MyBatis学习总结——多表关联查询与动态SQL
Posted best
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了MyBatis学习总结——多表关联查询与动态SQL相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、多表关联查询
1.1、一对一关系
1.1.1、执行环境
假定一个员工(emp)拥有一个登录用户(user),员工与用户表之间是一对一关系:
用户表:
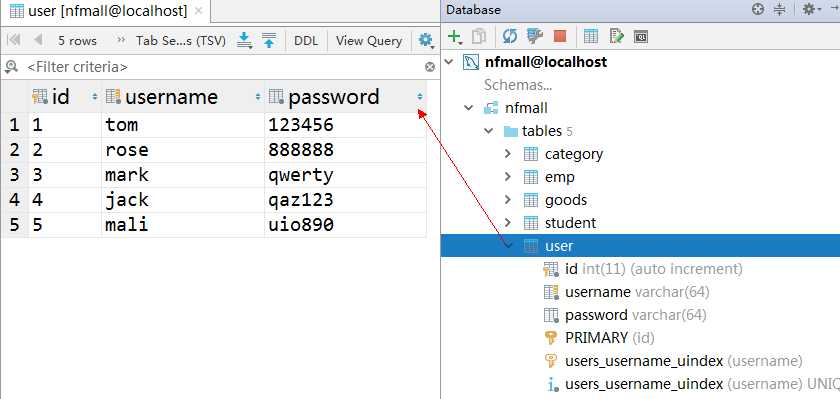
员工表:
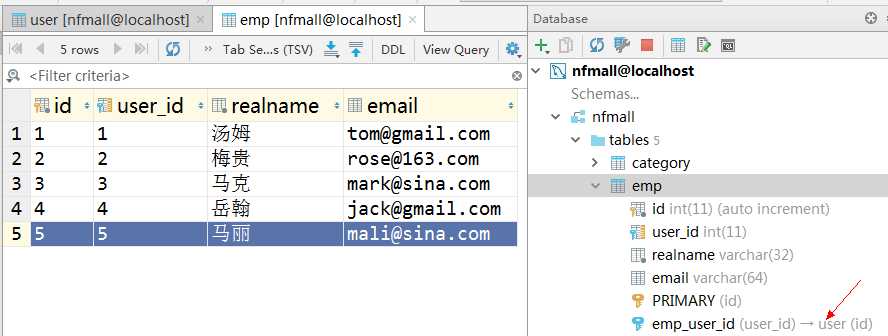
SQL:
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0; -- ---------------------------- -- Table structure for `user` -- ---------------------------- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user`; CREATE TABLE `user` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT ‘编号‘, `username` varchar(64) NOT NULL COMMENT ‘用户名‘, `password` varchar(64) NOT NULL COMMENT ‘密码‘, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), UNIQUE KEY `users_username_uindex` (`username`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=6 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT=‘用户表‘; -- ---------------------------- -- Records of user -- ---------------------------- INSERT INTO `user` VALUES (‘1‘, ‘tom‘, ‘123456‘); INSERT INTO `user` VALUES (‘2‘, ‘rose‘, ‘888888‘); INSERT INTO `user` VALUES (‘3‘, ‘mark‘, ‘qwerty‘); INSERT INTO `user` VALUES (‘4‘, ‘jack‘, ‘qaz123‘); INSERT INTO `user` VALUES (‘5‘, ‘mali‘, ‘uio890‘); SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0; -- ---------------------------- -- Table structure for `emp` -- ---------------------------- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `emp`; CREATE TABLE `emp` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT ‘编号‘, `user_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘用户编号‘, `realname` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT ‘姓名‘, `email` varchar(64) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘邮箱‘, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), KEY `emp_user_id` (`user_id`), CONSTRAINT `emp_user_id` FOREIGN KEY (`user_id`) REFERENCES `user` (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=7 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT=‘员工表‘; -- ---------------------------- -- Records of emp -- ---------------------------- INSERT INTO `emp` VALUES (‘1‘, ‘1‘, ‘汤姆‘, ‘[email protected]‘); INSERT INTO `emp` VALUES (‘2‘, ‘2‘, ‘梅贵‘, ‘[email protected]‘); INSERT INTO `emp` VALUES (‘3‘, ‘3‘, ‘马克‘, ‘[email protected]‘); INSERT INTO `emp` VALUES (‘4‘, ‘4‘, ‘岳翰‘, ‘[email protected]‘); INSERT INTO `emp` VALUES (‘5‘, ‘5‘, ‘马丽‘, ‘[email protected]‘);
关系:
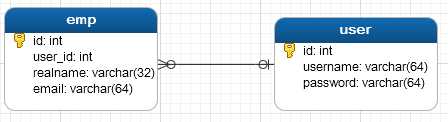
1.1.2、关联查询(1次查询)
实体:
用户:
package com.zhangguo.mybatis03.entities; /**用户POJO*/ public class User { private int id; private String username; private String password; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } }
员工:
package com.zhangguo.mybatis03.entities; /**员工POJO*/ public class Emp { private int id; /**用户编号*/ private int user_id; private String realname; private String email; /**用户对象*/ private User user; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public int getUser_id() { return user_id; } public void setUser_id(int user_id) { this.user_id = user_id; } public String getRealname() { return realname; } public void setRealname(String realname) { this.realname = realname; } public String getEmail() { return email; } public void setEmail(String email) { this.email = email; } public User getUser() { return user; } public Emp setUser(User user) { this.user = user; return this; } }
