数据结构(C语言版)严蔚敏---二叉树遍历操作二叉树的相关代码
Posted 坚持不懈的大白
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构(C语言版)严蔚敏---二叉树遍历操作二叉树的相关代码相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 二叉树的自下而上、从左到右的层次遍历算法
void LevelTraverse2(BiTree T)
BiTree Queue[100],Stack[100];
// 这里用数组代替队列和栈
int i=0,i1=0,j=0;
Queue[0] = T;
while(i1<=i)
T = Queue[i1++];
Stack[j++] = T;
if(T->left)
Queue[++i] = T->left;
if(T->right)
Queue[++i] = T->right;
while(j>0)
T = Stack[--j];
printf("%c",T->data);
printf("\\n");
【注意】代码中使用数组代替队列和栈。
运行结果如下:
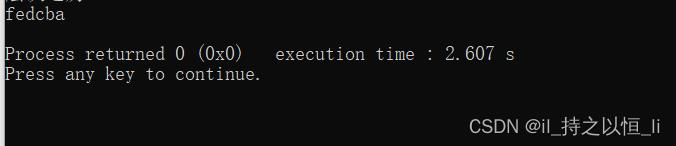
所表示的二叉树为:

使用队列和栈的参考代码为:
void LevelTraverse2(BiTree T)
Queue Q;
Stack S;
BiTree p;
// 定义队列和栈
//初始化队列和栈
if(T)
// 二叉树非空时
InitQueue(Q);
InitStack(S);
EnQueue(Q,T);
// 入队
while(!IsQueueEmpty(Q))
DeQueue(Q,p);
// 出队
Push(S,p);
// 入栈
if(p->lchild)
EnQueue(Q,p->lchild);
// 左孩子非空
if(p->rchild)
EnQueue(Q,p->rchild);
while(!IsStackEmpty(S))
Pop(S,p);
// 出栈
printf("%c",p->data);
思路为:利用原有的层次遍历算法(从上至下、从左至右),出队的同时将各节点入栈,在所有节点入栈后再从栈顶依次访问即可。
2.非递归算法求二叉树的高度
int BitDepth(BiTree T)
if(!T)
return 0;
// 如果二叉树为空
int f = 0,r = 0;
int level = 0,last = 1;
BiTree Queue[100];
Queue[r++] = T;
BiTree p;
while(f<r)
p = Queue[f++];
if(p->left)
Queue[r++] = p->left;
if(p->right)
Queue[r++] = p->right;
if(last == f)
level++;
last = r;
return level;
运行结果(所用的二叉树和上述一样):
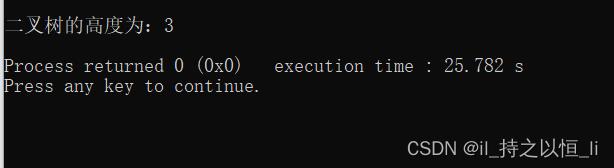
思路:采用层次遍历算法,设置变量level记录当前节点所在的层次,设置变量last指向当前层的最右节点,每次层次遍历出队时与last指针比较,若两者相同,则层数加1,并让last指向下一层的最右节点,直到遍历完成。
3. 线索二叉树的先序遍历
参考代码
main.cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef char ElemType;
typedef struct ThreadNode
ElemType data;
struct ThreadNode *lchild,*rchild;
int ltag,rtag;
ThreadNode,*ThreadBiTree;
// 先序线索二叉树的构建
void PreThread(ThreadBiTree &T,ThreadBiTree &pre)
if(T!=NULL)
if(T->lchild == NULL)
T->lchild = pre;
T->ltag = 1;
if(pre!=NULL && pre->rchild == NULL)
pre->rchild = T;
pre->rtag = 1;
pre = T;
if(T->ltag == 0)
PreThread(T->lchild,pre);
PreThread(T->rchild,pre);
void CreatePreThread(ThreadBiTree &T)
ThreadNode *pre = NULL;
if(T!=NULL)
PreThread(T,pre);
if(pre->rchild == NULL)
pre->rtag = 1;
void CreateBiTree(ThreadBiTree &T)
ElemType c;
c = getchar();
if(c == '#')
T = NULL;
else
T = (ThreadNode *)malloc(sizeof(ThreadNode));
T->data = c;
T->ltag = 0;
T->rtag = 0;
CreateBiTree(T->lchild);
CreateBiTree(T->rchild);
ThreadNode * NextNode(ThreadBiTree T)
if(T->ltag == 0) return T->lchild;
else
return T->rchild;
void PreOrder(ThreadBiTree T)
for(ThreadNode *p = T;p!=NULL;p=NextNode(p))
printf("%c",p->data);
int main()
ThreadBiTree T;
CreateBiTree(T);
CreatePreThread(T);
PreOrder(T);
return 0;
运行结果:
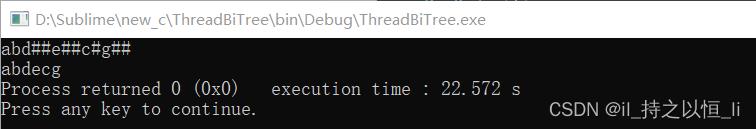
【注】:表示的二叉树为1相同

