图解分布式id生成算法SnowFlake
Posted gardenkeeper
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了图解分布式id生成算法SnowFlake相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
分布式id生成算法的有很多种,Twitter的SnowFlake就是其中经典的一种。
概述
SnowFlake算法生成id的结果是一个64bit大小的整数,它的结构如下图:
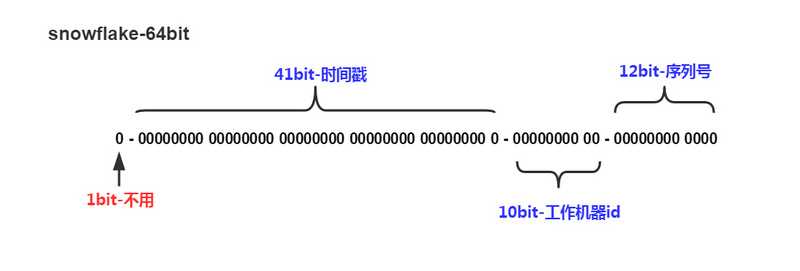
1位,不用。二进制中最高位为1的都是负数,但是我们生成的id一般都使用整数,所以这个最高位固定是0-
41位,用来记录时间戳(毫秒)。- 41位可以表示241?1个数字,
- 如果只用来表示正整数(计算机中正数包含0),可以表示的数值范围是:0 至 241?1,减1是因为可表示的数值范围是从0开始算的,而不是1。
- 也就是说41位可以表示241?1个毫秒的值,转化成单位年则是(241?1)/(1000?60?60?24?365)=69年
-
10位,用来记录工作机器id。- 可以部署在210=1024个节点,包括
5位datacenterId和5位workerId 5位(bit)可以表示的最大正整数是25?1=31,即可以用0、1、2、3、....31这32个数字,来表示不同的datecenterId或workerId
- 可以部署在210=1024个节点,包括
-
12位,序列号,用来记录同毫秒内产生的不同id。12位(bit)可以表示的最大正整数是212?1=4095,即可以用0、1、2、3、....4094这4095个数字,来表示同一机器同一时间截(毫秒)内产生的4095个ID序号
由于在Java中64bit的整数是long类型,所以在Java中SnowFlake算法生成的id就是long来存储的。
SnowFlake可以保证:
- 所有生成的id按时间趋势递增
- 整个分布式系统内不会产生重复id(因为有datacenterId和workerId来做区分)
Talk is cheap, show you the code
以下是Twitter官方原版的,用Scala写的,(我也不懂Scala,当成Java看即可):

1 /** Copyright 2010-2012 Twitter, Inc.*/ 2 package com.twitter.service.snowflake 3 4 import com.twitter.ostrich.stats.Stats 5 import com.twitter.service.snowflake.gen._ 6 import java.util.Random 7 import com.twitter.logging.Logger 8 9 /** 10 * An object that generates IDs. 11 * This is broken into a separate class in case 12 * we ever want to support multiple worker threads 13 * per process 14 */ 15 class IdWorker( 16 val workerId: Long, 17 val datacenterId: Long, 18 private val reporter: Reporter, 19 var sequence: Long = 0L) extends Snowflake.Iface { 20 21 private[this] def genCounter(agent: String) = { 22 Stats.incr("ids_generated") 23 Stats.incr("ids_generated_%s".format(agent)) 24 } 25 private[this] val exceptionCounter = Stats.getCounter("exceptions") 26 private[this] val log = Logger.get 27 private[this] val rand = new Random 28 29 val twepoch = 1288834974657L 30 31 private[this] val workerIdBits = 5L 32 private[this] val datacenterIdBits = 5L 33 private[this] val maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits) 34 private[this] val maxDatacenterId = -1L ^ (-1L << datacenterIdBits) 35 private[this] val sequenceBits = 12L 36 37 private[this] val workerIdShift = sequenceBits 38 private[this] val datacenterIdShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits 39 private[this] val timestampLeftShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits + datacenterIdBits 40 private[this] val sequenceMask = -1L ^ (-1L << sequenceBits) 41 42 private[this] var lastTimestamp = -1L 43 44 // sanity check for workerId 45 if (workerId > maxWorkerId || workerId < 0) { 46 exceptionCounter.incr(1) 47 throw new IllegalArgumentException("worker Id can‘t be greater than %d or less than 0".format(maxWorkerId)) 48 } 49 50 if (datacenterId > maxDatacenterId || datacenterId < 0) { 51 exceptionCounter.incr(1) 52 throw new IllegalArgumentException("datacenter Id can‘t be greater than %d or less than 0".format(maxDatacenterId)) 53 } 54 55 log.info("worker starting. timestamp left shift %d, datacenter id bits %d, worker id bits %d, sequence bits %d, workerid %d", 56 timestampLeftShift, datacenterIdBits, workerIdBits, sequenceBits, workerId) 57 58 def get_id(useragent: String): Long = { 59 if (!validUseragent(useragent)) { 60 exceptionCounter.incr(1) 61 throw new InvalidUserAgentError 62 } 63 64 val id = nextId() 65 genCounter(useragent) 66 67 reporter.report(new