Kafka consumer代码研究及核心逻辑分析
Posted benfly
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Kafka consumer代码研究及核心逻辑分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Kafka Consumer API是客户端的接口,封装了消息的接收,心跳的检测,consumer的rebalance等,此分析的代码基于kafka-clients-0.10.0.1 java版本
KafkaConsumer.pollOnce 是轮询的入口,完成一次轮询动作,包括consumer相关的所有逻辑,其逻辑过程如下:
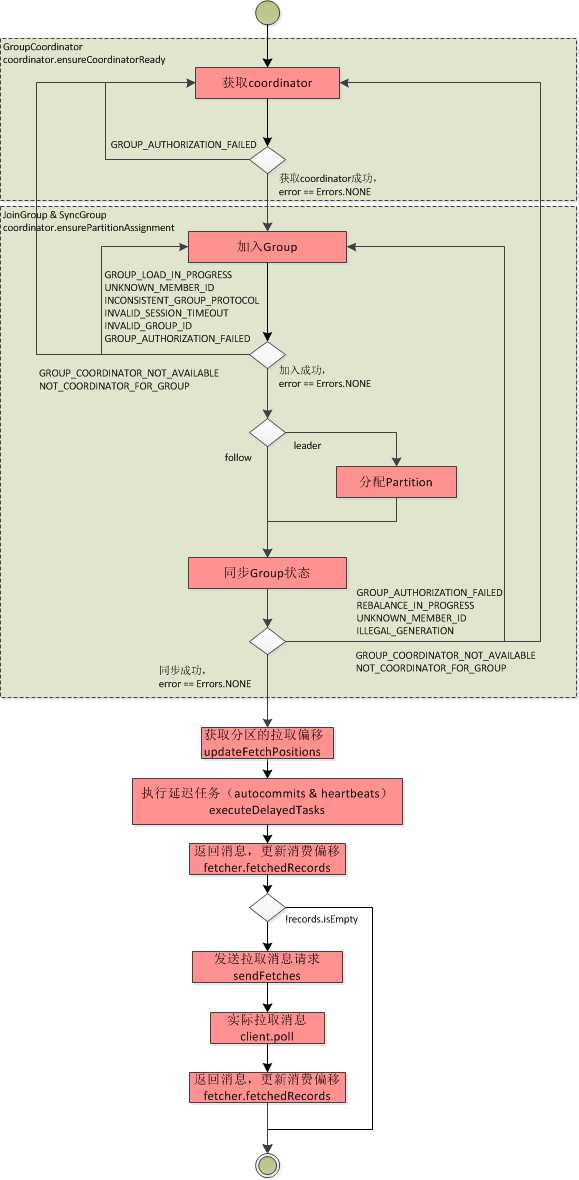
进一步,将相关的过程展开,如下图所示:
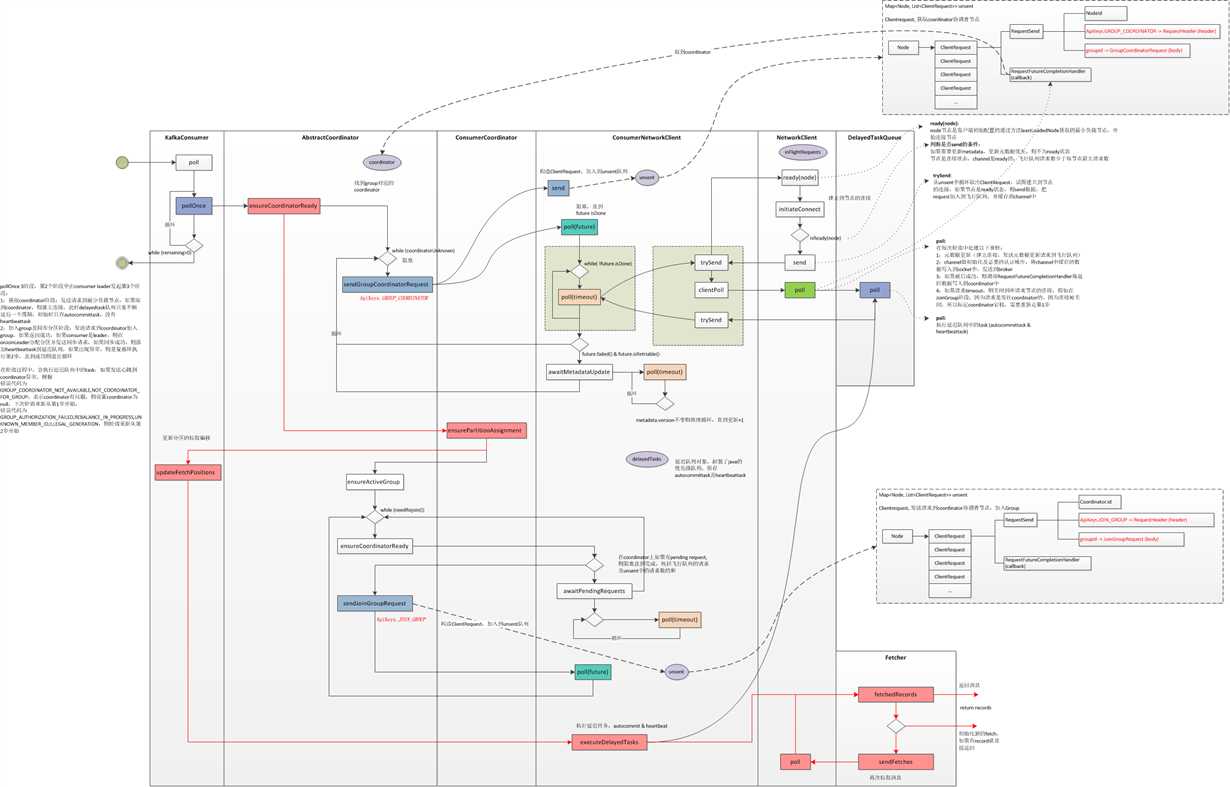
上图中红色线框表示pollOnce在一次轮询中的活动过程,其右边是相应展开的活动过程,在pollOnce是consumer的关键方法,所有相关的逻辑都在这方法中实现,包括消息的拉取,心跳检测,consumer的再平衡,偏移的自动提交及更新操作等,下面逐个分析
1:获取coordinator:ensureCoordinatorReady,请求为GroupCoordinatorRequest
对于consumer所在的group(不同的group以groupid区分),需要从所有的broker中找到一个coordinator,用户本地初始配置一个缺省的broker列表,从中找到一个最近最少负载的节点,构造请求GroupCoordinatorRequest后,放到ConsumerNetworkClient的unsent队列中,然后阻塞调用ConsumerNetworkClient的poll(future)方法,直到future isDone
private RequestFuture<Void> sendGroupCoordinatorRequest() { Node node = this.client.leastLoadedNode(); //找到最少负载节点 ...... GroupCoordinatorRequest metadataRequest = new GroupCoordinatorRequest(this.groupId); return client.send(node, ApiKeys.GROUP_COORDINATOR, metadataRequest) .compose(new RequestFutureAdapter<ClientResponse, Void>() { @Override public void onSuccess(ClientResponse response, RequestFuture<Void> future) { handleGroupMetadataResponse(response, future); } }); } } private void handleGroupMetadataResponse(ClientResponse resp, RequestFuture<Void> future) { ...... client.tryConnect(coordinator); //连接coordinator // start sending heartbeats only if we have a valid generation if (generation > 0) heartbeatTask.reset(); //如果generation >0,说明是重新连接coordinator后,则设置心跳延迟任务 future.complete(null); ...... }
在kafka 0.9 以前,consumer group是依赖ZK来维护的,但由于有“herd”及“split brain”问题,后重新设计,在新的版本中由broker集群中选择一个节点作为coordinator,以解决group中各个consumer的同步,如Rebalance,Failover,Partition Assignment,Offset Commit