接口:
package com.zhangguo.mybatis03.dao; import com.zhangguo.mybatis03.entities.Emp; /**员工数据访口*/ public interface EmpMapper { /**获得员工通过员工编号*/ Emp getEmpById_1(int id); }
映射:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.zhangguo.mybatis03.dao.EmpMapper"> <!--一对一查询,方法1,通过内联接--> <select id="getEmpById_1" resultMap="empMap_1" parameterType="int"> SELECT emp.id, emp.user_id, emp.realname, emp.email, `user`.username, `user`.`password` FROM emp INNER JOIN `user` ON emp.user_id = `user`.id where emp.id=#{id} </select> <!--员工关联查询结果映射--> <resultMap id="empMap_1" type="Emp"> <id property="id" column="id"></id> <result property="user_id" column="user_id"></result> <result property="realname" column="realname"></result> <result property="email" column="email"></result> <!--映射关系,指定属性与属性的类型--> <association property="user" javaType="User"> <id property="id" column="user_id"></id> <result property="username" column="username"></result> <result property="password" column="password"></result> </association> </resultMap> </mapper>
参数:

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <!-- 为这个mapper指定一个唯一的namespace,namespace的值习惯上设置成包名+sql映射文件名,这样就能够保证namespace的值是唯一的 例如namespace="me.gacl.mapping.classMapper"就是me.gacl.mapping(包名)+classMapper(classMapper.xml文件去除后缀) --> <mapper namespace="me.gacl.mapping.classMapper"> <!-- 根据班级id查询班级信息(带老师的信息) ##1. 联表查询 SELECT * FROM class c,teacher t WHERE c.teacher_id=t.t_id AND c.c_id=1; ##2. 执行两次查询 SELECT * FROM class WHERE c_id=1; //teacher_id=1 SELECT * FROM teacher WHERE t_id=1;//使用上面得到的teacher_id --> <!-- 方式一:嵌套结果:使用嵌套结果映射来处理重复的联合结果的子集 封装联表查询的数据(去除重复的数据) select * from class c, teacher t where c.teacher_id=t.t_id and c.c_id=1 --> <select id="getClass" parameterType="int" resultMap="ClassResultMap"> select * from class c, teacher t where c.teacher_id=t.t_id and c.c_id=#{id} </select> <!-- 使用resultMap映射实体类和字段之间的一一对应关系 --> <resultMap type="me.gacl.domain.Classes" id="ClassResultMap"> <id property="id" column="c_id"/> <result property="name" column="c_name"/> <association property="teacher" javaType="me.gacl.domain.Teacher"> <id property="id" column="t_id"/> <result property="name" column="t_name"/> </association> </resultMap> <!-- 方式二:嵌套查询:通过执行另外一个SQL映射语句来返回预期的复杂类型 SELECT * FROM class WHERE c_id=1; SELECT * FROM teacher WHERE t_id=1 //1 是上一个查询得到的teacher_id的值 --> <select id="getClass2" parameterType="int" resultMap="ClassResultMap2"> select * from class where c_id=#{id} </select> <!-- 使用resultMap映射实体类和字段之间的一一对应关系 --> <resultMap type="me.gacl.domain.Classes" id="ClassResultMap2"> <id property="id" column="c_id"/> <result property="name" column="c_name"/> <association property="teacher" column="teacher_id" select="getTeacher"/> </resultMap> <select id="getTeacher" parameterType="int" resultType="me.gacl.domain.Teacher"> SELECT t_id id, t_name name FROM teacher WHERE t_id=#{id} </select> </mapper>
