ID3决策树
Posted echoboy
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了ID3决策树相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
决策树
- 优点:计算复杂度不高,输出结果易于理解,对中间值的缺少不敏感,可以处理不相关特征数据
- 缺点:过拟合
决策树的构造
熵:混乱程度,信息的期望值
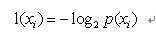
其中p(xi)是选择分类的概率
熵就是计算所有类别所有可能值包含的信息期望值,公式如下:
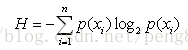 (公式2)
(公式2)
构造基本思路
信息增益 = 初始香农熵-新计算得到的香农熵(混乱程度下降的多少)
创建根节点(数据)
分裂:选择合适的特征进行分裂,采取的办法是遍历每个特征,然后计算并累加每个特征值的香农熵,与其他特征所计算出来的香农熵对比,选取信息增益最大的那个作为最大信息增益的特征节点进行分裂,分裂时,该特征有几个特征值,就会分裂成多少个树干,之后重复迭代分裂直至不能再分裂为止
好了!懂这些就可以直接上代码了!
from math import log import operator def calcShannonEnt(dataSet): "计算熵,熵代表不确定度,混乱程度" numEntries = len(dataSet) #训练样本总数 labelCounts = {} for featVec in dataSet: currentLabel = featVec[-1] #取标签 if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys(): labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0 labelCounts[currentLabel] += 1 #计算对应标签的数量 shannonEnt = 0.0 #初始化熵 for key in labelCounts: "遍历每个标签字典,标签字典中包含每个标签的数量" prob = float(labelCounts[key]) / numEntries #计算选择该分类的概率概率 shannonEnt -= prob * log(prob,2) return shannonEnt def createDataSet(): dataSet = [ [1,1,‘yes‘], [1,1,‘yes‘], [1,0,‘no‘], [0,1,‘no‘], [0,1,‘no‘], ] labels = [‘no surfacing‘,‘flippers‘] return dataSet,labels myDat , labels = createDataSet() ret = calcShannonEnt(myDat) print(ret) def splitDataSet(dataSet,axis,value): retDataSet = [] for featVec in dataSet: if featVec[axis] == value: "把选定特征为特定值的数据集分离出来" reducedFeatVec = featVec[:axis] reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:]) #把一个列表压缩进一个列表去而不是单纯append retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec) return retDataSet def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet): numFeatures = len(dataSet[0]) - 1 baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet) bestInfoGain = 0.0 #信息增益 bestFeature = -1 for i in range(numFeatures): "遍历特征,选择最大信息增益的特征" featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet] #按特征提取数据,用于分割数据 uniqueVals = set(featList) #去重 newEntropy = 0.0 for value in uniqueVals: "遍历每个不同的特征值,将遍历的每个特征值为节点进行分割,计算熵,累加,选择最大信息增益的特征" subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet,i,value)#分割数据集,将第几个特征为哪个特征值的数据分离出来 prob = len(subDataSet) / float(len(dataSet)) #计算这个特征为这个特征值的发生概率 newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet) infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy #信息增益:熵值的减少 if(infoGain > bestInfoGain): bestInfoGain = infoGain bestFeature = i return bestFeature def majorityCnt(classList): "最大投票器,用于数据集只有一个特征的时候" classcount = {} for vote in classList: if vote not in classcount.keys(): classcount[vote] =0 classcount += 1 sorteClassCount = sorted(classcount.items(),key=operator.itemgetter(1),reverse=True) #由大到小 字典的值排序 return sorteClassCount[0][0] def createTree(dataSet,labels): classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet] #取标签 if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList): "类别相同停止继续划分" return classList[0] if len(dataSet[0]) == 1: "停止划分,因为没有特征" return majorityCnt(classList) bestFeat = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet) bestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeat] mytree = {bestFeatLabel:{}} del(labels[bestFeat]) #该特征也被已划分节点,删除特征 featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet] #提取对于该节点信息增益最大的特征的所有特征值 uniqueVals = set(featValues) #去重 for value in uniqueVals: "为该节点下最大信息增益的特征的不重合特征值进行再次创建决策树" subLabels = labels[:] mytree[bestFeatLabel][value] = createTree(splitDataSet( dataSet,bestFeat,value ),subLabels) return mytree def classify(inputTree,featLabels,testVec): "训练完毕,用于预测" firstStr = inputTree.keys()[0] #取第一个节点 secondDict = inputTree[firstStr] featIndex = featLabels.index(firstStr) #查看这个特征的索引(查这是第几个特征) for key in secondDict.keys(): if testVec[featIndex] == key: if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == ‘dict‘: classLabel = classify(secondDict[key],featLabels,testVec) else: classLabel = secondDict[key] return classLabel def storeTree(inputTree,filename): "保存训练完毕的决策树模型" import pickle fw = open(filename,‘w‘) pickle.dump(inputTree,fw) fw.close() def grabTree(filename): "加载以保存的决策树模型" import pickle fr = open(filename) return pickle.load(filename,fr)
