论文学习:Deep residual learning for image recognition
Posted ryanxing
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了论文学习:Deep residual learning for image recognition相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
- I. Overview
- II. Degradation
- III. Solution & Deep residual learning
- IV. Implementation & Shortcut connections
Home page
https://github.com/KaimingHe/deep-residual-networksTensorFlow实现:
https://github.com/tensorpack/tensorpack/tree/master/examples/ResNet事实上TensorFlow已经内置了resnet:
https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/contrib/slim/python/slim/nets/resnet_v1.py2016 CVPR Best Paper Award ,2018年被引超12900次。
解决的问题:使深度网络更容易训练。
To ease the training of networks that are substantially deeper than those used previously.
I. Overview
首先,堆叠更多层,确实让特征提取更加有效。
Deep networks naturally integrate low/mid/highlevel features [49] and classifiers in an end-to-end multilayer fashion, and the “levels” of features can be enriched by the number of stacked layers (depth).
但网络太深的主要困难,在于梯度消失或爆炸:
An obstacle to answering this question was the notorious problem of vanishing/exploding gradients [14, 1, 8], which hamper convergence from the beginning.
前人的加速方法主要是标准化层和正则初始化:
This problem, however, has been largely addressed by normalized initialization [23, 8, 36, 12] and intermediate normalization layers [16], which enable networks with tens of layers to start converging for stochastic gradient descent (SGD) with backpropagation [22].
具体为什么标准化层可以加快训练,参考这篇博客及其相关论文。
当网络更深时,一个新的问题出现了。我们称之为 Degradation :
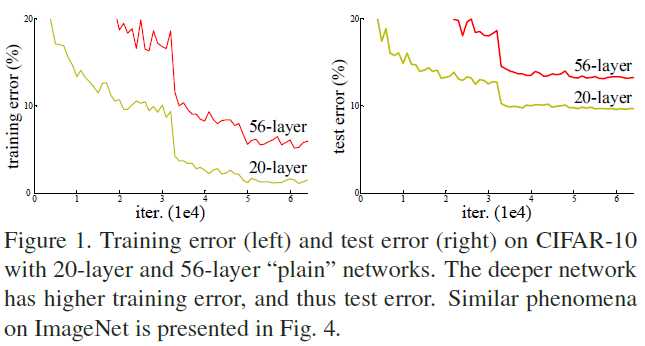
如图,在准确率基本饱和时,深层网络的训练误差比浅层网络还高。
实验证明,随着网络加深,这种退化越来越剧烈。
这是因为过拟合吗?
如果是过拟合,那么训练误差不应该随网络加深而上升(过拟合时训练误差应该很低)。
我们继续研究这个问题。
II. Degradation
我们先训练好一个 shallower architecture ,其能输出理想的结果。
然后,我们复制该 shallower architecture ,再加上一层或多层网络,得到一个 deeper model ,如图:

我们再训练 deeper model 。
理想情况下, added layers 只需要简单地实现 identity mapping 功能,就可以让训练误差不下降,甚至还有可能上升。
然而实验证实,deeper model 要么耗时过长,要么效果不如预期。
这是深度网络退化问题的一个实验说明。
III. Solution & Deep residual learning
为了解决退化问题,我们引入了 deep residual learning 。其根本思想是:
Instead of hoping each few stacked layers directly fit a desired underlying mapping, we explicitly let these layers fit a residual mapping.
比如,假设原映射是 (mathscr H(mathrm x)) ,那么我们希望非线性层真正学习的映射就是:
[
mathscr F(mathrm x) := mathscr H(mathrm x) - mathscr x
]
回到上一节的例子。
我们希望附加层能学到恒等映射,由于该层是非线性层,训练起来依然非常困难。
但是,如果我们学习的是残差映射,即全零的残差,显然容易多了。
思想类似于 SVM ,但是你怎么想不到!!!
IV. Implementation & Shortcut connections
思想有了,具体怎么实现呢?
忍不住了:何大神太牛逼了!!!!
回到刚刚的例子。假设:
- added layers 的目标映射是 (mathscr H) ;
- 原 shallower architecture 的输出,是 (mathscr H) 的输入 (mathrm x) 。
为了迫使前面的非线性层学习残差,我们假设网络输出就是残差的情况。
此时,我们应该在计算损失之前,让网络的输出 (mathscr H(mathrm x)) 与原始输入 (mathrm x) 求和。
因此网络如下:
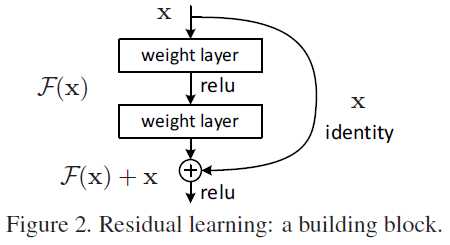
如此连接是可导的,因此可以应用反向传播算法。
当然,为什么学“全0”更简单,没有详细的理论分析,而需要大量的实验证明。
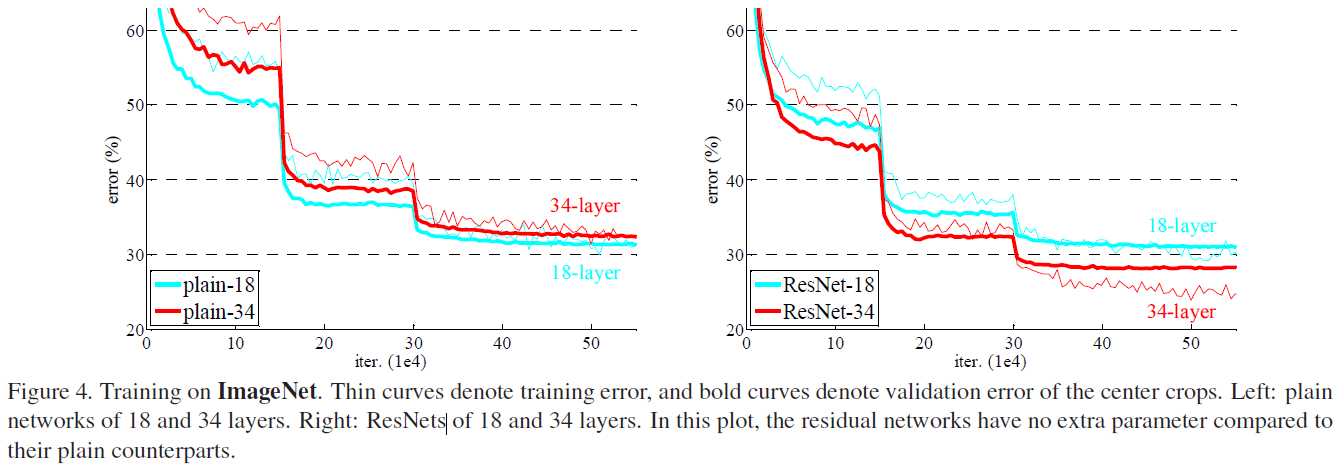
右图实验结果表明,左图的退化问题得到了有效解决。
以上是关于论文学习:Deep residual learning for image recognition的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章