HDU 5120 Intersection
Posted songorz
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了HDU 5120 Intersection相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Intersection
Time Limit: 4000/4000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 512000/512000 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 4238 Accepted Submission(s): 1623
Problem Description
Matt is a big fan of logo design. Recently he falls in love with logo made up by rings. The following figures are some famous examples you may know.

A ring is a 2-D figure bounded by two circles sharing the common center. The radius for these circles are denoted by r and R (r < R). For more details, refer to the gray part in the illustration below.
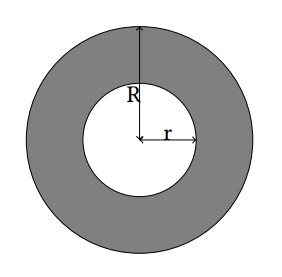
Matt just designed a new logo consisting of two rings with the same size in the 2-D plane. For his interests, Matt would like to know the area of the intersection of these two rings.

A ring is a 2-D figure bounded by two circles sharing the common center. The radius for these circles are denoted by r and R (r < R). For more details, refer to the gray part in the illustration below.

Matt just designed a new logo consisting of two rings with the same size in the 2-D plane. For his interests, Matt would like to know the area of the intersection of these two rings.
Input
The first line contains only one integer T (T ≤ 105), which indicates the number of test cases. For each test case, the first line contains two integers r, R (0 ≤ r < R ≤ 10).
Each of the following two lines contains two integers xi, yi (0 ≤ xi, yi ≤ 20) indicating the coordinates of the center of each ring.
Each of the following two lines contains two integers xi, yi (0 ≤ xi, yi ≤ 20) indicating the coordinates of the center of each ring.
Output
For each test case, output a single line “Case #x: y”, where x is the case number (starting from 1) and y is the area of intersection rounded to 6 decimal places.
Sample Input
2
2 3
0 0
0 0
2 3
0 0
5 0
Sample Output
Case #1: 15.707963
Case #2: 2.250778
Source
Recommend
liuyiding
参考代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define rep(i,a,n) for(int i=a;i<n;++i)
#define per(i,a,n) for(int i=n-1;i>=a;--i)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const double eps = 1e-10;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
const int maxn = 2500; //注意修改
int n;
//有的命名为sgn函数,高精度符号判断
int dcmp(double x)
{
//相等函数判断,减少精度问题
if(fabs(x) < eps) return 0;
else return x < 0 ? -1 : 1;
}
//点的定义
class Point
{
public:
double x, y;
Point(double x = 0, double y = 0): x(x), y(y) {} //构造函数,方便代码的编写
} point[maxn], pafter[maxn];
typedef Point Vector;// 从程序实现上,Vector只是Point的别名
//运算符重载
Vector operator + (const Vector &A, const Vector &B)
{
return Vector(A.x + B.x, A.y + B.y); //向量+向量=向量,点+向量=点
}
Vector operator - (const Vector &A, const Vector &B)
{
return Vector(A.x - B.x, A.y - B.y); //向量-向量=向量,点-向量-点
}
Vector operator * (const Vector &A, double p)
{
return Vector(A.x * p, A.y * p); //向量*数=向量 (数乘)
}
Vector operator / (const Vector &A, double p)
{
return Vector(A.x / p, A.y / p); //向量/数=向量 (数除)
}
double operator * (const Vector &A, const Vector &B)
{
return A.x * B.x + A.y * B.y; //向量(点乘)向量=数 (点乘)
}
bool operator < (const Point &A, const Point &B)
{
return A.x == B.x ? A.y < B.y : A.x < B.x; //按x值递增排序
}
bool operator == (const Point &A, const Point &B)
{
return dcmp(A.x - B.x) == 0 && dcmp(A.y - B.y) == 0; //判定两个点是否相同,用到dcmp精度判定