测试:
package com.zhangguo.mybatis03.dao; import com.zhangguo.mybatis03.entities.Emp; import org.junit.Assert; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.After; /** * EmpDao Tester. * * @author <Authors name> * @version 1.0 * @since <pre>09/30/2018</pre> */ public class EmpDaoTest { EmpMapper empDao; @Before public void before() throws Exception { empDao=new EmpDao(); } @After public void after() throws Exception { } /** * Method: getEmpById_1(int id) * 获得员工通过员工编号 */ @Test public void testGetEmpById_1() throws Exception { Emp entity=empDao.getEmpById_1(1); System.out.println(entity); Assert.assertNotNull(entity); } }
结果:
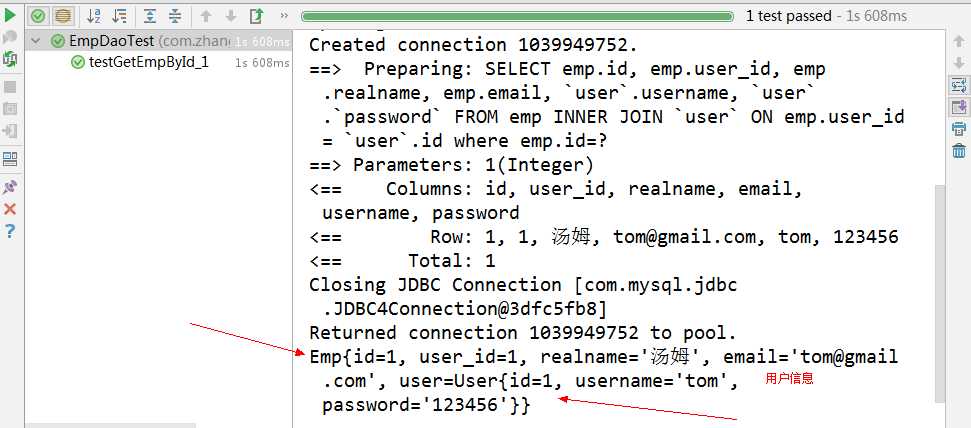
1.1.3、嵌套查询(2次查询)
实体:同上
接口:
/**获得员工通过员工编号,多次查询*/ Emp getEmpById_2(int id);
映射:
<!--一对一查询,方法2,通过多次查询(嵌套查询)--> <select id="getEmpById_2" resultMap="empMap_2"> SELECT emp.id, emp.user_id, emp.realname, emp.email FROM emp where id=#{id} </select> <!--员工多次查询结果映射--> <resultMap id="empMap_2" type="Emp"> <id property="id" column="id"></id> <result property="user_id" column="user_id"></result> <result property="realname" column="realname"></result> <result property="email" column="email"></result> <!--通过外键user_id再次发起查询,调用selectUserById获得User对象--> <association property="user" column="user_id" select="selectUserById"></association> </resultMap> <!--根据用户编号获得用户对象--> <select id="selectUserById" resultType="User"> SELECT `user`.id, `user`.username, `user`.`password` FROM `user` where id=#{id} </select>
测试:
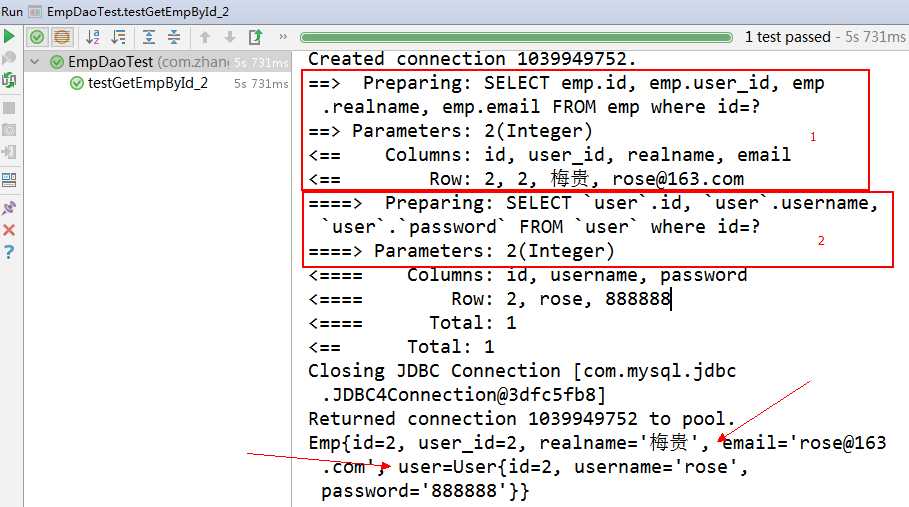
/** * Method: getEmpById_2(int id) * 获得员工通过员工编号,一对一方法二 */ @Test public void testGetEmpById_2() throws Exception { Emp entity=empDao.getEmpById_2(2); System.out.println(entity); Assert.assertNotNull(entity); }
结果:
MyBatis中使用association标签来解决一对一的关联查询,association标签可用的属性如下:
- property:对象属性的名称
- javaType:对象属性的类型
- column:所对应的外键字段名称
- select:使用另一个查询封装的结果
1.2、一对多关系
1.2.1、执行环境
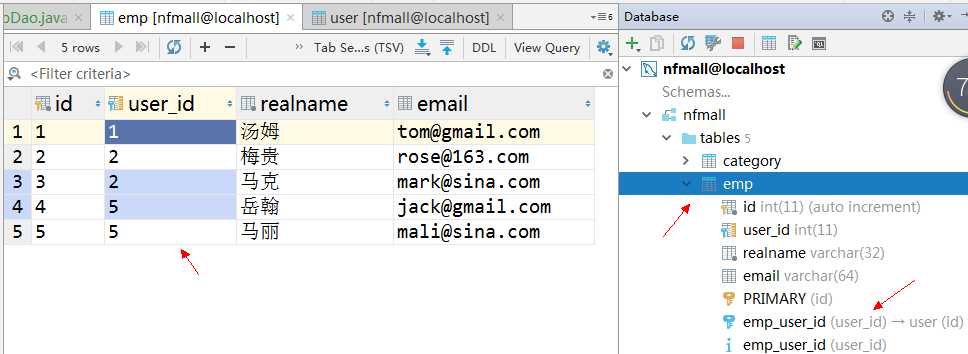
一个用户帐号可以被多个员工使用,形成一个一对多的关系,表中的数据如下:
员工表emp:
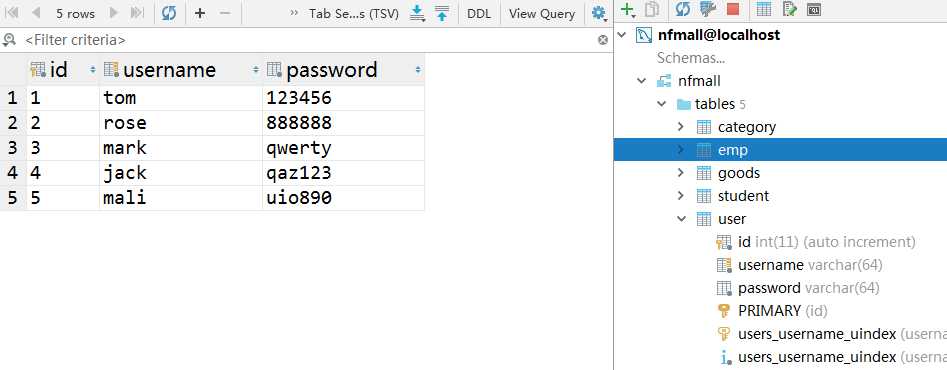
用户表user:
1.2.2、关联查询(1次查询)
实体:
员工:
package com.zhangguo.mybatis03.entities; /**员工POJO*/ public class Emp { private int id; /**用户编号*/ private int user_id; private String realname; private String email; /**用户对象*/ private User user; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public int getUser_id() { return user_id; } public void setUser_id(int user_id) { this.user_id = user_id; } public String getRealname() { return realname; } public void setRealname(String realname) { this.realname = realname; } public String getEmail() { return email; } public void setEmail(String email) { this.email = email; } public User getUser() { return user; } public Emp setUser(User user) { this.user = user; return this; } @Override public String toString() { return "Emp{" + "id=" + id + ", user_id=" + user_id + ", realname=‘" + realname + ‘‘‘ + ", email=‘" + email + ‘‘‘ + ", user=" + user + ‘}‘; } }
用户:
package com.zhangguo.mybatis03.entities; import java.util.List; /**用户POJO*/ public class User { private int id; private String username; private String password; /**员工集合,一个用户对象对应多个员工对象*/ private List<Emp> emps; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public List<Emp> getEmps() { return emps; } public User setEmps(List<Emp> emps) { this.emps = emps; return this; } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "id=" + id + ", username=‘" + username + ‘‘‘ + ", password=‘" + password + ‘‘‘ + ", emps=" + emps + ‘}‘; } }
接口:
/**获得用户通过用户编号,1对多级联查询*/ User getUserById_1(int id);
映射:
<!--一对多查询,方法1,通过内联接--> <select id="getUserById_1" resultMap="userMap_1" parameterType="int"> SELECT emp.id, emp.user_id, emp.realname, emp.email, `user`.username, `user`.`password` FROM emp INNER JOIN `user` ON emp.user_id = `user`.id where `user`.id=#{id} </select> <resultMap id="userMap_1" type="User"> <id property="id" column="user_id"></id> <result property="username" column="username"></result> <result property="password" column="password"></result> <collection property="emps" ofType="Emp"> <id property="id" column="id"></id> <result property="user_id" column="user_id"></result> <result property="realname" column="realname"></result> <result property="email" column="email"></result> </collection> </resultMap>
参考:

<!-- 根据classId查询对应的班级信息,包括学生,老师 --> <!-- 方式一: 嵌套结果: 使用嵌套结果映射来处理重复的联合结果的子集 SELECT * FROM class c, teacher t,student s WHERE c.teacher_id=t.t_id AND c.C_id=s.class_id AND c.c_id=1 --> <select id="getClass3" parameterType="int" resultMap="ClassResultMap3"> select * from class c, teacher t,student s where c.teacher_id=t.t_id and c.C_id=s.class_id and c.c_id=#{id} </select> <resultMap type="me.gacl.domain.Classes" id="ClassResultMap3"> <id property="id" column="c_id"/> <result property="name" column="c_name"/> <association property="teacher" column="teacher_id" javaType="me.gacl.domain.Teacher"> <id property="id" column="t_id"/> <result property="name" column="t_name"/> </association> <!-- ofType指定students集合中的对象类型 --> <collection property="students" ofType="me.gacl.domain.Student"> <id property="id" column="s_id"/> <result property="name" column="s_name"/> </collection> </resultMap> <!-- 方式二:嵌套查询:通过执行另外一个SQL映射语句来返回预期的复杂类型 SELECT * FROM class WHERE c_id=1; SELECT * FROM teacher WHERE t_id=1 //1 是上一个查询得到的teacher_id的值 SELECT * FROM student WHERE class_id=1 //1是第一个查询得到的c_id字段的值 --> <select id="getClass4" parameterType="int" resultMap="ClassResultMap4"> select * from class where c_id=#{id} </select> <resultMap type="me.gacl.domain.Classes" id="ClassResultMap4"> <id property="id" column="c_id"/> <result property="name" column="c_name"/> <association property="teacher" column="teacher_id" javaType="me.gacl.domain.Teacher" select="getTeacher2"></association> <collection property="students" ofType="me.gacl.domain.Student" column="c_id" select="getStudent"></collection> </resultMap> <select id="getTeacher2" parameterType="int" resultType="me.gacl.domain.Teacher"> SELECT t_id id, t_name name FROM teacher WHERE t_id=#{id} </select> <select id="getStudent" parameterType="int" resultType="me.gacl.domain.Student"> SELECT s_id id, s_name name FROM student WHERE class_id=#{id} </select>
测试:
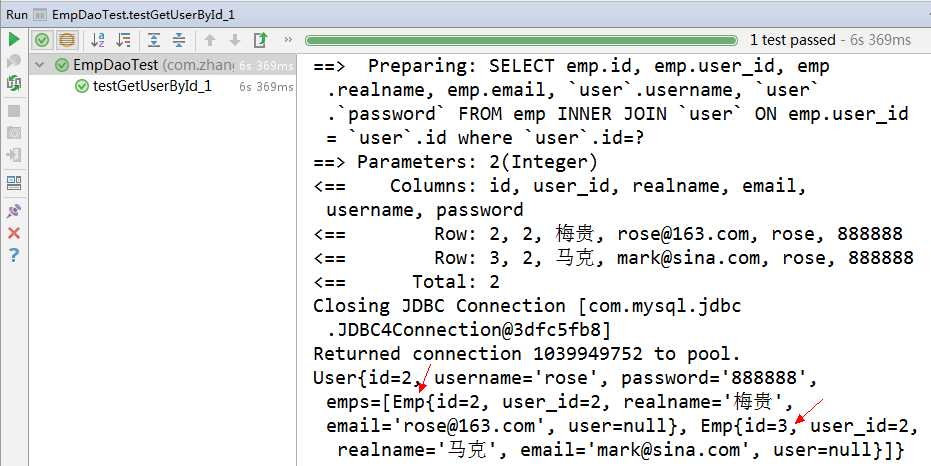
