ActiveMQ介绍与使用
Posted zhengxin95
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了ActiveMQ介绍与使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1 ActiveMQ介绍
1.1 什么是ActiveMQ
ActiveMQ 是Apache出品,最流行的,能力强劲的开源消息总线。ActiveMQ 是一个完全支持JMS1.1和J2EE 1.4规范的 JMS Provider实现,尽管JMS规范出台已经是很久的事情了,但是JMS在当今的J2EE应用中间仍然扮演着特殊的地位。
主要特点:
1. 多种语言和协议编写客户端。语言: Java, C, C++, C#, Ruby, Perl, Python, php。应用协议: OpenWire,Stomp REST,WS Notification,XMPP,AMQP
2. 完全支持JMS1.1和J2EE 1.4规范 (持久化,XA消息,事务)
3. 对Spring的支持,ActiveMQ可以很容易内嵌到使用Spring的系统里面去,而且也支持Spring2.0的特性
4. 通过了常见J2EE服务器(如 Geronimo,JBoss 4, GlassFish,WebLogic)的测试,其中通过JCA 1.5 resource adaptors的配置,可以让ActiveMQ可以自动的部署到任何兼容J2EE 1.4 商业服务器上
5. 支持多种传送协议:in-VM,TCP,SSL,NIO,UDP,JGroups,JXTA
6. 支持通过JDBC和journal提供高速的消息持久化
7. 从设计上保证了高性能的集群,客户端-服务器,点对点
8. 支持Ajax
9. 支持与Axis的整合
10. 可以很容易得调用内嵌JMS provider,进行测试
1.2 JMS介绍
JMS的全称是Java Message Service,即Java消息服务。用于在两个应用程序之间,或分布式系统中发送消息,进行异步通信。
它主要用于在生产者和消费者之间进行消息传递,生产者负责产生消息,而消费者负责接收消息。把它应用到实际的业务需求中的话我们可以在特定的时候利用生产者生成一消息,并进行发送,对应的消费者在接收到对应的消息后去完成对应的业务逻辑。
对于消息的传递有两种类型:
一种是点对点的,即一个生产者和一个消费者一一对应;
另一种是发布/订阅模式,即一个生产者产生消息并进行发送后,可以由多个消费者进行接收。
JMS定义了五种不同的消息正文格式,以及调用的消息类型,允许你发送并接收以一些不同形式的数据,提供现有消息格式的一些级别的兼容性。
· StreamMessage -- Java原始值的数据流
· MapMessage--一套名称-值对
· TextMessage--一个字符串对象
· ObjectMessage--一个序列化的 Java对象
· BytesMessage--一个字节的数据流
2ActiveMQ的安装
2.1 下载
进入http://activemq.apache.org/下载ActiveMQ
2.2 安装
安装步骤:
第一步:安装jdk,需要jdk1.7以上版本
第二步:解压缩activeMQ的压缩包。
第三步:进入bin目录。
启动:[[email protected] bin]# ./activemq start
停止:[[email protected] bin]# ./activemq stop
第四步:访问后台管理。
http://192.168.45.188:8161/admin
用户名:admin
密码:admin
3 ActiveMQ的使用方法
3.1 JMS消息发送模式
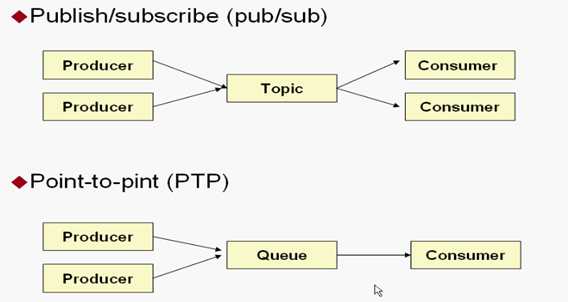
在点对点或队列模型下,一个生产者向一个特定的队列发布消息,一个消费者从该队列中读取消息。这里,生产者知道消费者的队列,并直接将消息发送到消费者的队列。这种模式被概括为:只有一个消费者将获得消息。生产者不需要在接收者消费该消息期间处于运行状态,接收者也同样不需要在消息发送时处于运行状态。每一个成功处理的消息都由接收者签收。
发布者/订阅者模型支持向一个特定的消息主题发布消息。0或多个订阅者可能对接收来自特定消息主题的消息感兴趣。在这种模型下,发布者和订阅者彼此不知道对方。这种模式好比是匿名公告板。这种模式被概括为:多个消费者可以获得消息.在发布者和订阅者之间存在时间依赖性。发布者需要建立一个订阅(subscription),以便客户能够购订阅。订阅者必须保持持续的活动状态以接收消息,除非订阅者建立了持久的订阅。在那种情况下,在订阅者未连接时发布的消息将在订阅者重新连接时重新发布。
3.1 JMS应用程序接口
ConnectionFactory 接口(连接工厂)
用户用来创建到JMS提供者的连接的被管对象。JMS客户通过可移植的接口访问连接,这样当下层的实现改变时,代码不需要进行修改。 管理员在JNDI名字空间中配置连接工厂,这样,JMS客户才能够查找到它们。根据消息类型的不同,用户将使用队列连接工厂,或者主题连接工厂。
Connection 接口(连接)
连接代表了应用程序和消息服务器之间的通信链路。在获得了连接工厂后,就可以创建一个与JMS提供者的连接。根据不同的连接类型,连接允许用户创建会话,以发送和接收队列和主题到目标。
Destination 接口(目标)
目标是一个包装了消息目标标识符的被管对象,消息目标是指消息发布和接收的地点,或者是队列,或者是主题。JMS管理员创建这些对象,然后用户通过JNDI发现它们。和连接工厂一样,管理员可以创建两种类型的目标,点对点模型的队列,以及发布者/订阅者模型的主题。
MessageConsumer 接口(消息消费者)
由会话创建的对象,用于接收发送到目标的消息。消费者可以同步地(阻塞模式),或异步(非阻塞)接收队列和主题类型的消息。
MessageProducer 接口(消息生产者)
由会话创建的对象,用于发送消息到目标。用户可以创建某个目标的发送者,也可以创建一个通用的发送者,在发送消息时指定目标。
Message 接口(消息)
是在消费者和生产者之间传送的对象,也就是说从一个应用程序创送到另一个应用程序。一个消息有三个主要部分:
消息头(必须):包含用于识别和为消息寻找路由的操作设置。
一组消息属性(可选):包含额外的属性,支持其他提供者和用户的兼容。可以创建定制的字段和过滤器(消息选择器)。
一个消息体(可选):允许用户创建五种类型的消息(文本消息,映射消息,字节消息,流消息和对象消息)。
消息接口非常灵活,并提供了许多方式来定制消息的内容。
Session 接口(会话)
表示一个单线程的上下文,用于发送和接收消息。由于会话是单线程的,所以消息是连续的,就是说消息是按照发送的顺序一个一个接收的。会话的好处是它支持事务。如果用户选择了事务支持,会话上下文将保存一组消息,直到事务被提交才发送这些消息。在提交事务之前,用户可以使用回滚操作取消这些消息。一个会话允许用户创建消息生产者来发送消
3.3 消息队列
把ActiveMQ依赖的jar包添加到工程中。
activemq-all-5.12.0.jar
使用maven工程,则添加jar包的依赖:
|
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.activemq</groupId> <artifactId>activemq-all</artifactId> <version>5.11.2</version> </dependency> |
3.3.1 Producer
|
public class QueueSender {
public static void main(String[] args) { //创建一个连接工厂 ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory("tcp://192.168.25.168:61616"); try { //从工厂对象中获得连接 Connection connection = connectionFactory.createConnection(); //开启连接 connection.start(); /* connection.createSession(paramA, paramB) A)paramA设置为true时: paramB的值忽略, acknowledgment mode被jms服务器设置 SESSION_TRANSACTED 。 当一个事务被提交的时候,消息确认就会自动发生。 B) paramA设置为false时: Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE为自动确认,当客户成功的从receive方法返回的时候,或者从 MessageListener.onMessage方法成功返回的时候,会话自动确认客户收到的消息。 Session.CLIENT_ACKNOWLEDGE 为客户端确认。客户端接收到消息后,必须调用javax.jms.Message的 acknowledge方法。jms服务器才会删除消息。(默认是批量确认) */ //开启一个回话,第一个参数指定不使用事务,第二个参数指定客户端接收消息的确认方式 Session session = connection.createSession(false, Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE); //创建一目的地Queue或者是Topic Queue queue = session.createQueue("mytestqueue"); //创建一个生产者 MessageProducer producer = session.createProducer(queue); //创建message TextMessage message = new ActiveMQTextMessage(); message.setText("hello"); //发送消息 producer.send(message); //关闭 producer.close(); session.close(); connection.close(); } catch (JMSException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }
} } |
3.3.2 Consumer
消费者有两种消费方法::
1、同步消费。通过调用消费者的receive方法从目的地中显式提取消息。receive方法可以一直阻塞到消息到达。
2、异步消费。客户可以为消费者注册一个消息监听器,以定义在消息到达时所采取的动作。
实现MessageListener接口,在MessageListener()方法中实现消息的处理逻辑。
3.3.2.1同步消费
|
public class QueueConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) { //创建一连接工厂 ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory("tcp://192.168.25.168:61616"); try { //创建一个连接 Connection connection = connectionFactory.createConnection(); //打开连接 connection.start(); //创建一个回话 Session session = connection.createSession(false, Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE); //创建一个目的地Destination Queue queue = session.createQueue("mytestqueue"); //创建一个消费者 MessageConsumer consumer = session.createConsumer(queue); while(true) { //设置接收者接收消息的时间,为了便于测试,这里定为100s Message message = consumer.receive(100000); if (message != null) { System.out.println(message); } else { //超时结束 break; }
} consumer.close(); session.close(); connection.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
} } |
3.3.2.2异步消费
|
public class QueueConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) { //创建一连接工厂 ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory("tcp://192.168.25.168:61616"); try { //创建一个连接 Connection connection = connectionFactory.createConnection(); //打开连接 connection.start(); //创建一个回话 Session session = connection.createSession(false, Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE); //创建一个目的地Destination Queue queue = session.createQueue("mytestqueue"); //创建一个消费者 MessageConsumer consumer = session.createConsumer(queue); consumer.setMessageListener(new MessageListener() {
@Override public void onMessage(Message message) { if (message instanceof TextMessage) { String text = ""; try { text = ((TextMessage)message).getText(); } catch (JMSException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(text); }