参考Kafka consumer 设计重构原文:
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/KAFKA/Consumer+Client+Re-Design
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/KAFKA/Kafka+Client-side+Assignment+Proposal
2:加入group,分配partition并同步group 状态及负载均衡:ensurePartitionAssignment,请求为JoinGroupRequest 及SyncGroupRequest
获取coordinator后,调用ensurePartitionAssignment,在内部又继续调用ensureActiveGroup方法,这个方法的主要功能就是Join Group 及Sync Group。在向coordinator准备发送JoinGroup请求前,如果在coordinator节点上还有未发出的请求(unsent及inflight队列),则需要阻塞等所有请求完成后再继续,sendJoinGroupRequest构造好JoinGroupRequest并放到unsent队列中,其中传入了回调类,用于处理响应
private RequestFuture<ByteBuffer> sendJoinGroupRequest() { if (coordinatorUnknown()) return RequestFuture.coordinatorNotAvailable(); // send a join group request to the coordinator log.info("(Re-)joining group {}", groupId); JoinGroupRequest request = new JoinGroupRequest( groupId, this.sessionTimeoutMs, this.memberId, protocolType(), metadata()); log.debug("Sending JoinGroup ({}) to coordinator {}", request, this.coordinator); return client.send(coordinator, ApiKeys.JOIN_GROUP, request) .compose(new JoinGroupResponseHandler()); }
在后面的client.poll(future)中阻塞调用,直到coordinator返回结果,回调处理函数JoinGroupResponseHandler.handle,如果返回结果错误码为Errors.NONE,则表明成功加入到group中,如果返回结果表示consumer是leader,则需要在onJoinLeader中继续,由leader分配分区信息,并告诉coordinator同步给其它的follow。而如果是follow,则在onJoinFollower中发送同步消息
private class JoinGroupResponseHandler extends CoordinatorResponseHandler<JoinGroupResponse, ByteBuffer> { @Override public void handle(JoinGroupResponse joinResponse, RequestFuture<ByteBuffer> future) { ......if (error == Errors.NONE) { ...... if (joinResponse.isLeader()) { onJoinLeader(joinResponse).chain(future); } else { onJoinFollower().chain(future); } } else if (error == Errors.GROUP_LOAD_IN_PROGRESS) { ......