AuditLogEntry(id, useragent, rand.nextLong)) 68 id 69 } 70 71 def get_worker_id(): Long = workerId 72 def get_datacenter_id(): Long = datacenterId 73 def get_timestamp() = System.currentTimeMillis 74 75 protected[snowflake] def nextId(): Long = synchronized { 76 var timestamp = timeGen() 77 78 if (timestamp < lastTimestamp) { 79 exceptionCounter.incr(1) 80 log.error("clock is moving backwards. Rejecting requests until %d.", lastTimestamp); 81 throw new InvalidSystemClock("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id for %d milliseconds".format( 82 lastTimestamp - timestamp)) 83 } 84 85 if (lastTimestamp == timestamp) { 86 sequence = (sequence + 1) & sequenceMask 87 if (sequence == 0) { 88 timestamp = tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp) 89 } 90 } else { 91 sequence = 0 92 } 93 94 lastTimestamp = timestamp 95 ((timestamp - twepoch) << timestampLeftShift) | 96 (datacenterId << datacenterIdShift) | 97 (workerId << workerIdShift) | 98 sequence 99 } 100 101 protected def tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp: Long): Long = { 102 var timestamp = timeGen() 103 while (timestamp <= lastTimestamp) { 104 timestamp = timeGen() 105 } 106 timestamp 107 } 108 109 protected def timeGen(): Long = System.currentTimeMillis() 110 111 val AgentParser = """([a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z-0-9]*)""".r 112 113 def validUseragent(useragent: String): Boolean = useragent match { 114 case AgentParser(_) => true 115 case _ => false 116 } 117 }
Scala是一门可以编译成字节码的语言,简单理解是在Java语法基础上加上了很多语法糖,例如不用每条语句后写分号,可以使用动态类型等等。抱着试一试的心态,我把Scala版的代码“翻译”成Java版本的,对scala代码改动的地方如下:

1 /** Copyright 2010-2012 Twitter, Inc.*/ 2 package com.twitter.service.snowflake 3 4 import com.twitter.ostrich.stats.Stats 5 import com.twitter.service.snowflake.gen._ 6 import java.util.Random 7 import com.twitter.logging.Logger 8 9 /** 10 * An object that generates IDs. 11 * This is broken into a separate class in case 12 * we ever want to support multiple worker threads 13 * per process 14 */ 15 class IdWorker( // | 16 val workerId: Long, // | 17 val datacenterId: Long, // |<--这部分改成Java的构造函数形式 18 private val reporter: Reporter,//日志相关,删 // | 19 var sequence: Long = 0L) // | 20 extends Snowflake.Iface { //接口找不到,删 // | 21 22 private[this] def genCounter(agent: String) = { // | 23 Stats.incr("ids_generated") // | 24 Stats.incr("ids_generated_%s".format(agent)) // |<--错误、日志处理相关,删 25 } // | 26 private[this] val exceptionCounter = Stats.getCounter("exceptions") // | 27 private[this] val log = Logger.get // | 28 private[this] val rand = new Random // | 29 30 val twepoch = 1288834974657L 31 32 private[this] val workerIdBits = 5L 33 private[this] val datacenterIdBits = 5L 34 private[this] val maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits) 35 private[this] val maxDatacenterId = -1L ^ (-1L << datacenterIdBits) 36 private[this] val sequenceBits = 12L 37 38 private[this] val workerIdShift = sequenceBits 39 private[this] val datacenterIdShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits 40 private[this] val timestampLeftShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits + datacenterIdBits 41 private[this] val sequenceMask = -1L ^ (-1L << sequenceBits) 42 43 private[this] var lastTimestamp = -1L 44 45 //----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// 46 // sanity check for workerId // 47 if (workerId > maxWorkerId || workerId < 0) { // 48 