装饰器
Posted bit-taozhen
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了装饰器相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
定义:
器字代表函数,装饰器本质是函数;装饰:装饰其他函数,就是为其他函数添加附加功能
原则:
1.不能修改被装饰函数的源代码(在不修改被装饰函数源代码的情况下为其添加功能)
2.不能修改被装饰的函数的调用函数,被装饰函数不知道被装饰了
实现装饰器需要了解:
1.函数及变量:内存存储函数方式与存储变量一样:内存中存储函数体,再指向函数名
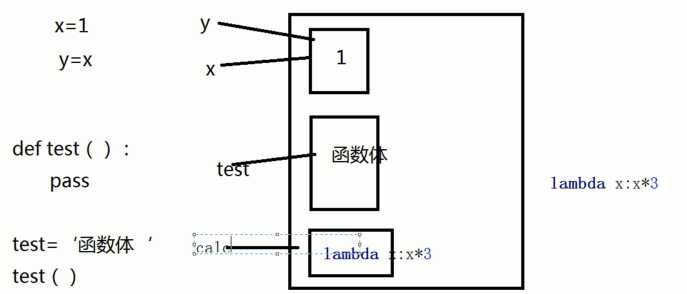
2.高阶函数
a.把一个函数名当作实参传给另外个函数(在不修改被装饰函数源代码的情况下为其添加功能)
b.返回值中包含函数名(不修改函数的调用方式)
1 import time 2 def bar():#bar是这个函数的门牌号 3 time.sleep(2) 4 print(‘in the bar‘) 5 def test1(func):#不是装饰器,是因为函数的调用方式test1(bar)被更改了 6 start_time=time.time() 7 func() 8 stop_time=time.time() 9 print(‘the func fun time is %s‘ % (stop_time-start_time)) 10 11 test1(bar) #func=bar
运行结果:

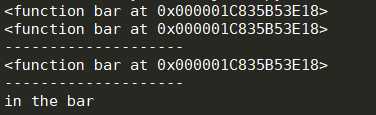
1 import time 2 def bar():#bar是这个函数的门牌号 3 time.sleep(2) 4 print(‘in the bar‘) 5 6 def test2(func): 7 print(func) 8 return func 9 10 print(test2(bar)) 11 print(‘--------------------‘) 12 bar=test2(bar) 13 print(‘--------------------‘) 14 bar()
运行结果:
3.嵌套函数:在已定义的函数内部再定义函数
1 def foo(): 2 print(‘in the foo‘) 3 def bar():#bar具有局部变量的特性 4 print(‘in the bar‘)
通过高阶函数和嵌套函数实现装饰器功能:
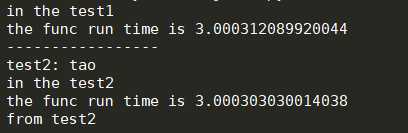
1 import time 2 3 def timer(func):#在被装饰函数之外嵌套装饰器函数,添加装饰功能 4 def deco(*args,**kwargs):#不固定参数参数 5 start_time=time.time() 6 result=func(*args,**kwargs)#被装饰的函数在这运行 7 stop_time=time.time() 8 print(‘the func run time is %s‘ % (stop_time-start_time)) 9 10 return result#加入了返回值 11 return deco#timer这个函数返回了deco函数的地址 12 13 @timer#@timer等于test1=timer(test1):返回了deco函数的内存地址赋给了test1,此时test1是新的test1,这时的test1已经有了装饰器的功能 14 def test1(): 15 time.sleep(3) 16 print(‘in the test1‘) 17 18 @timer#test2=timer(test2),deco=test2 19 def test2(name): 20 time.sleep(3) 21 print(‘test2:‘,name) 22 print(‘in the test2‘) 23 return ‘from test2‘#加入了返回,装饰器内的函数也要加返回 24 25 test1() 26 print(‘-----------------‘) 27 print(test2(‘tao‘))#print打印函数的返回值
运行结果:
所以说,装饰器就是将被装饰函数在装饰器函数内执行,再将装饰器函数赋予被装饰函数名,之后再执行被装饰函数时就相当于执行了装饰器函数,即在没有改变被装饰函数的源代码和调用方式的情况下,实现了装饰的功能。
实现加入参数的装饰器:
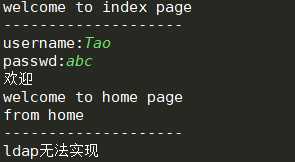
1 user,passwd=‘Tao‘,‘abc‘ 2 def auth(auth_type):#与未加参数的装饰器区别:装饰器多加了一个参数,要多嵌套一层函数;auth返回的仍是wrapper这个函数 3 def outer_wrapper(func):#注意加入的参数和func的位置 4 def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):#auth函数返回out_wrapper,out_wrapper函数返回wrapper,所以auth函数返回的仍是wrapper这个函数 5 6 #判断参数 7 if auth_type==‘local‘: 8 username = input(‘username:‘).strip() 9 password = input(‘passwd:‘).strip() 10 11 if user == username and passwd == password: 12 print(‘欢迎‘) 13 res = func(*args, **kwargs) #当被装饰函数有返回值时 14 return res 15 else: 16 exit(‘错误‘) 17 18 #判断参数 19 elif auth_type==‘ldap‘: 20 print(‘ldap无法实现‘) 21 22 return wrapper 23 24 return outer_wrapper 25 26 27 28 def index(): 29 print(‘welcome to index page‘) 30 31 @auth(auth_type=‘local‘)#auth返回了wrapper这个函数赋给了home 32 def home(): 33 print(‘welcome to home page‘) 34 return "from home" #加入了返回,装饰器内的函数也要加返回 35 36 @auth(auth_type=‘ldap‘)#auth返回了wrapper这个函数赋给了bbs 37 def bbs(): 38 print(‘welcome to bbs page‘) 39 40 index() 41 print(‘--------------------‘) 42 print(home())#打印函数的返回值即from home 43 print(‘--------------------‘) 44 bbs()
运行结果:
以上是关于装饰器的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章