TensorFlow训练MNIST数据集 —— 卷积神经网络
Posted laishenghao
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了TensorFlow训练MNIST数据集 —— 卷积神经网络相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前面两篇随笔实现的单层神经网络 和多层神经网络, 在MNIST测试集上的正确率分别约为90%和96%。在换用多层神经网络后,正确率已有很大的提升。这次将采用卷积神经网络继续进行测试。
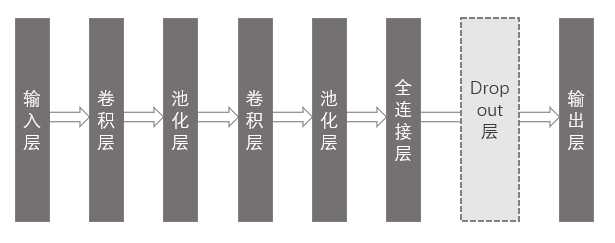
1、模型基本结构
如下图所示,本次采用的模型共有8层(包含dropout层)。其中卷积层和池化层各有两层。
在整个模型中,输入层负责数据输入;卷积层负责提取图片的特征;池化层采用最大池化的方式,突出主要特征,并减少参数维度;全连接层再将个特征组合起来;dropout层可以减少每次训练的计算量,并可以一定程度上避免过拟合问题;最后输出层再综合各特征数据,得出最终结果。
Dropout层起始并没有增加训练参数,只是随机的将某些节点间的连接弧断开,使其在本次中暂时的不参与训练。
2、数据预处理
首先读取用于训练的数据。
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets(‘./data/mnist‘, one_hot=True)
在前面的输入层中,输入的每个样本都是一维的数据,而卷积神经网络的样本数据将是多维的。因此我们需要将读取到的数据再reshape一下,使其符合要求。
data.reshape([batchSize, 28, 28, 1])
3、输入层
输入层的shape为:bitchSize * 28 * 28 * 1,第一个参数表示每个mini-batch的样本数量,由传入None可以让TensorFlow自动推断;后面三个参数表示每个样本的高为28,宽为28,通道数为1。
inputLayer = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 28, 28, 1])
4、卷积层
第一个卷积层的卷积核大小为5 * 5,数量为32个。padding方式采用‘SAME’。第二个卷积层类似,只是通道数,输出维度不一样。
1 convFilter1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, 1, 32], mean=0, stddev=0.1)) 2 convBias1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([32], mean=0, stddev=0.1)) 3 convLayer1 = tf.nn.conv2d(input=inputLayer, filter=convFilter1, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) 4 convLayer1 = tf.add(convLayer1, convBias1) 5 convLayer1 = tf.nn.relu(convLayer1)
5、池化层
滑动窗口的大小为 2 * 2,在高和宽的维度上的滑动步幅也为2,其他维度为1。本模型中第二个池化层与第一个池化层一样。
poolLayer1 = tf.nn.max_pool(value=convLayer1, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding=‘SAME‘)
6、全连接层
全连接层将前面在每个样本中提取到的多维特征展开成一维,作为全连接层的输入。
1 fullWeight = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[7 * 7 * 64, 1024], mean=0, stddev=0.1)) 2 fullBias = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[1024], mean=0.0, stddev=0.1)) 3 fullInput = tf.reshape(poolLayer2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64]) 4 fullLayer = tf.add(tf.matmul(fullInput, fullWeight), fullBias) 5 fullLayer = tf.nn.relu(fullLayer)
7、Dropout层
dropout层可以防止过拟合问题。这里指定的保留率为0.8。
dropLayer = tf.nn.dropout(fullLayer, keep_prob=0.8)
8、输出层
最终输出10个数字的分类。
1 outputWeight = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[1024, 10], mean=0.0, stddev=0.1)) 2 outputBias = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[10], mean=0, stddev=0.1)) 3 outputLayer = tf.add(tf.matmul(dropLayer, outputWeight), outputBias)
模型的其他部分与前面的多层神经网络差不多,这里不再赘述。
9、模型在训练集与测试集上的表现
从模型图上可以看到,本次采用的模型的复杂度比前面的多层神经网络高很多。正因如此,每次迭代计算也比前面的耗时的多,后者单次耗时为前者的1500多倍。可见虽然只增加了几层(当然除了层数的增加还有节点数的增加),但增加的计算量非常的多。
下面两张图为卷积神经网络前面部分和后面部分迭代的输出结果,可以发现到最后卷积神经网络在训练集上已经接近100%的准确率。
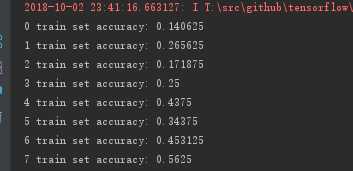
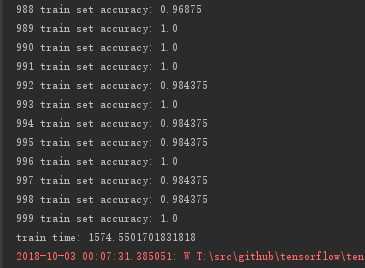
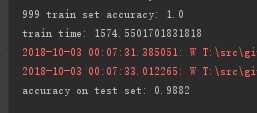
在测试集上的准确率也达到了 98% 到 99%,比多层神经网络提供了约2个百分点。
附:
完整代码如下:

1 import tensorflow as tf 2 from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data 3 import time 4 5 # 读取数据 6 mnist = input_data.read_data_sets(‘./data/mnist‘, one_hot=True) 7 8 # 输入层 9 inputLayer = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 28, 28, 1]) 10 11 # 卷积层(1) 12 convFilter1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, 1, 32], mean=0, stddev=0.1)) 13 convBias1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([32], mean=0, stddev=0.1)) 14 convLayer1 = tf.nn.conv2d(input=inputLayer, filter=convFilter1, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) 15 convLayer1 = tf.add(convLayer1, convBias1) 16 convLayer1 = tf.nn.relu(convLayer1) 17 18 # 池化层(1) 19 poolLayer1 = tf.nn.max_pool(value=convLayer1, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) 20 21 # 卷积层(2) 22 convFilter2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, 32, 64], mean=0, stddev=0.1)) 23 convBias2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([64], mean=0, stddev=0.1)) 24 convLayer2 = tf.nn.conv2d(input=poolLayer1, filter=convFilter2, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) 25 convLayer2 = tf.add(convLayer2, convBias2) 26 convLayer2 = tf.nn.relu(convLayer2) 27 28 # 池化层(2) 29 poolLayer2 = tf.nn.max_pool(value=convLayer2, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) 30 31 # 全连接层 32 fullWeight = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[7 * 7 * 64, 1024], mean=0, stddev=0.1)) 33 fullBias = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[1024], mean=0.0, stddev=0.1)) 34 fullInput = tf.reshape(poolLayer2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64]) 35 fullLayer = tf.add(tf.matmul(fullInput, fullWeight), fullBias) 36 fullLayer = tf.nn.relu(fullLayer) 37 38 # dropout层 39 dropLayer = tf.nn.dropout(fullLayer, keep_prob=0.8) 40 41 # 输出层 42 outputWeight = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[1024, 10], mean=0.0, stddev=0.1)) 43 outputBias = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[10], mean=0, stddev=0.1)) 44 outputLayer = tf.add(tf.matmul(dropLayer, outputWeight), outputBias) 45 46 # 标签 47 outputLabel = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 10]) 48 49 # 损失函数及目标函数 50 loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2(labels=outputLabel, logits=outputLayer)) 51 target = tf.train.AdamOptimizer().minimize(loss) 52 53 # 记录起始训练时间 54 startTime = time.time() 55 56 # 训练 57 with tf.Session() as sess: 58 sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) 59 batchSize = 64 60 for i in range(1000): 61 batch = mnist.train.next_batch(batchSize) 62 inputData = batch[0].reshape([batchSize, 28, 28, 1]) 63 labelData = batch[1] 64 sess.run([target, loss], feed_dict={inputLayer: inputData, outputLabel: labelData}) 65 66 corrected = tf.equal(tf.argmax(outputLabel, 1), tf.argmax(outputLayer, 1)) 67 accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(corrected, tf.float32)) 68 accuracyValue = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={inputLayer: inputData, outputLabel: labelData}) 69 print(i, ‘train set accuracy:‘, accuracyValue) 70 71 # 打印结束时间 72 endTime = time.time() 73 print(‘train time:‘, endTime - startTime) 74 75 # 测试 76 corrected = tf.equal(tf.argmax(outputLabel, 1), tf.argmax(outputLayer, 1)) 77 accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(corrected, tf.float32)) 78 testImages = mnist.test.images.reshape([-1, 28, 28, 1]) 79 testLabels = mnist.test.labels 80 accuracyValue = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={inputLayer: testImages, outputLabel: testLabels}) 81 print("accuracy on test set:", accuracyValue) 82 83 sess.close()
本文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/laishenghao/p/9738912.html
以上是关于TensorFlow训练MNIST数据集 —— 卷积神经网络的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