exceptionCounter.incr(1) //<--错误处理相关,删 // 49 throw new IllegalArgumentException("worker Id can‘t be greater than %d or less than 0".format(maxWorkerId)) //这 50 // |-->改成:throw new IllegalArgumentException //部 51 // (String.format("worker Id can‘t be greater than %d or less than 0",maxWorkerId)) //分 52 } //放 53 //到 54 if (datacenterId > maxDatacenterId || datacenterId < 0) { //构 55 exceptionCounter.incr(1) //<--错误处理相关,删 //造 56 throw new IllegalArgumentException("datacenter Id can‘t be greater than %d or less than 0".format(maxDatacenterId)) //函 57 // |-->改成:throw new IllegalArgumentException //数 58 // (String.format("datacenter Id can‘t be greater than %d or less than 0",maxDatacenterId)) //中 59 } // 60 // 61 log.info("worker starting. timestamp left shift %d, datacenter id bits %d, worker id bits %d, sequence bits %d, workerid %d", // 62 timestampLeftShift, datacenterIdBits, workerIdBits, sequenceBits, workerId) // 63 // |-->改成:System.out.printf("worker...%d...",timestampLeftShift,...); // 64 //----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// 65 66 //-------------------------------------------------------------------// 67 //这个函数删除错误处理相关的代码后,剩下一行代码:val id = nextId() // 68 //所以我们直接调用nextId()函数可以了,所以在“翻译”时可以删除这个函数 // 69 def get_id(useragent: String): Long = { // 70 if (!validUseragent(useragent)) { // 71 exceptionCounter.incr(1) // 72 throw new InvalidUserAgentError //删 73 } //除 74 // 75 val id = nextId() // 76 genCounter(useragent) // 77 // 78 reporter.report(new AuditLogEntry(id, useragent, rand.nextLong)) // 79 id // 80 } // 81 //-------------------------------------------------------------------// 82 83 def get_worker_id(): Long = workerId // | 84 def get_datacenter_id(): Long = datacenterId // |<--改成Java函数 85 def get_timestamp() = System.currentTimeMillis // | 86 87 protected[snowflake] def nextId(): Long = synchronized { // 改成Java函数 88 var timestamp = timeGen() 89 90 if (timestamp < lastTimestamp) { 91 exceptionCounter.incr(1) // 错误处理相关,删 92 log.error("clock is moving backwards. Rejecting requests until %d.", lastTimestamp); // 改成System.err.printf(...) 93 throw new InvalidSystemClock("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id for %d milliseconds".format( 94 lastTimestamp - timestamp)) // 改成RumTimeException 95 } 96 97 if (lastTimestamp == timestamp) { 98 sequence = (sequence + 1) & sequenceMask 99 if (sequence == 0) { 100 timestamp = tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp) 101 } 102 } else { 103 sequence = 0 104 } 105 106 lastTimestamp = timestamp 107 ((timestamp - twepoch) << timestampLeftShift) | // |<--加上关键字return 108 (datacenterId << datacenterIdShift) | // | 109 (workerId << workerIdShift) | // | 110 sequence // | 111 } 112 113 protected def tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp: Long): Long = { // 改成Java函数 114 var timestamp = timeGen() 115 while (timestamp <= lastTimestamp) { 116 timestamp = timeGen() 117 } 118 timestamp // 加上关键字return 119 } 120 121 protected def timeGen(): Long = System.currentTimeMillis() // 改成Java函数 122 123 val AgentParser = """([a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z-0-9]*)""".r // | 124 // | 125 def validUseragent(useragent: String): Boolean = useragent match { // |<--日志相关,删 126 case AgentParser(_) => true // | 127 case _ => false // | 128 } // | 129 }
改出来的Java版:

1 public class IdWorker{ 2 3 private long workerId; 4 private long datacenterId; 5 private long sequence; 6 7 public IdWorker(long workerId, long datacenterId, long sequence){ 8 // sanity check for workerId 9 if (workerId > maxWorkerId || workerId < 0) { 10 throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("worker Id can‘t be greater than %d or less than 0",maxWorkerId)); 11 } 12 if (datacenterId > maxDatacenterId || datacenterId < 0) { 13 throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("datacenter Id can‘t be greater than %d or less than 0",maxDatacenterId)); 14 } 15 System.out.printf("worker starting. timestamp left shift %d, datacenter id bits %d, worker id bits %d, sequence bits %d, workerid %d", 16 timestampLeftShift, datacenterIdBits, workerIdBits, sequenceBits, workerId); 17 18 this.workerId = workerId; 19 this.datacenterId = datacenterId; 20 this.sequence = sequence; 21 } 22 23 private long twepoch = 1288834974657L; 24 25 private long workerIdBits = 5L; 26 private long datacenterIdBits = 5L; 27 private long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits); 28 private long maxDatacenterId = -1L ^ (-1L << datacenterIdBits); 29 private long sequenceBits = 12L; 30 31 private long workerIdShift = sequenceBits; 32 private long datacenterIdShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits; 33 private long timestampLeftShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits + datacenterIdBits; 34 private long sequenceMask = -1L ^ (-1L << sequenceBits); 35 36 private long lastTimestamp = -1L; 37 38 public long getWorkerId(){ 39 return workerId; 40 } 41 42 public long getDatacenterId(){ 43 return datacenterId; 44 } 45 46 public long getTimestamp(){ 47 return System.currentTimeMillis(); 48 } 49 50 public synchronized long nextId() { 51 long timestamp = timeGen(); 52 53 if (timestamp < lastTimestamp) { 54 System.err.printf("clock is moving backwards. Rejecting requests until %d.", lastTimestamp); 55 throw new RuntimeException(String.format("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id for %d milliseconds", 56 lastTimestamp - timestamp)); 57 } 58 59 if (lastTimestamp == timestamp) { 60 sequence = (sequence + 1) & sequenceMask; 61 if (sequence == 0) { 62 timestamp = tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp); 63 } 64 } else { 65 sequence = 0; 66 } 67 68 lastTimestamp = timestamp; 69 return ((timestamp - twepoch) << timestampLeftShift) | 70 (datacenterId << datacenterIdShift) | 71 (workerId << workerIdShift) | 72 sequence; 73 } 74 75 private long tilNextMillis(long lastTimestamp) { 76 long timestamp = timeGen(); 77 while (timestamp <= lastTimestamp) { 78 timestamp = timeGen(); 79 } 80 return timestamp; 81 } 82 83 private long timeGen(){ 84 return System.currentTimeMillis(); 85 } 86 87 //---------------测试--------------- 88 public static void main(String[] args) { 89 IdWorker worker = new IdWorker(1,1,1); 90 for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) { 91 System.out.println(worker.nextId()); 92 } 93 } 94 95 }
代码理解
上面的代码中,有部分位运算的代码,如:
1 sequence = (sequence + 1) & sequenceMask; 2 3 private long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits); 4 5 return ((timestamp - twepoch) << timestampLeftShift) | 6 (datacenterId << datacenterIdShift) | 7 (workerId << workerIdShift) | 8 sequence;
为了能更好理解,我对相关知识研究了一下。
负数的二进制表示
在计算机中,负数的二进制是用补码来表示的。
假设我是用Java中的int类型来存储数字的,
int类型的大小是32个二进制位(bit),即4个字节(byte)。(1 byte = 8 bit)
那么十进制数字3在二进制中的表示应该是这样的:
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000011 // 3的二进制表示,就是原码
那数字-3在二进制中应该如何表示?