} }); System.in.read(); //关闭 consumer.close(); session.close(); connection.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
} } |
3.4 发布者/订阅者
3.4.1 Producer
|
public class TopicProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) { //创建连接工厂 ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory("tcp://192.168.25.168:61616"); try { //创建连接 Connection connection = connectionFactory.createConnection(); //开启连接 connection.start(); //创建一个回话 Session session = connection.createSession(false, Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE); //创建一个Destination,queue或者Topic Topic topic = session.createTopic("mytopic"); //创建一个生成者 MessageProducer producer = session.createProducer(topic); //创建一个消息 TextMessage textMessage = new ActiveMQTextMessage(); textMessage.setText("hello my topic"); //发送消息 producer.send(textMessage); //关闭 producer.close(); session.close(); connection.close(); } catch (JMSException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } |
3.4.2 Consumer
|
public class TopicConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) { //创建连接工厂 ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory("tcp://192.168.25.168:61616"); try { //创建连接 Connection connection = connectionFactory.createConnection(); connection.start(); //创建一个会话 Session session = connection.createSession(false, Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE); //创建一个目标 Destination destination = session.createTopic("mytopic"); //创建一个消费者 MessageConsumer consumer = session.createConsumer(destination); //接收消息 consumer.setMessageListener(new MessageListener() {
@Override public void onMessage(Message message) {
System.out.println(message);
} }); //暂停 System.in.read(); //关闭 consumer.close(); session.close(); connection.close();
} catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } |
4 ActiveMQ整合Spring
4.1 配置ConnectionFactory
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:jms="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jms" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/jms http://www.springframework.org/schema/jms/spring-jms-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 真正可以产生Connection的ConnectionFactory,由对应的 JMS服务厂商提供 --> <bean id="targetConnectionFactory" class="org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory"> <property name="brokerURL" value="tcp://192.168.25.168:61616" /> </bean> <!-- Spring用于管理真正的ConnectionFactory的ConnectionFactory --> <bean id="connectionFactory" class="org.springframework.jms.connection.SingleConnectionFactory"> <!-- 目标ConnectionFactory对应真实的可以产生JMS Connection的ConnectionFactory --> <property name="targetConnectionFactory" ref="targetConnectionFactory" /> </bean> </beans> |
4.2 配置生产者
4.2.1 Spring配置文件
|
<!-- 配置生产者 --> <!-- Spring提供的JMS工具类,它可以进行消息发送、接收等 --> <bean id="jmsTemplate" class="org.springframework.jms.core.JmsTemplate"> <!-- 这个connectionFactory对应的是我们定义的Spring提供的那个ConnectionFactory对象 --> <property name="connectionFactory" ref="connectionFactory" /> </bean> <!--这个是队列目的地,点对点的 --> <bean id="queueDestination" class="org.apache.activemq.command.ActiveMQQueue"> <constructor-arg> <value>queue</value> </constructor-arg> </bean> <!--这个是主题目的地,一对多的 --> <bean id="topicDestination" class="org.apache.activemq.command.ActiveMQTopic"> <constructor-arg value="topic" /> </bean> |
