MIT-6.828 Lab 2实验报告
Posted gatsby123
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了MIT-6.828 Lab 2实验报告相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
MIT-6.828 Lab 2: Memory Management实验报告
tags:mit-6.828 os
概述
本文主要介绍lab2,讲的是操作系统内存管理,从内容上分为三部分:
- 第一部分讲的是物理内存管理,要进行内存管理首先需要知道哪些物理内存是空闲的,哪些是被使用的。还需要实现一些函数对这些物理内存进行管理。
- 第二部分讲的是虚拟内存。一个虚拟地址如何被映射到物理地址,将实现一些函数来操作页目录和页表从而达到映射的目的。
- 第三部分讲的是内核的地址空间。将结合第一部分和第二部分的成果,来对内核地址空间进行映射。
Part 1: Physical Page Management
通过lab1可以总结出如下的物理内存分布图:
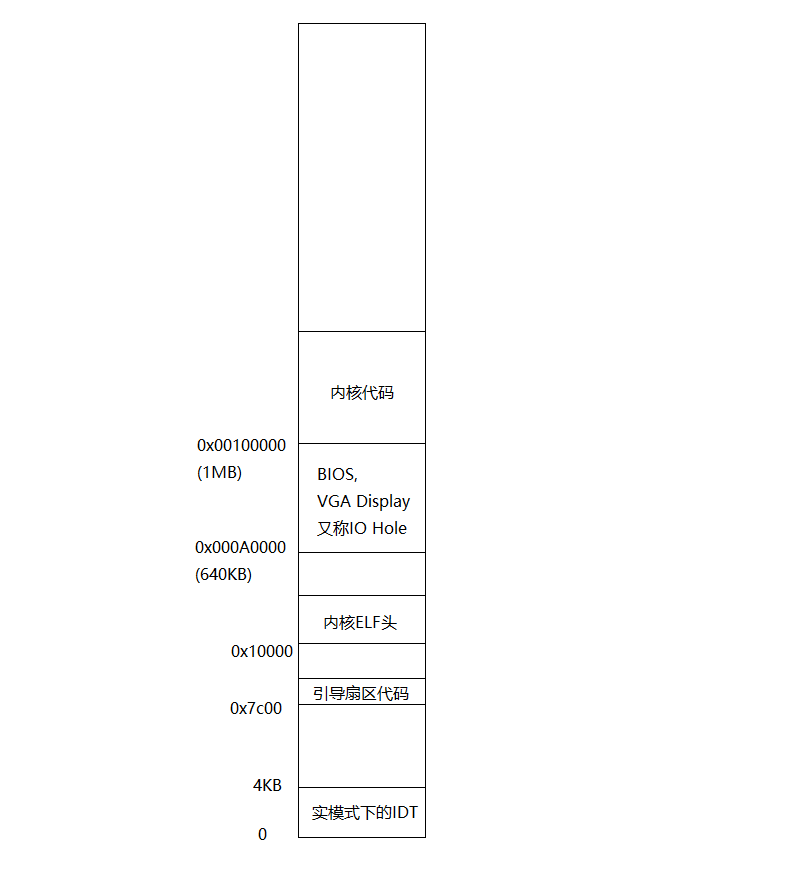
大致上可以分为三部分:
- 0x00000~0xA0000:这部分叫做basemem,是可用的。
- 接着是0xA0000~0x100000:这部分叫做IO Hole,不可用。
再接着就是0x100000以上的部分:这部分叫做extmem,可用。
kern/pmap.c中的i386_detect_memory()统计有多少可用的物理内存,将总共的可用物理内存页数保存到全局变量npages中,basemem部分可用的物理内存页数保存到npages_basemem中。Exercise 1:
需要我们写一个物理内存页的allocator。要求实现kern/pmap.c文件中的boot_alloc(),mem_init(),page_init(),page_alloc(),page_free()。check_page_free_list()和check_page_alloc()中会有一些测试用例,如果没有通过两个函数则说明代码有问题,一种类型TDD的开发流程。
从lab1知道,进入内核后首先调用的是i386_init(),该函数会调用mem_init()。mem_init()调用其他工具函数实现内核内存管理。该函数首先调用i386_detect_memory()来计算有多少可以的物理内存页保存到npages和npages_basemem中。然后调用boot_alloc()。
boot_alloc()实现如下:
static void *
boot_alloc(uint32_t n)
{
static char *nextfree; // virtual address of next byte of free memory
char *result;
// Initialize nextfree if this is the first time.