我们可以反过来想想,因为-3+3=0,
在二进制运算中把-3的二进制看成未知数x来求解,
求解算式的二进制表示如下:
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000011 //3,原码 + xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx //-3,补码 ----------------------------------------------- 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000
反推x的值,3的二进制加上什么值才使结果变成 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000?:
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000011 //3,原码 + 11111111 11111111 11111111 11111101 //-3,补码 ----------------------------------------------- 1 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000
反推的思路是3的二进制数从最低位开始逐位加1,使溢出的1不断向高位溢出,直到溢出到第33位。然后由于int类型最多只能保存32个二进制位,所以最高位的1溢出了,剩下的32位就成了(十进制的)0。
补码的意义就是可以拿补码和原码(3的二进制)相加,最终加出一个“溢出的0”
以上是理解的过程,实际中记住公式就很容易算出来:
- 补码 = 反码 + 1
- 补码 = (原码 - 1)再取反码
因此-1的二进制应该这样算:
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001 //原码:1的二进制 11111111 11111111 11111111 11111110 //取反码:1的二进制的反码 11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 //加1:-1的二进制表示(补码)
用位运算计算n个bit能表示的最大数值
比如这样一行代码:
1 private long workerIdBits = 5L; 2 private long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits);
上面代码换成这样看方便一点:
1 long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << 5L)
咋一看真的看不准哪个部分先计算,于是查了一下Java运算符的优先级表: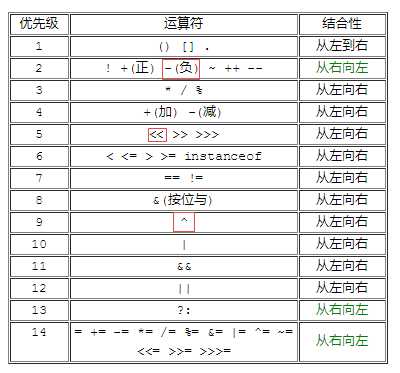
所以上面那行代码中,运行顺序是:
- -1 左移 5,得结果a
- -1 异或 a
long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << 5L)的二进制运算过程如下:
-1 左移 5,得结果a :
11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 //-1的二进制表示(补码) 11111 11111111 11111111 11111111 11100000 //高位溢出的不要,低位补0 11111111 11111111 11111111 11100000 //结果a
-1 异或 a :
11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 //-1的二进制表示(补码) ^ 11111111 11111111 11111111 11100000 //两个操作数的位中,相同则为0,不同则为1 --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 00000000 00000000 00000000 00011111 //最终结果31
最终结果是31,二进制 00000000 00000000 00000000 00011111 转十进制可以这么算:
那既然现在知道算出来 long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << 5L) 中的 maxWorkerId = 31,有什么含义?为什么要用左移5来算?如果你看过概述部分,请找到这段内容看看:
5位(bit)可以表示的最大正整数是25?1=31,即可以用0、1、2、3、....31这32个数字,来表示不同的datecenterId或workerId-1L ^ (-1L << 5L)结果是31,25?1的结果也是31,所以在代码中,-1L ^ (-1L << 5L)的写法是利用位运算计算出5位能表示的最大正整数是多少
用mask防止溢出
有一段有趣的代码:
sequence = (sequence + 1) & sequenceMask;
分别用不同的值测试一下,你就知道它怎么有趣了:
long seqMask = -1L ^ (-1L << 12L); //计算12位能耐存储的最大正整数,相当于:2^12-1 = 4095 System.out.println("seqMask: "+seqMask); System.out.println(1L & seqMask); System.out.println(2L & seqMask); System.out.println(3L & seqMask); System.out.println(4L & seqMask); System.out.println(4095L & seqMask); System.out.println(4096L & seqMask); System.out.println(4097L & seqMask); System.out.println(4098L & seqMask); /** seqMask: 4095 1 2 3 4 4095 0 1 2 */
这段代码通过位与运算保证计算的结果范围始终是 0-4095 !
