计算几何
Posted cloud-king
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了计算几何相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、基本向量运算


板子:
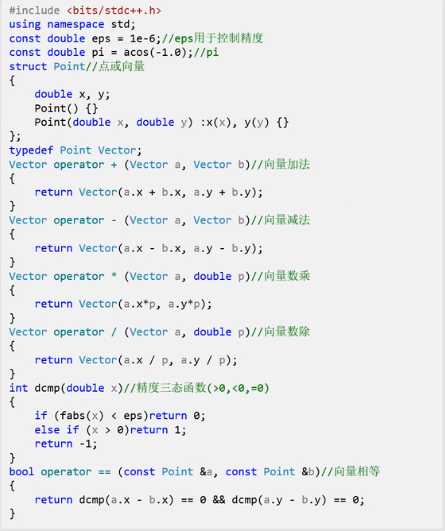
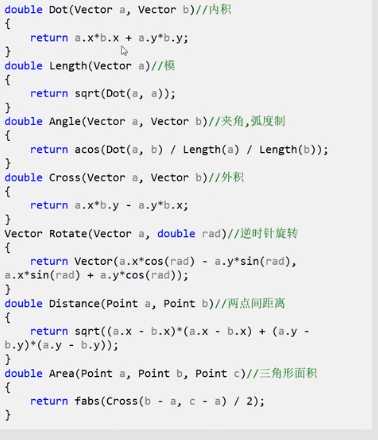
例:线段求交点,点到直线的面积
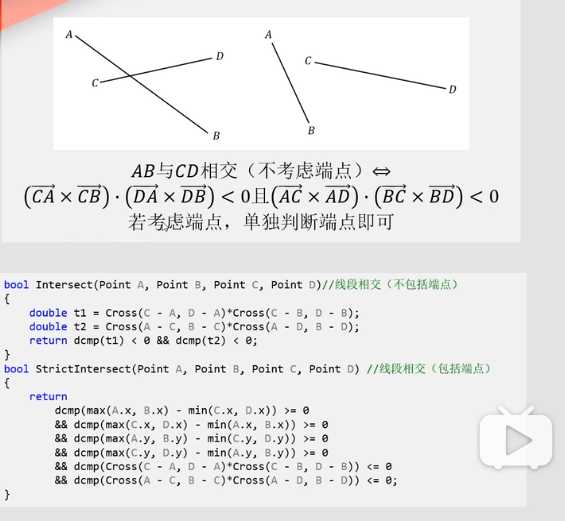
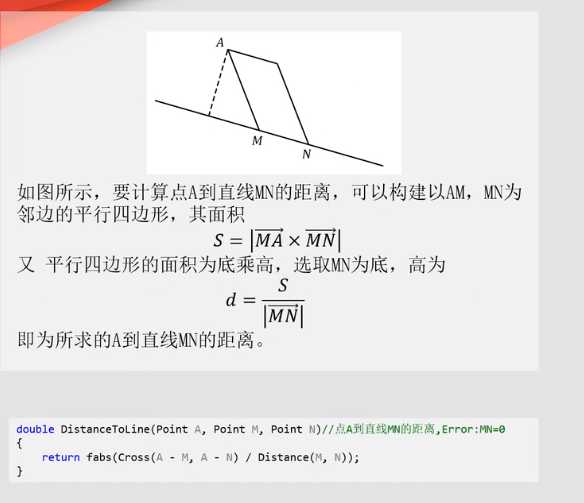
直线求交点,点在多边形内