【注】:表示的二叉树的先序遍历为:abcdf,中序遍历为:cbdaf
4. 求孩子兄弟表示法存储的森林(树)的叶子节点数
思路:其实就是求孩子兄弟表示法表示的二叉树中左孩子指针(左孩子指针表示当前节点的第一个孩子)为空的节点个数。
参考代码:
main.cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef char ElemType;
// 树的孩子兄弟表示法
typedef struct CSNode
ElemType data;
struct CSNode *firstchild,*nextsibling;
CSNode,*CSTree;
void CreateCSTree(CSTree &T)
char ch;
ch = getchar();
if(ch == '#')
T = NULL;
else
T = (CSNode *)malloc(sizeof(CSNode));
T->data = ch;
CreateCSTree(T->firstchild);
CreateCSTree(T->nextsibling);
int getLeafNodes(CSTree T)
if(T == NULL)
return 0;
if(T && T->firstchild == NULL)
return 1 + getLeafNodes(T->nextsibling);
else
return getLeafNodes(T->firstchild) + getLeafNodes(T->nextsibling);
int main()
CSTree T;
CreateCSTree(T);
// 创建树
int num = getLeafNodes(T);
printf("树的叶子节点个数为:%d",num);
return 0;
运行结果:
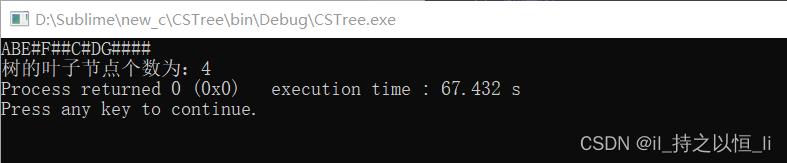
【注】:运行结果表示的是一棵树,不是森林,表示的树如下:
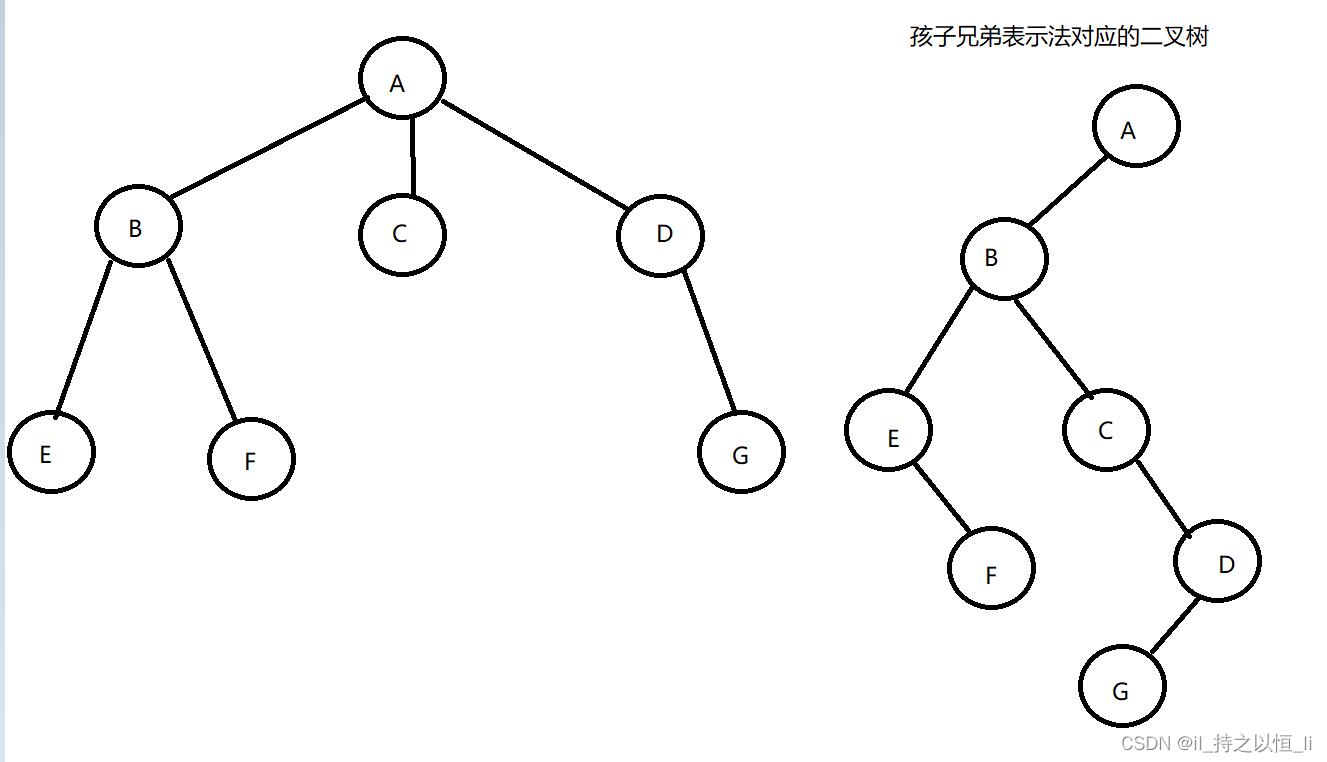

【注】:表示的为森林,表示的森林如下:

以上是关于数据结构(C语言版)严蔚敏---二叉树遍历操作二叉树的相关代码的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章