用位运算汇总结果
还有另外一段诡异的代码:
return ((timestamp - twepoch) << timestampLeftShift) | (datacenterId << datacenterIdShift) | (workerId << workerIdShift) | sequence;
为了弄清楚这段代码,
首先 需要计算一下相关的值:
private long twepoch = 1288834974657L; //起始时间戳,用于用当前时间戳减去这个时间戳,算出偏移量 private long workerIdBits = 5L; //workerId占用的位数:5 private long datacenterIdBits = 5L; //datacenterId占用的位数:5 private long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits); // workerId可以使用的最大数值:31 private long maxDatacenterId = -1L ^ (-1L << datacenterIdBits); // datacenterId可以使用的最大数值:31 private long sequenceBits = 12L;//序列号占用的位数:12 private long workerIdShift = sequenceBits; // 12 private long datacenterIdShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits; // 12+5 = 17 private long timestampLeftShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits + datacenterIdBits; // 12+5+5 = 22 private long sequenceMask = -1L ^ (-1L << sequenceBits);//4095 private long lastTimestamp = -1L;
其次 写个测试,把参数都写死,并运行打印信息,方便后面来核对计算结果:
//---------------测试--------------- public static void main(String[] args) { long timestamp = 1505914988849L; long twepoch = 1288834974657L; long datacenterId = 17L; long workerId = 25L; long sequence = 0L; System.out.printf(" timestamp: %d ",timestamp); System.out.printf("twepoch: %d ",twepoch); System.out.printf("datacenterId: %d ",datacenterId); System.out.printf("workerId: %d ",workerId); System.out.printf("sequence: %d ",sequence); System.out.println(); System.out.printf("(timestamp - twepoch): %d ",(timestamp - twepoch)); System.out.printf("((timestamp - twepoch) << 22L): %d ",((timestamp - twepoch) << 22L)); System.out.printf("(datacenterId << 17L): %d " ,(datacenterId << 17L)); System.out.printf("(workerId << 12L): %d ",(workerId << 12L)); System.out.printf("sequence: %d ",sequence); long result = ((timestamp - twepoch) << 22L) | (datacenterId << 17L) | (workerId << 12L) | sequence; System.out.println(result); } /** 打印信息: timestamp: 1505914988849 twepoch: 1288834974657 datacenterId: 17 workerId: 25 sequence: 0 (timestamp - twepoch): 217080014192 ((timestamp - twepoch) << 22L): 910499571845562368 (datacenterId << 17L): 2228224 (workerId << 12L): 102400 sequence: 0 910499571847892992 */
代入位移的值得之后,就是这样:
return ((timestamp - 1288834974657) << 22) | (datacenterId << 17) | (workerId << 12) | sequence;
对于尚未知道的值,我们可以先看看概述 中对SnowFlake结构的解释,再代入在合法范围的值(windows系统可以用计算器方便计算这些值的二进制),来了解计算的过程。
当然,由于我的测试代码已经把这些值写死了,那直接用这些值来手工验证计算结果即可:
long timestamp = 1505914988849L; long twepoch = 1288834974657L; long datacenterId = 17L; long workerId = 25L; long sequence = 0L;
设:timestamp = 1505914988849,twepoch = 1288834974657 1505914988849 - 1288834974657 = 217080014192 (timestamp相对于起始时间的毫秒偏移量),其(a)二进制左移22位计算过程如下: |<--这里开始左右22位 ? 00000000 00000000 000000|00 00110010 10001010 11111010 00100101 01110000 // a = 217080014192 00001100 10100010 10111110 10001001 01011100 00|000000 00000000 00000000 // a左移22位后的值(la) |<--这里后面的位补0
设:datacenterId = 17,其(b)二进制左移17位计算过程如下: |<--这里开始左移17位 00000000 00000000 0|0000000 ?00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00010001 // b = 17 0000000?0 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 0010001|0 00000000 00000000 // b左移17位后的值(lb) |<--这里后面的位补0
设:workerId = 25,其(c)二进制左移12位计算过程如下: |<--这里开始左移12位 ?00000000 0000|0000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00011001? // c = 25 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001 1001|0000 00000000? // c左移12位后的值(lc) |<--这里后面的位补0