/** * Method: getUserById_1(int id) * 获得用户过用户编号,级联查询 */ @Test public void testGetUserById_1() throws Exception { User entity=empDao.getUserById_1(2); System.out.println(entity); Assert.assertNotNull(entity); }
结果:
1.1.3、嵌套查询(2次查询)
实体:
接口:
映射:
测试:
结果:
MyBatis中使用collection标签来解决一对多的关联查询,ofType属性指定集合中元素的对象类型。
二、动态SQL
2.1、什么是动态SQL
MyBatis的动态SQL是基于OGNL的表达式的。它对SQL语句进行灵活的操作,通过表达式判断来实现对SQL的灵活拼接、组装。
mybatis核心对sql语句进行灵活操作,通过表达式进行判断,对sql进行灵活拼接、组装。
主要通过以下标签:if,where,choose(when,otherwise),trim,set,foreach。
2.2、if条件判断
根据 username 和 sex 来查询数据。如果username为空,那么将只根据sex来查询;反之只根据username来查询
首先不使用 动态SQL 来书写
<select id="selectUserByUsernameAndSex" resultType="user" parameterType="com.ys.po.User"> <!-- 这里和普通的sql 查询语句差不多,对于只有一个参数,后面的 #{id}表示占位符,里面不一定要写id, 写啥都可以,但是不要空着,如果有多个参数则必须写pojo类里面的属性 --> select * from user where username=#{username} and sex=#{sex} </select>
上面的查询语句,我们可以发现,如果 #{username} 为空,那么查询结果也是空,如何解决这个问题呢?使用 if 来判断
<select id="selectUserByUsernameAndSex" resultType="user" parameterType="com.ys.po.User"> select * from user where <if test="username != null"> username=#{username} </if> <if test="username != null"> and sex=#{sex} </if> </select>
<!-- 2 if(判断参数) - 将实体类不为空的属性作为where条件 --> <select id="getStudentList_if" resultMap="resultMap_studentEntity" parameterType="liming.student.manager.data.model.StudentEntity"> SELECT ST.STUDENT_ID, ST.STUDENT_NAME, ST.STUDENT_SEX, ST.STUDENT_BIRTHDAY, ST.STUDENT_PHOTO, ST.CLASS_ID, ST.PLACE_ID FROM STUDENT_TBL ST WHERE <if test="studentName !=null "> ST.STUDENT_NAME LIKE CONCAT(CONCAT(‘%‘, #{studentName, jdbcType=VARCHAR}),‘%‘) </if> <if test="studentSex != null and studentSex != ‘‘ "> AND ST.STUDENT_SEX = #{studentSex, jdbcType=INTEGER} </if> <if test="studentBirthday != null "> AND ST.STUDENT_BIRTHDAY = #{studentBirthday, jdbcType=DATE} </if> <if test="classId != null and classId!= ‘‘ "> AND ST.CLASS_ID = #{classId, jdbcType=VARCHAR} </if> <if test="classEntity != null and classEntity.classId !=null and classEntity.classId !=‘ ‘ "> AND ST.CLASS_ID = #{classEntity.classId, jdbcType=VARCHAR} </if> <if test="placeId != null and placeId != ‘‘ "> AND ST.PLACE_ID = #{placeId, jdbcType=VARCHAR} </if> <if test="placeEntity != null and placeEntity.placeId != null and placeEntity.placeId != ‘‘ "> AND ST.PLACE_ID = #{placeEntity.placeId, jdbcType=VARCHAR} </if> <if test="studentId != null and studentId != ‘‘ "> AND ST.STUDENT_ID = #{studentId, jdbcType=VARCHAR} </if> </select>
这样写我们可以看到,如果 sex 等于 null,那么查询语句为 select * from user where username=#{username},但是如果usename 为空呢?那么查询语句为 select * from user where and sex=#{sex},这是错误的 SQL 语句,如何解决呢?请看下面的 where 语句
2.3、if+where条件
<select id="selectUserByUsernameAndSex" resultType="user" parameterType="com.ys.po.User"> select * from user <where> <if test="username != null"> username=#{username} </if> <if test="username != null"> and sex=#{sex} </if> </where> </select>
这个“where”标签会知道如果它包含的标签中有返回值的话,它就插入一个‘where’。此外,如果标签返回的内容是以AND 或OR 开头的,则它会剔除掉。
2.4、if+set设置值
当update语句中没有使用if标签时,如果有一个参数为null,都会导致错误。
当在update语句中使用if标签时,如果前面的if没有执行,则或导致逗号多余错误。使用set标签可以将动态的配置SET 关键字,和剔除追加到条件末尾的任何不相关的逗号。如果set包含的内容为空的话则会出错。
使用if+set标签修改后,如果某项为null则不进行更新,而是保持数据库原值。
同理,上面的对于查询 SQL 语句包含 where 关键字,如果在进行更新操作的时候,含有 set 关键词,我们怎么处理呢?
