里面有n个花棚,编号1~n,每个花棚里有一定数量的花ai。小豪花园的路十分神奇,可以使得任意两个花棚之间仅有一条最短路,即形成树结构,其中根节点是1号花棚。
现在小豪打算修缮一下他的花园,重新分配每个花棚里花的数量。为了能方便快捷地知道花园的情况,小豪现在需要你的帮助。具体地说,小豪共有m个操作。操作有三种:
1 u k表示如果一个花棚在以u号花棚为根的子树中,那么小豪会把这个花棚花的数量模k;
2 u x表示小豪将u号花棚花的数量变成x;
3 u v表示小豪询问从u号花棚走到v号花棚总共能看到的花的数量。
你能帮助小豪吗?
【输入格式】
第一行有两个正整数n和m,代表花棚的数量和小豪操作的个数。
接下来n-1行,每行两个正整数u,v(1≤u,v≤n,u≠v),表示u号花棚与v号花棚直接有路相连。
下一行有n个非负整数a1,a2,…,an,表示起始时每个花棚中花的数量。
接下来m行,一行表示一个操作,格式如题所述。(可参考样例)
【输出格式】
对于每个操作3输出一行一个整数,表示结果。
【样例输入】
8 7
1 2
2 3
2 4
2 5
1 6
6 7
6 8
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
3 3 6
1 2 3
2 2 4
3 4 8
2 3 11
1 1 5
3 3 7
【样例输出】
12
20
9
【数据范围】
对于20%的数据,n,m≤2000;
对于另外30%的数据,无操作1;
对于100%的数据,n,m≤105,ai,x,k≤108,k≥1。
题目分析
这题是线段树(树状数组)、DFS序的综合应用。
首先对于50%的数据,就是裸的树链剖分。也有时间复杂度少一个log n的做法,见下文。
比较难搞的就是操作1,对子树取模,利用DFS序可以变成区间取模。
区间取模问题的做法很简单,就是不断找区间的最大值,一个一个地进行取模操作直至最大值小于要模的值。可以证明,这样 做操作1的总时间复杂度不超过O((n + m) log x + m log n) (x 表示花的数量的最大值,下同)。注意到 一个数模了另一个数后要么不变,要么至多变为原来的一半,如此一个数(若没有修改)最多只能变 化log x次,且修改总共最多m次,因此所有数被修改的总次数不超过(n + m) log x。这个结果加上查找 最大值的时间即可得上述时间复杂度O((n + m) log x + m log n)。
如此操作1和操作2都是单点修改,而操作3是路经询问。路经询问不好处理,可以通过差分变成子 树修改和单点询问。记f[u]表示u到根节点花的数量和,这样对于一个询问(u, v),设w是u和v的最近公 共祖先,询问的答案就是f[u] + f[v] ? 2 ? f[w] + a[w];对于一个修改操作a[u] → x,则需要把u的子树 中所有f加上x ? a[u]。利用DFS序,这两个操作用树状数组或者线段树即可完成。
上述做法时间复杂度O((n + m) log n log x + m log n)。若无上段所述的转化,直接用树链剖分,时 间复杂度是O((n + m) log2 n log x + m log n),可能会超时。
参考代码
1 //1024程序员日快乐qwq 2 //树剖 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <cstdio> 5 #include <cstring> 6 #include <algorithm> 7 #include <cctype> 8 #include <cstdlib> 9 10 using namespace std; 11 //#define DEBUG(x) cerr << #x << "=" << x << endl 12 13 const int S = 1 << 20; 14 char frd[S], *hed = frd + S; 15 const char *tal = hed; 16 17 inline char nxtChar() 18 { 19 if (hed == tal) 20 fread(frd, 1, S, stdin), hed = frd; 21 return *hed++; 22 } 23 24 template <class T> 25 inline void read(T &res) 26 { 27 char ch; 28 while (ch = nxtChar(), !isdigit(ch)); 29 res = ch ^ 48; 30 while (ch = nxtChar(), isdigit(ch)) 31 res = res * 10 + ch - 48; 32 } 33 34 template <class T> 35 inline void put(T x) 36 { 37 if (x > 9) put(x / 10); 38 putchar(x % 10 + 48); 39 } 40 41 typedef long long ll; 42 const int N = 1e5 + 5, M = 2e5 + 5, L = 4e5 + 5; 43 int dep[N], fa[N], val[N], sze[N], son[N], pos[N], idx[N], top[N]; 44 ll sum[L]; int mx[L], n, m, T; 45 46 struct Edge 47 { 48 int to; Edge *nxt; 49 }p[M], *lst[N], *P = p; 50 51 inline void addEdge(int x, int y) 52 { 53 (++P)->nxt = lst[x]; lst[x] = P; P->to = y; 54 (++P)->nxt = lst[y]; lst[y] = P; P->to = x; 55 } 56 57 inline void dfs1(int x) 58 { 59 dep[x] = dep[fa[x]] + 1; sze[x] = 1; 60 for (Edge *e = lst[x]; e; e = e->nxt) 61 { 62 int y = e->to; 63 if (y == fa[x]) continue; 64 fa[y] = x; 65 dfs1(y); 66 sze[x] += sze[y]; 67 if (sze[y] > sze[son[x]]) son[x] = y; 68 } 69 } 70 71 inline void dfs2(int x) 72 { 73 if (son[x]) 74 { 75 top[son[x]] = top[x]; 76 pos[son[x]] = ++T; 77 idx[T] = son[x]; 78 dfs2(son[x]); 79 } 80 int y; 81 for (Edge *e = lst[x]; e; e = e->nxt) 82 if (!top[y = e->to]) 83 { 84 top[y] = y; 85 pos[y] = ++T; 86 idx[T] = y; 87 dfs2(y); 88 } 89 } 90 91 inline void init() 92 { 93 dfs1(1); 94 top[1] = pos[1] = idx[1] = T = 1; 95 dfs2(1); 96 } 97 98 #define sL s << 1 99 #define sR s << 1 | 1 100 101 template <class T> 102 inline T idMax(T x, T y) {return val[x] > val[y] ? x : y;} 103 104 inline void Uptdate(int s) 105 { 106 mx[s] = idMax(mx[sL], mx[sR]); 107 sum[s] = sum[sL] + sum[sR]; 108 } 109 110 inline void Build(int s, int l, int r) 111 { 112 if (l == r) 113 return (void)(mx[s] = idx[l], sum[s] = val[idx[l]]); 114 int mid = l + r >> 1; 115 Build(sL, l, mid); Build(sR, mid + 1, r); 116 Uptdate(s); 117 } 118 119 inline void Modify(int s, int l, int r, int x, int v) 120 { 121 if (l == r) return (void)(sum[s] = v); 122 int mid = l + r >> 1; 123 if (x <= mid) Modify(sL, l, mid, x, v); 124 else Modify(sR, mid + 1, r, x, v); 125 Uptdate(s); 126 } 127 128 inline ll querySum(int s, int l, int r, int x, int y) 129 { 130 if (l == x && r == y) return sum[s]; 131 int mid = l + r >> 1; 132 if (y <= mid) 133 return querySum(sL, l, mid, x, y); 134 else if (x > mid) 135 return querySum(sR, mid + 1, r, x, y); 136 else 137 return querySum(sL, l, mid, x, mid) 138 + querySum(sR, mid + 1, r, mid + 1, y); 139 } 140 141 inline int queryMax(int s, int l, int r, int x, int y) 142 { 143 if (l == x && r == y) return mx[s]; 144 int mid = l + r >> 1; 145 if (y <= mid) 146 return queryMax(sL, l, mid, x, y); 147 else if (x > mid) 148 return queryMax(sR, mid + 1, r, x, y); 149 else 150 return idMax(queryMax(sL, l, mid, x, mid), 151 queryMax(sR, mid + 1, r, mid + 1, y)); 152 } 153 154 inline ll pathQuery(int x, int y) 155 { 156 ll res = 0; 157 while (top[x] != top[y]) 158 { 159 if (dep[top[x]] < dep[top[y]]) swap(x, y); 160 res += querySum(1, 1, T, pos[top[x]], pos[x]); 161 x = fa[top[x]]; 162 } 163 if (dep[x] < dep[y]) swap(x, y); 164 return res + querySum(1, 1, T, pos[y], pos[x]); 165 } 166 167 