}
//点乘叉乘
double dot(const Vector &A, const Vector &B)
{
return A.x * B.x + A.y * B.y; //向量(叉乘)向量=向量 (叉乘)
}
double operator ^ (const Vector &A, const Vector &B)
{
return A.x * B.y - A.y * B.x;
}
double cross(const Vector &A, const Vector &B)
{
return A.x * B.y - A.y * B.x;
}
//模长面积
double abs(const Vector &A)
{
return sqrt(dot(A, A)); //计算向量模长
}
double area2(const Point &A, const Point &B, const Point &C)
{
return cross(B - A, C - A) ; //计算平行四边形方向面积
}
double PolygonArea(Point *p, int n)
{
double area = 0; //计算多边形的有向面积
rep(i, 1, n - 1)
{
area += cross(p[i] - p[0], p[i + 1] - p[0]);
}
return area / 2.0;
}
//旋转
Vector rotate(Vector A, double rad)
{
return Vector(A.x * cos(rad) - A.y * sin(rad), A.x * sin(rad) + A.y * cos(rad)); //旋转rad弧度
}
Vector normal(Vector A)
{
double l = abs(A); //计算单位法线,左转90
return Vector(-A.y / l, A.x / l);
}
double torad(double deg)
{
return deg / 180 * acos(-1); //角度转弧度
}
//线段定义
class Line
{
public:
Point s, e;
Line() {}
Line(Point _s, Point _e)
{
s = _s;
e = _e;
}
} line[maxn];
bool inter(Line l1, Line l2)
{
return (
max(l1.s.x, l1.e.x) >= min(l2.s.x, l2.e.x) &&
max(l2.s.x, l2.e.x) >= min(l1.s.x, l1.e.x) &&
max(l1.s.y, l1.e.y) >= min(l2.s.y, l2.e.y) &&
max(l2.s.y, l2.e.y) >= min(l1.s.y, l1.e.y) &&
dcmp((l2.s - l1.s) ^ (l1.s - l1.e)) * dcmp((l2.e-l1.s) ^ (l1.s - l1.e)) < 0 &&
dcmp((l1.s - l2.s) ^ (l2.s - l2.e)) * dcmp((l1.e-l2.s) ^ (l2.s - l2.e)) < 0
) ;
}
bool inter(Point a1, Point a2, Point b1, Point b2)
{
Line l1(a1, a2), l2(b1, b2);
return inter(l1, l2);
}
bool cmp(Point a, Point b)
{
if(a.x == b.x) return a.y < b.y;
else return a.x < b.x;
}
double dist(Point a, Point b)
{
return sqrt((a - b) * (a - b));
}
//求两直线交点
Point getinter(Line l1, Line l2)
{
Vector v = l1.s - l1.e;
Vector w = l2.s - l2.e;
Vector u = l1.e-l2.e;
double t = cross(w, u) / cross(v, w);
return l1.e+v * t;
}
Point getinter(Point a1, Point a2, Point b1, Point b2)
{
Line l1(a1, a2);
Line l2(b1, b2);
return getinter(l1, l2);
}
//判定点和线段的关系,
//0:不在线段所在直线上
//1:在线段内(不含端点)
//2:在线段端点
//3:在线段两侧的射线上
int online(Point a, Line l)
{
if(dcmp(cross(l.s - a, l.e-a)) != 0) return 0;
double pans = dcmp(dot(l.s - a, l.e-a));
if(pans < 0) return 1;
else if(pans == 0) return 2;
else if(pans > 0) return 3;
}
int online(Point a, Point b1, Point b2)
{
Line l(b1, b2);
return online(a, l);
}
int sgn(double x)
{
if(fabs(x) < eps) return 0;
if(x < 0) return -1;
else return 1;
}
double Area_of_overlap(Point c1, double r1, Point c2, double r2)
{
double d = dist(c1, c2);
if(r1 + r2 < d + eps) return 0;
if(d < fabs(r1 - r2) + eps)
{
double r = min(r1, r2);
return PI * r * r;
}
double x = (d * d + r1 * r1 - r2 * r2) / (2 * d);
double t1 = acos(x / r1);
double t2 = acos((d - x) / r2);
return r1 * r1 * t1 + r2 * r2 * t2 - d * r1 * sin(t1);
}
int t;
double RR, rr;
double xx1, yy1, xx2, yy2;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> t;
rep(tt, 1, t + 1)
{
cin >> rr >> RR >> xx1 >> yy1 >> xx2 >> yy2;
double ans1, ans2, ans3, ans4;
ans1 = Area_of_overlap(Point(xx1, yy1), RR, Point(xx2, yy2), RR);
ans2 = Area_of_overlap(Point(xx1, yy1), RR, Point(xx2, yy2), rr);
ans3 = Area_of_overlap(Point(xx1, yy1), rr, Point(xx2, yy2), RR);
ans4 = Area_of_overlap(Point(xx1, yy1), rr, Point(xx2, yy2), rr);
cout << "Case #" << tt << ": ";
cout << fixed << setprecision(6) << ans1 - ans2 - ans3 + ans4 << endl;
}
return 0;
}
以上是关于HDU 5120 Intersection的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章