<!-- 根据 id 更新 user 表的数据 --> <update id="updateUserById" parameterType="com.ys.po.User"> update user u <set> <if test="username != null and username != ‘‘"> u.username = #{username}, </if> <if test="sex != null and sex != ‘‘"> u.sex = #{sex} </if> </set> where id=#{id} </update>
这样写,如果第一个条件 username 为空,那么 sql 语句为:update user u set u.sex=? where id=?
如果第一个条件不为空,那么 sql 语句为:update user u set u.username = ? ,u.sex = ? where id=?
2.5、choose(when,otherwise) 开关
有时候,我们不想用到所有的查询条件,只想选择其中的一个,查询条件有一个满足即可,使用 choose 标签可以解决此类问题,类似于 Java 的 switch 语句
<select id="selectUserByChoose" resultType="com.ys.po.User" parameterType="com.ys.po.User"> select * from user <where> <choose> <when test="id !=‘‘ and id != null"> id=#{id} </when> <when test="username !=‘‘ and username != null"> and username=#{username} </when> <otherwise> and sex=#{sex} </otherwise> </choose> </where> </select>
也就是说,这里我们有三个条件,id,username,sex,只能选择一个作为查询条件
如果 id 不为空,那么查询语句为:select * from user where id=?
如果 id 为空,那么看username 是否为空,如果不为空,那么语句为 select * from user where username=?;
如果 username 为空,那么查询语句为 select * from user where sex=?
2.6、trim裁剪
trim标记是一个格式化的标记,可以完成set或者是where标记的功能
①、用 trim 改写上面第二点的 if+where 语句
<select id="selectUserByUsernameAndSex" resultType="user" parameterType="com.ys.po.User"> select * from user <!-- <where> <if test="username != null"> username=#{username} </if> <if test="username != null"> and sex=#{sex} </if> </where> --> <trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and | or"> <if test="username != null"> and username=#{username} </if> <if test="sex != null"> and sex=#{sex} </if> </trim> </select>
prefix:前缀
prefixoverride:去掉第一个and或者是or
②、用 trim 改写上面第三点的 if+set 语句
<!-- 根据 id 更新 user 表的数据 --> <update id="updateUserById" parameterType="com.ys.po.User"> update user u <!-- <set> <if test="username != null and username != ‘‘"> u.username = #{username}, </if> <if test="sex != null and sex != ‘‘"> u.sex = #{sex} </if> </set> --> <trim prefix="set" suffixOverrides=","> <if test="username != null and username != ‘‘"> u.username = #{username}, </if> <if test="sex != null and sex != ‘‘"> u.sex = #{sex}, </if> </trim> where id=#{id} </update>
suffix:后缀
suffixoverride:去掉最后一个逗号(也可以是其他的标记,就像是上面前缀中的and一样)
十分强大!可以自定义添加前后缀,与之对应的属性是prefix和suffix。同时通过prefixOverrides和suffixOverrides分别来覆盖首尾部的内容,即忽略不必要的前后缀。就是说它可以充当where标签,也可以充当set标签啦~
例:
充当where标签:
<trim prefix = "where" prefixOverrides="and|or" > ... </trim>
充当set标签:
<trim prefix="set" suffixOverrides=","> ... </trim>
例子:动态添加用户属性
<insert id="find" resultType="Admin"> insert into admin <trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=","> <if test = "aname != null and aname !=‘‘ "> aname, </if> <if test = "city != null and city !=‘‘ "> city, </if> <if test = "age != null and age !=‘‘ "> age, </if> </trim> <trim prefix="values(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=","> <if test = "aname != null and aname !=‘‘ "> #{aname}, </if> <if test = "city != null and city !=‘‘ "> #{city}, </if> <if test = "age != null and age !=‘‘ "> #{age}, </if> </trim> </insert>
上面相应的语句为:insert into admin (…) values(…);。通过trim标签用()包裹,以及自动忽略尾部的逗号。
2.7、SQL 片段
有时候可能某个 sql 语句我们用的特别多,为了增加代码的重用性,简化代码,我们需要将这些代码抽取出来,然后使用时直接调用。
比如:假如我们需要经常根据用户名和性别来进行联合查询,那么我们就把这个代码抽取出来,如下:
<!-- 定义 sql 片段 --> <sql id="selectUserByUserNameAndSexSQL"> <if test="username != null and username != ‘‘"> AND username = #{username} </if> <if test="sex != null and sex != ‘‘"> AND sex = #{sex} </if> </sql>
引用 sql 片段
<select id="selectUserByUsernameAndSex" resultType="user" parameterType="com.ys.po.User"> select * from user <trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and | or"> <!-- 引用 sql 片段,如果refid 指定的不在本文件中,那么需要在前面加上 namespace --> <include refid="selectUserByUserNameAndSexSQL"></include> <!-- 在这里还可以引用其他的 sql 片段 --> </trim> </select>
注意:①、最好基于 单表来定义 sql 片段,提高片段的可重用性
②、在 sql 片段中不要包括 where
2.8、foreach循环
foreach的主要用在构建in条件中,他可以迭代一个集合。foreach元素的属性主要有:item,index,collection,open,separator,close。
下面对属性进行简单的介绍:
item:表示集合中每一个元素进行迭代时的别名。
index:指定一个名字,用于表示在迭代过程中每次迭代的位置。