‘‘‘ 绘制决策树 ‘‘‘ import matplotlib.pyplot as plt decisionNode = dict(boxstyle="sawtooth", fc="0.8") leafNode = dict(boxstyle="round4", fc="0.8") arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle="<-") def getNumLeafs(myTree): numLeafs = 0 firstStr = list(myTree)[0] secondDict = myTree[firstStr] for key in secondDict.keys(): if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == ‘dict‘:#test to see if the nodes are dictonaires, if not they are leaf nodes numLeafs += getNumLeafs(secondDict[key]) else: numLeafs += 1 return numLeafs def getTreeDepth(myTree): maxDepth = 0 firstStr = list(myTree)[0] secondDict = myTree[firstStr] for key in secondDict.keys(): if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == ‘dict‘:#test to see if the nodes are dictonaires, if not they are leaf nodes thisDepth = 1 + getTreeDepth(secondDict[key]) else: thisDepth = 1 if thisDepth > maxDepth: maxDepth = thisDepth return maxDepth def plotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType): createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords=‘axes fraction‘, xytext=centerPt, textcoords=‘axes fraction‘, va="center", ha="center", bbox=nodeType, arrowprops=arrow_args) def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, txtString): xMid = (parentPt[0]-cntrPt[0])/2.0 + cntrPt[0] yMid = (parentPt[1]-cntrPt[1])/2.0 + cntrPt[1] createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString, va="center", ha="center", rotation=30) def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt):#if the first key tells you what feat was split on numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree) #this determines the x width of this tree depth = getTreeDepth(myTree) firstStr = list(myTree)[0] #the text label for this node should be this cntrPt = (plotTree.xOff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs))/2.0/plotTree.totalW, plotTree.yOff) plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, nodeTxt) plotNode(firstStr, cntrPt, parentPt, decisionNode) secondDict = myTree[firstStr] plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff - 1.0/plotTree.totalD for key in secondDict.keys(): if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == ‘dict‘:#test to see if the nodes are dictonaires, if not they are leaf nodes plotTree(secondDict[key], cntrPt, str(key)) #recursion else: #it‘s a leaf node print the leaf node plotTree.xOff = plotTree.xOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalW plotNode(secondDict[key], (plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, leafNode) plotMidText((plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, str(key)) plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalD #if you do get a dictonary you know it‘s a tree, and the first element will be another dict def createPlot(inTree): fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor=‘white‘) fig.clf() axprops = dict(xticks=[], yticks=[]) createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False, **axprops) #no ticks #createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False) #ticks for demo puropses plotTree.totalW = float(getNumLeafs(inTree)) plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree)) plotTree.xOff = -0.5/plotTree.totalW; plotTree.yOff = 1.0 plotTree(inTree, (0.5, 1.0), ‘‘) plt.show() #def createPlot(): # fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor=‘white‘) # fig.clf() # createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False) #ticks for demo puropses # plotNode(‘a decision node‘, (0.5, 0.1), (0.1, 0.5), decisionNode) # plotNode(‘a leaf node‘, (0.8, 0.1), (0.3, 0.8), leafNode) # plt.show() def retrieveTree(i): listOfTrees = [{‘no surfacing‘: {0: ‘no‘, 1: {‘flippers‘: {0: ‘no‘, 1: ‘yes‘}}}}, {‘no surfacing‘: {0: ‘no‘, 1: {‘flippers‘: {0: {‘head‘: {0: ‘no‘, 1: ‘yes‘}}, 1: ‘no‘}}}} ] return listOfTrees[i] thisTree = retrieveTree(1) createPlot(thisTree)
以上是关于ID3决策树的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章