Servlet源码级别进行详解
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Servlet源码级别进行详解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.首先我们先看看Servlet的类结构图,然后再分别介绍其中的接口方法
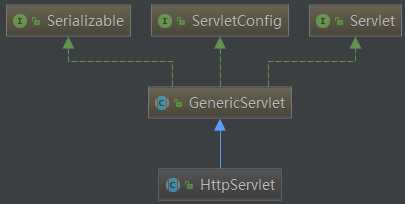
由上图可以看到,Servlet和ServletConfig都是顶层接口类,而GenericServlet实现了这两个顶层类,然后HttpServlet实现了GenericServlet类.所以要实现一个Servlet直接就可以继承HttpServlet.
2.Servlet接口代码
public interface Servlet { //容器在启动的被调用,仅调用一次 void init(ServletConfig var1) throws ServletException; //获取Servlet配置 ServletConfig getServletConfig(); //处理具体请求 void service(ServletRequest var1, ServletResponse var2) throws ServletException, IOException; //获取Servlet的相关信息 String getServletInfo(); //Servlet销毁后释放资源 void destroy(); }
其中,init方法接收一个ServletConfig参数,由容器传入.ServletConfig就是Servlet的配置,在web.xml中定义Servlet时通过init-param标签配置的参数由ServletConfig保存.
3.ServletConfig接口定义
public interface ServletConfig { //用于获取Servlet名,web.xml中定义的servlet-name String getServletName(); //获取应用本身(非常重要) ServletContext getServletContext(); //获取init-param中的配置参数 String getInitParameter(String var1); //获取配置的所有init-param名字集合 Enumeration<String> getInitParameterNames(); }
ServletConfig是Servlet级别,而ServletContext是Context(也就是Application)级别.ServletContext通常利用setAttribute方法保存Application的属性.
4.Servlet第一个实现类GenericServlet
GenericServlet是Servlet的默认实现,是与具体协议无关的,主要做了三件事.
1) 实现了ServletConfig接口,可以调用ServletConfig里面的方法.
public abstract class GenericServlet implements Servlet, ServletConfig, Serializable
2) 提供了无参的init方法
public void init() throws ServletException {}
3)提供了2个log方法,一个记录日志,一个记录异常.
public void log(String msg) { this.getServletContext().log(this.getServletName() + ": " + msg); } public void log(String message, Throwable t) { this.getServletContext().log(this.getServletName() + ": " + message, t); }
5.基于协议的HttpServlet
HttpSerVlet是基于Http协议实现的Servlet基类,我们在写Servlet的时候直接继承它就行了.SpringMVC中的DispatchServlet就是继承了HttpServlet.HttpServlet重新了service方法,而service方法首先将ServletRequest和ServletResponse转成HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse,然后根据Http不同类型的请求,再路由到不同的处理方法进行处理.
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException { HttpServletRequest request; HttpServletResponse response; try {//直接对请求类型进行强转 request = (HttpServletRequest)req; response = (HttpServletResponse)res; } catch (ClassCastException var6) { throw new ServletException("non-HTTP request or response"); } //调用Http的请求方法处理 this.service(request, response); }
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { String method = req.getMethod();//获取请求类型 long lastModified; //根据请求类型进行路由 if(method.equals("GET")) { lastModified = this.getLastModified(req); if(lastModified == -1L) { this.doGet(req, resp); } else { long ifModifiedSince; try { ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader("If-Modified-Since"); } catch (IllegalArgumentException var9) { ifModifiedSince = -1L; } if(ifModifiedSince < lastModified / 1000L * 1000L) { this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified); this.doGet(req, resp); } else { resp.setStatus(304); } } } else if(method.equals("HEAD")) { lastModified = this.getLastModified(req); this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified); this.doHead(req, resp); } else if(method.equals("POST")) { this.doPost(req, resp); } else if(method.equals("PUT")) { this.doPut(req, resp); } else if(method.equals("DELETE")) { this.doDelete(req, resp); } else if(method.equals("OPTIONS")) { this.doOptions(req, resp); } else if(method.equals("TRACE")) { this.doTrace(req, resp); } else { String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented"); Object[] errArgs = new Object[]{method}; errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs); resp.sendError(501, errMsg); } }
以上是关于Servlet源码级别进行详解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章