open:表示以什么开始。
separator:每次迭代以什么分割。
close:以什么关闭。
collection:最重要且必须指定的有三种情况:
1.如果传入的是单独参数的List类型时,collection的属性值为list。
2.如果传入的是单独参数的数组时,collection的属性值为array。
3.如果传入多个参数时,我们把多个参数放入map中,单参数也可以放入map中。map中的key就是参数名,所以collection属性值就是传入的List或者array对象在Map里的key。
需求:我们需要查询 user 表中 id 分别为1,2,3的用户
sql语句:select * from user where id=1 or id=2 or id=3
select * from user where id in (1,2,3)
①、建立一个 UserVo 类,里面封装一个 List<Integer> ids 的属性
package com.ys.vo; import java.util.List; public class UserVo { //封装多个用户的id private List<Integer> ids; public List<Integer> getIds() { return ids; } public void setIds(List<Integer> ids) { this.ids = ids; } }
②、我们用 foreach 来改写 select * from user where id=1 or id=2 or id=3
<select id="selectUserByListId" parameterType="com.ys.vo.UserVo" resultType="com.ys.po.User"> select * from user <where> <!-- collection:指定输入对象中的集合属性 item:每次遍历生成的对象 open:开始遍历时的拼接字符串 close:结束时拼接的字符串 separator:遍历对象之间需要拼接的字符串 select * from user where 1=1 and (id=1 or id=2 or id=3) --> <foreach collection="ids" item="id" open="and (" close=")" separator="or"> id=#{id} </foreach> </where> </select>
测试:
//根据id集合查询user表数据 @Test public void testSelectUserByListId(){ String statement = "com.ys.po.userMapper.selectUserByListId"; UserVo uv = new UserVo(); List<Integer> ids = new ArrayList<>(); ids.add(1); ids.add(2); ids.add(3); uv.setIds(ids); List<User> listUser = session.selectList(statement, uv); for(User u : listUser){ System.out.println(u); } session.close(); }
③、我们用 foreach 来改写 select * from user where id in (1,2,3)
<select id="selectUserByListId" parameterType="com.ys.vo.UserVo" resultType="com.ys.po.User"> select * from user <where> <!-- collection:指定输入对象中的集合属性 item:每次遍历生成的对象 open:开始遍历时的拼接字符串 close:结束时拼接的字符串 separator:遍历对象之间需要拼接的字符串 select * from user where 1=1 and id in (1,2,3) --> <foreach collection="ids" item="id" open="and id in (" close=") " separator=","> #{id} </foreach> </where> </select>
其实动态 sql 语句的编写往往就是一个拼接的问题,为了保证拼接准确,我们最好首先要写原生的 sql 语句出来,然后在通过 mybatis 动态sql 对照着改。
参考:

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <!-- namespace的名字需要跟接口的类名一致 --> <mapper namespace="cn.bdqn.dao.UserMapper"> <!-- 1、resultMap属性:type为java实体类;id为此resultMap的标识 2、resultMap的子元素: id – 一般对应到数据库中该行的ID,设置此项可以提高Mybatis性能. result – 映射到JavaBean 的某个“简单类型”属性,String,int等. association – 映射到JavaBean 的某个“复杂类型”属性,其他JavaBean类. collection –复杂类型集合 --> <!--根据roleId获取用户列表: 当数据库中的字段信息与对象的属性不一致时需要通过resultMap来映射 --> <!-- <resultMap type="User" id="seachUserResult"> <result property="id" column="id"/> <result property="userCode" column="userCode"/> <result property="userName" column="userName"/> <result property="roleId" column="roleId"/> <result property="roleName" column="roleName"/> </resultMap> <select id="getUserListByRoleId" parameterType="Role" resultMap="seachUserResult"> select u.*,r.roleName as roleName from user u,role r where u.roleId = r.id and u.roleId = #{id} </select> --> <!-- 根据roleId获取用户列表 association start--> <resultMap type="User" id="seachUserResult"> <result property="id" column="id"/> <result property="userCode" column="userCode" /> <result property="userName" column="userName" /> <result property="roleId" column="roleId" /> <!-- <association property="role" javaType="Role" > <result property="id" column="id"/> <result property="roleCode" column="roleCode"/> <result property="roleName" column="roleName"/> </association> --> <association property="role" javaType="Role" resultMap="roleMap"/> </resultMap> <resultMap type="Role" id="roleMap"> <result property="id" column="id"/> <result property="roleCode" column="roleCode"/> <result property="roleName" column="roleName"/> </resultMap> <select id="getUserListByRoleId" parameterType="Role" resultMap="seachUserResult"> select u.*,r.roleCode as roleCode,r.roleName as roleName from user u,role r where u.roleId = r.id and u.roleId = #{id} </select> <!-- association end--> <!