设:sequence = 0,其二进制如下: 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 0000?0000 00000000? // sequence = 0 现在知道了每个部分左移后的值(la,lb,lc),代码可以简化成下面这样去理解: return ((timestamp - 1288834974657) << 22) | (datacenterId << 17) | (workerId << 12) | sequence; ----------------------------- | |简化 |/ ----------------------------- return (la) | (lb) | (lc) | sequence;
上面的管道符号|在Java中也是一个位运算符。其含义是:x的第n位和y的第n位 只要有一个是1,则结果的第n位也为1,否则为0,因此,我们对四个数的位或运算如下:
1 | 41 | 5 | 5 | 12 0|0001100 10100010 10111110 10001001 01011100 00|00000|0 0000|0000 00000000 //la 0|000000?0 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00|10001|0 0000|0000 00000000 //lb 0|0000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00|00000|1 1001|0000 00000000 //lc or 0|0000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00|00000|0 0000|?0000 00000000? //sequence ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 0|0001100 10100010 10111110 10001001 01011100 00|10001|1 1001|?0000 00000000? //结果:910499571847892992
结果计算过程:
1) 从至左列出1出现的下标(从0开始算):
0000 1 1 00 1 0 1 000 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 000 1 00 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0000 1 000 1 1 1 00 1? 0000 0000 0000 59 58 55 53 49 47 45 44 43 42 41 39 35 32 30 28 27 26 21 17 16 15 12
2) 各个下标作为2的幂数来计算,并相加:
2^59+2^58+2^55+2^53+2^49+2^47+2^45+2^44+2^43+2^42+2^41+2^39+2^35+2^32+2^30+2^28+2^27+2^26+2^21+2^17+2^16+2^15+2^12
2^59} : 576460752303423488 2^58} : 288230376151711744 2^55} : 36028797018963968 2^53} : 9007199254740992 2^49} : 562949953421312 2^47} : 140737488355328 2^45} : 35184372088832 2^44} : 17592186044416 2^43} : 8796093022208 2^42} : 4398046511104 2^41} : 2199023255552 2^39} : 549755813888 2^35} : 34359738368 2^32} : 4294967296 2^30} : 1073741824 2^28} : 268435456 2^27} : 134217728 2^26} : 67108864 2^21} : 2097152 2^17} : 131072 2^16} : 65536 2^15} : 32768 + 2^12} : 4096 ---------------------------------------- 910499571847892992
计算截图: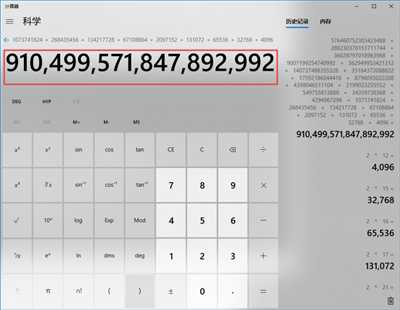
跟测试程序打印出来的结果一样,手工验证完毕!
观察
1 | 41 | 5 | 5 | 12 0|0001100 10100010 10111110 10001001 01011100 00| | | //la 0| |10001| | //lb 0| | |1 1001| //lc or 0| | | |?0000 00000000? //sequence ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 0|0001100 10100010 10111110 10001001 01011100 00|10001|1 1001|?0000 00000000? //结果:910499571847892992
上面的64位我按1、41、5、5、12的位数截开了,方便观察。
-
纵向观察发现:- 在41位那一段,除了la一行有值,其它行(lb、lc、sequence)都是0,(我爸其它)
- 在左起第一个5位那一段,除了lb一行有值,其它行都是0
- 在左起第二个5位那一段,除了lc一行有值,其它行都是0
- 按照这规律,如果sequence是0以外的其它值,12位那段也会有值的,其它行都是0
-
横向观察发现:- 在la行,由于左移了5+5+12位,5、5、12这三段都补0了,所以la行除了41那段外,其它肯定都是0
- 同理,lb、lc、sequnece行也以此类推
- 正因为左移的操作,使四个不同的值移到了SnowFlake理论上相应的位置,然后四行做
位或运算(只要有1结果就是1),就把4段的二进制数合并成一个二进制数。
结论:
所以,在这段代码中
return ((timestamp - 1288834974657) << 22) | (datacenterId << 17) | (workerId << 12) | sequence;
左移运算是为了将数值移动到对应的段(41、5、5,12那段因为本来就在最右,因此不用左移)。
然后对每个左移后的值(la、lb、lc、sequence)做位或运算,是为了把各个短的数据合并起来,合并成一个二进制数。
最后转换成10进制,就是最终生成的id
扩展
在理解了这个算法之后,其实还有一些扩展的事情可以做:
- 根据自己业务修改每个位段存储的信息。算法是通用的,可以根据自己需求适当调整每段的大小以及存储的信息。
- 解密id,由于id的每段都保存了特定的信息,所以拿到一个id,应该可以尝试反推出原始的每个段的信息。反推出的信息可以帮助我们分析。比如作为订单,可以知道该订单的生成日期,负责处理的数据中心等等。
阅读原文 https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000011282426
以上是关于图解分布式id生成算法SnowFlake的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