4.2.2 发送消息
|
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) { //创建spring容器 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //获得JmsTemplate对象 JmsTemplate template = (JmsTemplate) applicationContext.getBean("jmsTemplate"); //获得Destination ActiveMQQueue queue = (ActiveMQQueue) applicationContext.getBean("queueDestination"); //发送消息 template.send(queue, new MessageCreator() {
@Override public Message createMessage(Session session) throws JMSException { return session.createTextMessage("hello"); } });
} } |
4.3 配置消费者
那么消费者是通过Spring为我们封装的消息监听容器MessageListenerContainer实现的,它负责接收信息,并把接收到的信息分发给真正的MessageListener进行处理。每个消费者对应每个目的地都需要有对应的MessageListenerContainer。
对于消息监听容器而言,除了要知道监听哪个目的地之外,还需要知道到哪里去监听,也就是说它还需要知道去监听哪个JMS服务器,这是通过在配置MessageConnectionFactory的时候往里面注入一个ConnectionFactory来实现的。
所以在配置一个MessageListenerContainer的时候有三个属性必须指定:
1、一个是表示从哪里监听的ConnectionFactory
2、一个是表示监听什么的Destination;
3、一个是接收到消息以后进行消息处理的MessageListener。
常用的MessageListenerContainer实现类是DefaultMessageListenerContainer。
4.3.1 MessageListener
|
public class MyMessageListener implements MessageListener { @Override public void onMessage(Message message) { System.out.println(message); } }
|
4.3.2 Spring配置文件
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:jms="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jms" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/jms http://www.springframework.org/schema/jms/spring-jms-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 真正可以产生Connection的ConnectionFactory,由对应的 JMS服务厂商提供 --> <bean id="targetConnectionFactory" class="org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory"> <property name="brokerURL" value="tcp://192.168.25.168:61616" /> </bean> <bean id="connectionFactory" class="org.springframework.jms.connection.SingleConnectionFactory"> <property name="targetConnectionFactory" ref="targetConnectionFactory" /> </bean> <!--这个是队列目的地,点对点的 --> <bean id="queueDestination" class="org.apache.activemq.command.ActiveMQQueue"> <constructor-arg> <value>queue</value> </constructor-arg> </bean> <!--这个是主题目的地,一对多的 --> <bean id="topicDestination" class="org.apache.activemq.command.ActiveMQTopic"> <constructor-arg value="topic" /> </bean> <!-- 配置监听器 --> <bean id="myMessageListener" class="cn.itcast.mq.spring.MyMessageListener" /> <!-- 消息监听容器 --> <bean id="jmsContainer" class="org.springframework.jms.listener.DefaultMessageListenerContainer"> <property name="connectionFactory" ref="connectionFactory" /> <property name="destination" ref="queueDestination" /> <property name="messageListener" ref="myMessageListener" /> </bean> </beans> |
4.3.3 接收消息
|
public class Consumer {
public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext-consumer.xml"); try { System.in.read(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } }
} |
以上是关于ActiveMQ介绍与使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章