...... } } private RequestFuture<ByteBuffer> onJoinFollower() { SyncGroupRequest request = new SyncGroupRequest(groupId, ...); //同步组请求
return sendSyncGroupRequest(request); } private RequestFuture<ByteBuffer> onJoinLeader(JoinGroupResponse joinResponse) { try { // perform the leader synchronization and send back the assignment for the group Map<String, ByteBuffer> groupAssignment = performAssignment(...); //leader分配分区 SyncGroupRequest request = new SyncGroupRequest(...); //leader同步组 return sendSyncGroupRequest(request); } catch (RuntimeException e) { return RequestFuture.failure(e); } }
在onJoinLeader中,调用performAssignment方法,根据broker配置的group protocol(如range,roundrobin)来分配group member所消费的TopicPartition,然后发送同步请求SyncGroupRequest到coordinator,而其它的group member则为follow,也同理发送请求,从coordinator获取所对应的分配状态,在完成JoinGroup和SyncGroup后,在onJoinComplete更新partition分配状态
3:更新拉取偏移:updateFetchPositions
参见 https://www.cnblogs.com/benfly/p/9830784.html 偏移管理
4:执行延迟任务:executeDelayedTasks
延迟任务包括AutoCommitTask和HeartbeatTask,延迟任务是每隔一个周期执行的任务,自动提交任务的周期是auto.commit.interval.ms,心跳任务的周期是 heartbeat.interval.ms,延迟任务保存在延迟队列中的DelayedTaskQueue,在到达指定周期后,执行延迟任务,比如提交偏移或心跳检测
自动提交任务和心跳任务实现了延迟任务接口,并实现了任务运行方法run
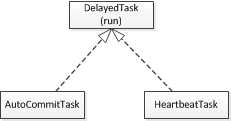
延迟队列中的task,会在每次poll时调用其中的run方法,执行具体任务
- 自动提交任务
在KafkaConsumer实例化时,会创建消费者协调器对象,
private KafkaConsumer(ConsumerConfig config, Deserializer<K> keyDeserializer, Deserializer<V> valueDeserializer) { try { this.coordinator = new ConsumerCoordinator(this.client, //创建消费者协调器 ....... } }
在消费者协调器ConsumerCoordinator中,有一个自动提交任务成员
public final class ConsumerCoordinator extends AbstractCoordinator { private final AutoCommitTask autoCommitTask; //自动提交任务对象 }
而在消费者协调器对象的创建过程中,如果默认配置为自动提交,则初始化自动提交任务并设置一个提交任务
public ConsumerCoordinator(ConsumerNetworkClient client, .......) { ....... if (autoCommitEnabled) { //如果配置为自动提交任务,则初始化自动提交任务对象 this.autoCommitTask = new AutoCommitTask(autoCommitIntervalMs); this.autoCommitTask.reschedule(); //在延迟队列中添加任务,设定延迟执行时间 } else { this.autoCommitTask = null; } ...... }
public class ConsumerNetworkClient implements Closeable { private final DelayedTaskQueue delayedTasks = new DelayedTaskQueue(); //延迟队列,保存了自动提交任务项及心跳任务项 public void schedule(DelayedTask task, long at) { delayedTasks.add(task, at); } }
- 心跳检测任务
在消费者JoinGroup成功后,会开始设置心跳任务
public void ensureActiveGroup() { ....... while (needRejoin()) { ensureCoordinatorReady(); ...... RequestFuture<ByteBuffer> future = sendJoinGroupRequest(); //申请加入Group future.addListener(new RequestFutureListener<ByteBuffer>() { @Override public void onSuccess(ByteBuffer value) { // handle join completion in the callback so that the callback will be invoked // even if the consumer is woken up before finishing the rebalance onJoinComplete(generation, memberId, protocol, value); needsJoinPrepare = true; heartbeatTask.reset(); //加入Group成功,设置心跳任务 } @Override public void onFailure(RuntimeException e) { // we handle failures below after the request finishes. if the join completes // after having been woken up, the exception is ignored and we will rejoin } }); ...... } }
5:消息的拉取及消费
参见 https://www.cnblogs.com/benfly/p/9830784.html 消息的拉取及消费
以上是关于Kafka consumer代码研究及核心逻辑分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章