int main() 168 { 169 freopen("flower.in", "r", stdin); 170 freopen("flower.out", "w", stdout); 171 172 read(n); read(m); 173 for (int i = 1, u, v; i < n; ++i) 174 read(u), read(v), addEdge(u, v); 175 for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) 176 read(val[i]); 177 init(); Build(1, 1, T); 178 179 int opt, u, v, w; 180 while (m--) 181 { 182 read(opt); read(u); read(v); 183 switch (opt) 184 { 185 case 1: 186 while (w = queryMax(1, 1, T, pos[u], pos[u] + sze[u] - 1), val[w] >= v) 187 val[w] %= v, Modify(1, 1, T, pos[w], val[w]); 188 break; 189 190 case 2: 191 val[u] = v; 192 Modify(1, 1, T, pos[u], val[u]); 193 break; 194 195 case 3: 196 put(pathQuery(u, v)), putchar(‘ ‘); 197 break; 198 } 199 } 200 201 fclose(stdin); fclose(stdout); 202 return 0; 203 }
T2
遗传病
1s 256MB
【题目描述】
众所周知,近亲结婚的后代患遗传病的概率会大大增加。如果某一基因按常染色体隐性遗传方式,其子女就可能因为是突变纯合子而发病。因此,近亲婚配增加了某些常染色体隐性遗传疾病的发生风险。
现在有n个人,每个人都有一个遗传特征值ai,设第i个人和j个人结婚,那么风险系数为gcd(ai,aj),法律规定只有风险系数为1时两个人才能结婚。
F同学开了一个婚姻介绍所,这n个人可能会来登记,当然也有可能登记后取消,也有可能取消后再登记。F同学的任务就是,求出当前所有登记的人中,有多少对人是可以结婚的。刚开始所有人都没有登记。
为出题需要,不考虑性别,基因突变和染色体变异等QAQ。
【输入格式】
第一行两个整数n和q,n表示人数,q表示登记和登出的总次数。
第二行n个整数a1,a2,…,an,意义如上所述。
接下来q行,每行一个整数x。如果当前第x个人没有登记,那么第x个人登记;如果当前第x个人已经登记了,那么取消其登记。
【输出格式】
一共q行,第i行表示第i个操作后,当前所有登记的人中有多少对人是可以结婚的。
【样例输入】
5 6
1 2 3 4 6
1
2
3
4
5
1
【样例输出】
0
1
3
5
6
2
【数据范围】
对于30%的数据,1≤n,q≤1000;
对于100%的数据,1≤n,q≤100000,1≤ai≤500000。
题目分析
本题考察容斥原理。
30%数据,每加入或删除一个数,扫一下已经登记的人求一下gcd即可,时间复杂度O(n^2)
100%数据,考虑容斥原理。
比如加入一个数30,那么60的质因数集合为{2,3,5}(重复的去掉)
两个数互质等价于质因数集合交集问空集。
记|S|为当且已登记的人中质因数集合的子集有S的人数,其中S是一个质因数集合
特别地,记|{1}|=当前已登记的人数
与30互质的个数=|{1}|-|{2}|-|{3}|-|{5}|+|{2,3}|+|{2,5}|+|{3,5}|-|{2,3,5}|
因为2*3*5*7*11*13*17=510510>500000,所以每个数最多只有6个质因数(重复的去掉)
2^6=64,时间复杂度为O(64n)。
参考代码
1 //1024程序员日快乐qwq 2 //容斥原理 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <cstdio> 5 #include <cstring> 6 #include <algorithm> 7 8 using namespace std; 9 //#define DEBUG(x) cerr << #x << "=" << x << endl 10 const int MAXN = 100005; 11 12 int n, q, tot, las; 13 int a[MAXN], ccount[MAXN * 5]; 14 int rec[MAXN * 5][10]; 15 bool vis[MAXN * 5]; 16 17 inline void Divide(int pos) 18 { 19 int x = a[pos]; 20 for (int i = 2; i * i <= x; i++) 21 { 22 if (x % i == 0) 23 { 24 rec[a[pos]][++rec[a[pos]][0]] = i; 25 while (x % i == 0) x /= i; 26 } 27 } 28 if (x > 1) rec[a[pos]][++rec[a[pos]][0]] = x; 29 } 30 31 inline int Calc(int x) 32 { 33 int ans = 0; 34 int End = (1 << rec[x][0]) - 1; 35 for (int i = 1; i <= End; i++) 36 { 37 int tmp = 1, cnt = 0; 38 for (int j = 