-- 获取指定用户的地址列表(user表-address表:1对多关系) collection start--> <resultMap type="User" id="userMap"> <id property="id" column="userId"/> <collection property="addressList" ofType="Address"> <id property="id" column="a_id"/> <result property="postCode" column="postCode"/> <result property="addressContent" column="addressContent"/> </collection> </resultMap> <select id="getAddressListByUserId" parameterType="User" resultMap="userMap"> select *,a.id as a_id from user u,address a where u.id=a.userId and u.id=#{id} </select> <!-- collection end --> <resultMap type="User" id="seachUser"> <result property="id" column="id"/> <result property="userCode" column="userCode"/> <result property="userName" column="userName"/> <result property="roleId" column="roleId"/> <result property="roleName" column="roleName"/> </resultMap> <!-- <select id="searchUserList" parameterType="User" resultMap="seachUser"> select u.*,r.roleName as roleName from user u,role r where u.roleId = r.id and u.roleId = #{roleId} and u.userCode like CONCAT (‘%‘,#{userCode},‘%‘) //防止sql注入 and u.userName like CONCAT (‘%‘,#{userName},‘%‘) </select> --> <!-- 1、有些时候,sql语句where条件中,需要一些安全判断,例如按性别检索,如果传入的参数是空的,此时查询出的结果很可能是空的,也许我们需要参数为空时,是查出全部的信息。这是我们可以使用动态sql,增加一个判断,当参数不符合要求的时候,我们可以不去判断此查询条件。 2、mybatis 的动态sql语句是基于OGNL表达式的。可以方便的在 sql 语句中实现某些逻辑. 总体说来mybatis 动态SQL 语句主要有以下几类: if 语句 (简单的条件判断) choose (when,otherwize) ,相当于java 语言中的 switch ,与 jstl 中的choose 很类似. trim (对包含的内容加上 prefix,或者 suffix 等,前缀,后缀) where (主要是用来简化sql语句中where条件判断的,能智能的处理 and or ,不必担心多余导致语法错误) set (主要用于更新时) foreach (在实现 mybatis in 语句查询时特别有用) --> <!-- if(判断参数) - 将实体类不为空的属性作为where条件 --> <select id="searchUserList" parameterType="User" resultMap="seachUser"> select u.*,r.roleName as roleName from user u,role r where u.roleId = r.id <if test="roleId!=null"> and u.roleId = #{roleId} </if> <if test="userCode != null"> and u.userCode like CONCAT (‘%‘,#{userCode},‘%‘) </if> <if test="userName != null"> and u.userName like CONCAT (‘%‘,#{userName},‘%‘) </if> </select> <select id="count" resultType="int"> select count(1) from user </select> <insert id="add" parameterType="User"> insert into user (userCode,userName,userPassword) values (#{userCode},#{userName},#{userPassword}) </insert> <!-- if/set(判断参数) - 将实体类不为空的属性更新 --> <!-- <update id="update" parameterType="User"> update user <set> <if test="userCode != null and userCode != ‘‘">userCode=#{userCode},</if> <if test="userName != null">userName=#{userName},</if> <if test="userPassword != null">userPassword=#{userPassword},</if> <if test="roleId != null">roleId=#{roleId}</if> </set> where id=#{id} </update> --> <!-- if/trim代替set(判断参数) - 将实体类不为空的属性更新 --> <update id="update" parameterType="User"> update user <trim prefix="set" suffixOverrides=","> <if test="userCode != null and userCode != ‘‘">userCode=#{userCode},</if> <if test="userName != null">userName=#{userName},</if> <if test="userPassword != null">userPassword=#{userPassword},</if> <if test="roleId != null">roleId=#{roleId}</if> </trim> where id=#{id} </update> <!--注意: 你可以传递一个List实例或者数组作为参数对象传给MyBatis。 当你这么做的时候,MyBatis会自动将它包装在一个Map中,用名称在作为键。 List实例将会以“list”作为键,而数组实例将会以“array”作为键。 配置文件中的parameterType是可以不配置的--> <resultMap type="User" id="userMapByDep"> <result property="id" column="id"/> <result property="userCode" column="userCode"/> <result property="userName" column="userName"/> </resultMap> <!-- foreach(循环array参数) - 作为where中in的条件 --> <select id="getUserByDepId_foreach_array" resultMap="userMapByDep"> select * from user where depId in <foreach collection="array" item="depIds" open="(" separator="," close=")"> #{depIds} </foreach> </select> <!-- foreach(循环List<String>参数) - 作为where中in的条件 --> <select id="getUserByDepId_foreach_list" resultMap="userMapByDep"> select * from user where depId in <foreach collection="list" item="depIdList" open="(" separator="," close=")"> #{depIdList} </foreach> </select> <delete id="delete" parameterType="User"> delete from user where id=#{id} </delete> <select id="getUserList" resultType="User"> select * from user </select> </mapper>
以上是关于MyBatis学习总结——多表关联查询与动态SQL的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