多边形面积,凸包
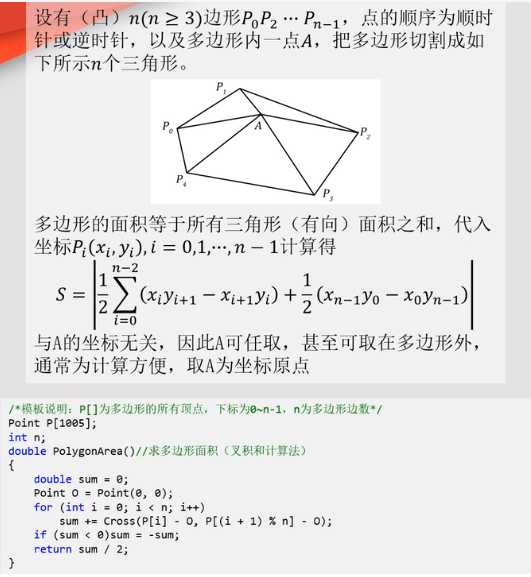

凸包板子,根据圆心角求点的坐标

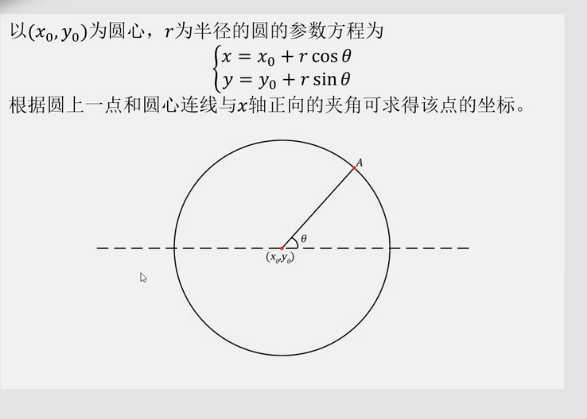
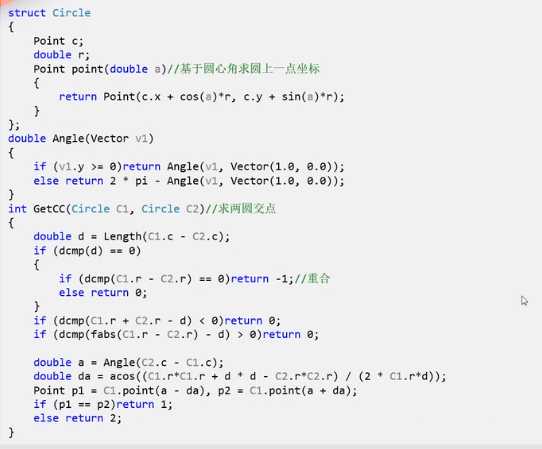
两圆求交点

二、Graham‘s Scan求凸包
例:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1348 凸包模板题
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int maxn=1006; const double pi=acos(-1.0); struct node{ double x,y; }p[maxn],P[maxn]; int n,tot; double ans; double X(node A,node B,node C) //求差积 { return (B.x-A.x)*(C.y-A.y)-(C.x-A.x)*(B.y-A.y); } double len(node A,node B){ //两点距离 return sqrt((A.x-B.x)*(A.x-B.x)+(A.y-B.y)*(A.y-B.y)); } bool cmp(node A,node B){ //极角扫描比较; double pp=X(p[0],A,B); if(pp>0)return true; if(pp<0)return false; return len(p[0],A)<len(p[0],B); } int main() { int t,l; scanf("%d",&t); for(int cas=1;cas<=t;cas++) { if(cas!=1)printf(" "); scanf("%d%d",&n,&l); ans=2*pi*l; //圆的面积 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%lf%lf",&p[i].x,&p[i].y); if(n==1){ printf("%.0f ",ans); }else if(n==2){ printf("%.0f ",ans+len(p[0],p[1])); }else{ for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { if(p[i].y<p[0].y){ //将p[0]设为左下角最小的点; swap(p[i],p[0]); }else if(p[i].y==p[0].y&&p[i].x<p[0].x){ swap(p[i],p[0]); } } sort(p+1,p+n,cmp); P[0]=p[0]; P[1]=p[1]; tot=1; for(int i=2;i<n;i++) //模拟栈的工作; { while(tot>0&&X(P[tot-1],P[tot],p[i])<=0)tot--; tot++; P[tot]=p[i]; } for(int i=0;i<tot;i++) ans+=len(P[i],P[i+1]); ans+=len(P[0],P[tot]); printf("%.0f ",ans); } } }
以上是关于计算几何的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章