0; j < rec[x][0]; j++) 39 if (((1 << j) & i) > 0) 40 { 41 tmp *= rec[x][j + 1]; 42 cnt++; 43 } 44 if (cnt % 2 == 1) ans += ccount[tmp]; 45 else ans -= ccount[tmp]; 46 } 47 return ans; 48 } 49 50 inline void Update(int x, int delta) 51 { 52 int End = (1 << rec[x][0]) - 1; 53 for (int i = 1; i <= End; i++) 54 { 55 int tmp = 1; 56 for (int j = 0; j < rec[x][0]; j++) 57 if (((1 << j) & i) > 0) 58 tmp *= rec[x][j + 1]; 59 ccount[tmp] += delta; 60 } 61 } 62 63 int main() 64 { 65 freopen("disease.in", "r", stdin); 66 freopen("disease.out", "w", stdout); 67 scanf("%d%d", &n, &q); 68 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d", &a[i]); 69 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 70 { 71 if (!rec[a[i]][0]) Divide(i); 72 } 73 memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)); 74 for (int i = 1, t = 0, add = 0; i <= q; i++) 75 { 76 scanf("%d",&t); 77 if (!vis[t]) 78 { 79 vis[t] = 1; 80 add = tot; 81 if(a[t] != 1) add -= Calc(a[t]); 82 else ccount[1] ++; 83 Update(a[t], 1); 84 printf("%d ", las + add); 85 las = las + add; 86 tot++; 87 } 88 else 89 { 90 vis[t] = 0; 91 add = tot - 1; 92 Update(a[t], -1); 93 if (a[t] != 1) add -= Calc(a[t]); 94 else ccount[1] --; 95 printf("%d ", las - add); 96 las = las - add; 97 tot--; 98 } 99 } 100 return 0; 101 }
T3
道路
2s 512MB
【问题描述】
我们看见了一个由m行n列的1*1的格子组成的矩阵,每个格子(i,j)有对应的高度h[i][j]和初始的一个非负权值v[i][j]。我们可以随便选择一个格子作为起点,然后在接下来的每一步当中,我们能且只能到达与当前格子有边相邻的四个格子中的高度不超过当前格子高度的格子,每当我们到达一个新格子(包括一开始选择的初始格子),我们就能得到该格子的权值分,然后该格子的权值就会等概率变成不比当前的权值大的一个非负权值。每一个格子在满足前面条件情况下,可以走任意多次。
我们希望得到一个最大的期望权值和路径,并给出这个最大的期望权值和。
【输入格式】
第一行两个正整数表示m,n。
接下来的m行,每行n个正整数,表示h[i][j]。
接下来的m行,每行n个非负整数,表示v[i][j]。
【输出格式】
一行一个实数,表示所求的最大期望权值和,保留整数。
【输入样例】
1 3
1 2 1
1 2 3
【输出样例】
5
【数据范围】
对于30%的数据,保证n,m不超过100。
对于另外20%的数据,保证不存在相同的高度的格子。
对于70%的数据,所有权值不超过106。
对于100%的数据,保证n,m不超过1000,所有权值与高度不超过109。
题目分析
我们首先可以通过设一个概率的dp:f[i]表示原价值为i重复走无限多次的期望总价值。
然后可以得到以下式子:
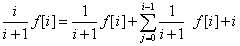
化简可得:
![]()
然后,我们就把连通的同高度点缩成一个点,然后对剩余的DAG做一个dp去维护最大权路径就可以了。
关于同一高度点的处理证明:相同高度点可以多次访问,即可以得到这一块的所有权值。权值非负可以得到贪心正确。
特判可以保证网络流不会死循环。
参考代码
1 //1024程序员日快乐qwq 2 //DAG上的DP 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <cstdio> 6 #include <algorithm> 7 #include <vector> 8 9 using namespace std; 10 //#define DEBUG(x) cerr << #x << "=" << x << endl 11 const int maxn = 1024; 12 const int dx[4] = {-1, 1, 0, 0}; 13 const int dy[4] = {0, 0, -1, 1}; 14 15 inline int read() 16 { 17 char ch, c; 18 int res; 19 while (ch = getchar(), ch < ‘0‘ || ch > ‘9‘) c = ch; 20 res = ch - 48; 21 while (ch = getchar(), ch >= ‘0‘ && ch <= ‘9‘) 22 res = (res << 3) + (res << 1) + ch - 48; 23 if (c == ‘-‘) res = -res; 24 return res; 25 } 26 27 vector <int> edge[maxn * maxn]; 28 int belonging[maxn][maxn], sum = 0; 29 long long keyvalue[maxn * maxn]; 30 int m, n, height[maxn][maxn], value[maxn][maxn]; 31 int lix[maxn * maxn], liy[maxn * maxn], hh, tt; 32 long long f[maxn * maxn], ans = 0; 33 34 int bfs(int tx, int ty) 35 { 36 lix[hh = tt = 1] = tx; 37 liy[hh] = ty; 38 keyvalue[sum] += value[lix[hh]][liy[hh]]; 39 belonging[lix[hh]][liy[hh]] = sum; 40 for (; hh <= tt; hh++) 41 { 42 int x = lix[hh], y = liy[hh]; 43 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) 44 { 45 int nx = x + dx[i], ny = y + dy[i]; 46 if (nx == 0 || nx > m || ny == 0 || ny > n || height[nx][ny] != height[x][y] || belonging[nx][ny] != 0) continue; 47 tt++; 48 lix[tt] = nx; 49 liy[tt] = ny; 50 keyvalue[sum] += value[nx][ny]; 51 belonging[nx][ny] = sum; 52 } 53 } 54 if (tt > 1) keyvalue[sum] *= 2; 55 return 0; 56 } 57 58 long long dp(int x) 59 { 60 if (f[x] != -1) return f[x]; 61 f[x] = 0; 62 for (int j = 0; j < edge[x].size(); j++) 63 f[x] = max(f[x], dp(edge[x][j])); 64 f[x] += keyvalue[x]; 65 return f[x]; 66 } 67 68 int main() 69 { 70 freopen("road.in", "r", stdin); 71 freopen("road.out", "w", stdout); 72 m = read(); 73 n = read(); 74 memset(f, -1, sizeof(f)); 75 for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) 76 { 77 for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) 78 { 79 height[i][j] = read(); 80 } 81 } 82 for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) 83 { 84 for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) 85 { 86 value[i][j] = read(); 87 } 88 } 89 for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) 90 { 91 for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) 92 { 93 if (!belonging[i][j]) 94 { 95 sum++; 96 bfs(i, j); 97 } 98 } 99 } 100 for (int x = 1; x <= m; x++) 101 { 102 for (int y = 1; y <= n; y++) 103 { 104 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) 105 { 106 int nx = x + dx[i], ny = y + dy[i]; 107 if (nx == 0 || nx > m || ny == 0 || ny > n || height[nx][ny] >= height[x][y]) continue; 108 edge[belonging[x][y]].push_back(belonging[nx][ny]); 109 } 110 } 111 } 112 for (int i = 1; i <= sum; i++) 113 ans = max(ans, dp(i)); 114 cout << ans; 115 puts(""); 116 return 0; 117 }
以上是关于[OI - 模拟考] LYOI2018模拟考N的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章