03-树1 树的同构 (25 分)
Posted interim
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了03-树1 树的同构 (25 分)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
03-树1 树的同构 (25 分)
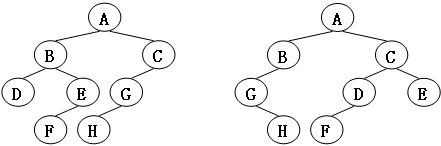
给定两棵树T1和T2。如果T1可以通过若干次左右孩子互换就变成T2,则我们称两棵树是“同构”的。例如图1给出的两棵树就是同构的,因为我们把其中一棵树的结点A、B、G的左右孩子互换后,就得到另外一棵树。而图2就不是同构的。
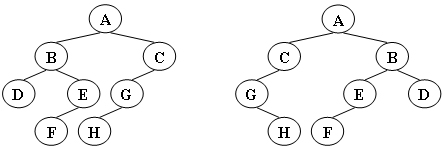
图1
图2
输入格式:
输入给出2棵二叉树树的信息。对于每棵树,首先在一行中给出一个非负整数N (≤10),即该树的结点数(此时假设结点从0到N?1编号);随后N行,第i行对应编号第i个结点,给出该结点中存储的1个英文大写字母、其左孩子结点的编号、右孩子结点的编号。如果孩子结点为空,则在相应位置上给出“-”。给出的数据间用一个空格分隔。注意:题目保证每个结点中存储的字母是不同的。
输出格式:
如果两棵树是同构的,输出“Yes”,否则输出“No”。
输入样例1(对应图1):
8
A 1 2
B 3 4
C 5 -
D - -
E 6 -
G 7 -
F - -
H - -
8
G - 4
B 7 6
F - -
A 5 1
H - -
C 0 -
D - -
E 2 -
输出样例1:
Yes
输入样例2(对应图2):
8
B 5 7
F - -
A 0 3
C 6 -
H - -
D - -
G 4 -
E 1 -
8
D 6 -
B 5 -
E - -
H - -
C 0 2
G - 3
F - -
A 1 4
输出样例2:
No
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Diagnostics; using System.Net; using System.Text; using System.Xml; struct Point { public string C; public string X; public string Y; public Point(string v1, string v2, string v3) : this() { this.C = v1; this.X = v2; this.Y = v3; } } class P { public XmlDocument doc = new XmlDocument(); public P(string v2) : this(int.Parse(v2)) { } List<Point> tempList = new List<Point>(); public P(int v1) { if (v1 > 0) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); for (int i = 0; i < v1; i++) { var temp = Console.ReadLine().Split(new[] { " " }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries); tempList.Add(new Point(temp[0], temp[1], temp[2])); sb.Append(temp[1]); sb.Append(temp[2]); } var item = new Point(); string sss = sb.ToString(); for (int i = 0; i < v1; i++) { if (!sss.Contains(i + "")) { item = tempList[i]; } } var xNode = doc.CreateNode(XmlNodeType.Element, "item", ""); var attr1 = doc.CreateAttribute("x"); attr1.Value = item.X; var attr2 = doc.CreateAttribute("y"); attr2.Value = item.Y; var attr3 = doc.CreateAttribute("n"); attr3.Value = item.C; xNode.Attributes.Append(attr1); xNode.Attributes.Append(attr2); xNode.Attributes.Append(attr3); GetNodes(xNode); doc.AppendChild(xNode); } } private void GetNodes(XmlNode xNode) { int x = -1; int y = -1; if (int.TryParse(xNode.Attributes["x"].Value, out x)) { var item = tempList[x]; var node = doc.CreateNode(XmlNodeType.Element, "item", ""); var attr1 = doc.CreateAttribute("x"); attr1.Value = item.X; var attr2 = doc.CreateAttribute("y"); attr2.Value = item.Y; var attr3 = doc.CreateAttribute("n"); attr3.Value = item.C; node.Attributes.Append(attr1); node.Attributes.Append(attr2); node.Attributes.Append(attr3); GetNodes(node); xNode.AppendChild(node); } if (int.TryParse(xNode.Attributes["y"].Value, out y)) { var item = tempList[y]; var node = doc.CreateNode(XmlNodeType.Element, "item", ""); var attr1 = doc.CreateAttribute("x"); attr1.Value = item.X; var attr2 = doc.CreateAttribute("y"); attr2.Value = item.Y; var attr3 = doc.CreateAttribute("n"); attr3.Value = item.C; node.Attributes.Append(attr1); node.Attributes.Append(attr2); node.Attributes.Append(attr3); GetNodes(node); xNode.AppendChild(node); } } } class T { static bool 对比(XmlNode p1, XmlNode p2) { if (p1.Attributes["n"] .Value== p2.Attributes["n"].Value) { if (p1.ChildNodes.Count == 0 && p2.ChildNodes.Count == 0) { return true; } if (p1.ChildNodes.Count == 1 && p2.ChildNodes.Count == 1) { return 对比(p1.ChildNodes[0], p2.ChildNodes[0]); } if (p1.ChildNodes.Count == 2 && p2.ChildNodes.Count == 2) { var b00 = 对比(p1.ChildNodes[0], p2.ChildNodes[0]); var b11 = 对比(p1.ChildNodes[1], p2.ChildNodes[1]); var b10 = 对比(p1.ChildNodes[1], p2.ChildNodes[0]); var b01 = 对比(p1.ChildNodes[0], p2.ChildNodes[1]); return (b00 && b11) || (b10 && b01); } } return false; } static void Main(string[] args) { P p1 = new P(Console.ReadLine()); P p2 = new P(Console.ReadLine()); if (p1.doc.ChildNodes.Count == 0 && p2.doc.ChildNodes.Count == 0) { Console.WriteLine("Yes"); return; } else { bool b = 对比(p1.doc.ChildNodes[0], p2.doc.ChildNodes[0]); if (b) Console.WriteLine("Yes"); else Console.WriteLine("No"); } } }
以上是关于03-树1 树的同构 (25 分)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章