// ‘end‘ is a magic symbol automatically generated by the linker,
// which points to the end of the kernel‘s bss segment:
// the first virtual address that the linker did *not* assign
// to any kernel code or global variables.
if (!nextfree) {
extern char end[]; //在/kern/kernel.ld中定义的符号,位于bss段的末尾
nextfree = ROUNDUP((char *) end, PGSIZE);
}
// Allocate a chunk large enough to hold ‘n‘ bytes, then update
// nextfree. Make sure nextfree is kept aligned
// to a multiple of PGSIZE.
//
// LAB 2: Your code here.
result = nextfree;
nextfree = ROUNDUP((char *)result + n, PGSIZE);
cprintf("boot_alloc memory at %x, next memory allocate at %x
", result, nextfree);
return result;
}该函数维护一个static的指针nextfree,初始值是end,end是定义在/kern/kernel.ld中定义的符号,位于bss段的末尾。也就是说从内核的末尾开始分配物理内存。需要添加的代码是:
result = nextfree;
nextfree = ROUNDUP((char *)result + n, PGSIZE);
cprintf("boot_alloc memory at %x, next memory allocate at %x
", result, nextfree);
return result;每次调用都返回nextfree,然后根据参数n更新nextfree的值,使其指向下一个空闲地址处。
mem_init()调用boot_alloc(),将返回值赋给全局变量kern_pgdir,kern_pgdir保存的是内核页目录的物理地址。
接着根据mem_init()中的注释:
// Allocate an array of npages ‘struct PageInfo‘s and store it in ‘pages‘.
// The kernel uses this array to keep track of physical pages: for
// each physical page, there is a corresponding struct PageInfo in this
// array. ‘npages‘ is the number of physical pages in memory. Use memset
// to initialize all fields of each struct PageInfo to 0.在mem_init()中补充如下代码:
pages = (struct PageInfo*)boot_alloc(sizeof(struct PageInfo) * npages); //分配足够大的空间(PGSIZE的倍数)保存pages数组
memset(pages, 0, sizeof(struct PageInfo) * npages);这段代码分配足够的的内存空间保存pages数组,pages数组的每一项是一个PageInfo结构,对应一个物理页的信息,定义在inc/memlayout.h中。
接下来mem_init()调用page_init()。
page_init()实现如下:
// --------------------------------------------------------------
// Tracking of physical pages.
// The ‘pages‘ array has one ‘struct PageInfo‘ entry per physical page.
// Pages are reference counted, and free pages are kept on a linked list.
// --------------------------------------------------------------
//
// Initialize page structure and memory free list.
// After this is done, NEVER use boot_alloc again. ONLY use the page
// allocator functions below to allocate and deallocate physical
// memory via the page_free_list.
//
void
page_init(void)
{
// The example code here marks all physical pages as free.
// However this is not truly the case. What memory is free?
// 1) Mark physical page 0 as in use.
// This way we preserve the real-mode IDT and Bios structures
// in case we ever need them. (Currently we don‘t, but...)
// 2) The rest of base memory, [PGSIZE, npages_basemem * PGSIZE)
// is free.
// 3) Then comes the IO hole [IOPHYSMEM, EXTPHYSMEM), which must
// never be allocated.
// 4) Then extended memory [EXTPHYSMEM, ...).
// Some of it is in use, some is free. Where is the kernel
// in physical memory? Which pages are already in use for
// page tables and other data structures?
//
// Change the code to reflect this.
// NB: DO NOT actually touch the physical memory corresponding to
// free pages!
// 这里初始化pages中的每一项,建立page_free_list链表
// 已使用的物理页包括如下几部分:
// 1)第一个物理页是IDT所在,需要标识为已用
// 2)[IOPHYSMEM, EXTPHYSMEM)称为IO hole的区域,需要标识为已用。
// 3)EXTPHYSMEM是内核加载的起始位置,终止位置可以由boot_alloc(0)给出(理由是boot_alloc()分配的内存是内核的最尾部),这块区域也要标识
size_t i;
size_t io_hole_start_page = (size_t)IOPHYSMEM / PGSIZE;
size_t kernel_end_page = PADDR(boot_alloc(0)) / PGSIZE; //这里调了半天,boot_alloc返回的是虚拟地址,需要转为物理地址
for (i = 0; i < npages; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
pages[i].pp_ref = 1;
pages[i].pp_link = NULL;
} else if (i >= io_hole_start_page && i < kernel_end_page) {
pages[i].pp_ref = 1;
pages[i].pp_link = NULL;
} else {
pages[i].pp_ref = 0;
pages[i].pp_link = page_free_list;
page_free_list = &pages[i];
}
}
}这个函数的主要作用是初始化之前分配的pages数组,并且构建一个PageInfo链表,保存空闲的物理页,表头是全局变量page_free_list。具体实现看注释。
以上是关于MIT-6.828 Lab 2实验报告的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章