buildroot使用介绍
Posted arnoldlu
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了buildroot使用介绍相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
buildroot是Linux平台上一个构建嵌入式Linux系统的框架。整个Buildroot是由Makefile脚本和Kconfig配置文件构成的。你可以和编译Linux内核一样,通过buildroot配置,menuconfig修改,编译出一个完整的可以直接烧写到机器上运行的Linux系统软件(包含boot、kernel、rootfs以及rootfs中的各种库和应用程序)。
使用buildroot搭建基于qemu的虚拟开发平台,参考《通过buildroot+qemu搭建ARM-Linux虚拟开发环境》。
1. buildroot入门
首先如何使用buildroot,1.选择一个defconfig;2.根据需要配置buildroot;3.编译buildroot;4.在qemu或者目标板上运行buildroot构建的系统。
1.1 buildroot目录介绍
进入buildroot首先映入眼帘的是一系列目录,简要介绍如下:
. ├── arch: 存放CPU架构相关的配置脚本,如arm/mips/x86,这些CPU相关的配置,在制作工具链时,编译uboot和kernel时很关键. ├── board ├── boot ├── CHANGES ├── Config.in ├── Config.in.legacy ├── configs: 放置开发板的一些配置参数. ├── COPYING ├── DEVELOPERS ├── dl: 存放下载的源代码及应用软件的压缩包. ├── docs: 存放相关的参考文档. ├── fs: 放各种文件系统的源代码. ├── linux: 存放着Linux kernel的自动构建脚本. ├── Makefile ├── Makefile.legacy ├── output: 是编译出来的输出文件夹. │ ├── build: 存放解压后的各种软件包编译完成后的现场. │ ├── host: 存放着制作好的编译工具链,如gcc、arm-linux-gcc等工具. │ ├── images: 存放着编译好的uboot.bin, zImage, rootfs等镜像文件,可烧写到板子里, 让linux系统跑起来. │ ├── staging │ └── target: 用来制作rootfs文件系统,里面放着Linux系统基本的目录结构,以及编译好的应用库和bin可执行文件. (buildroot根据用户配置把.ko .so .bin文件安装到对应的目录下去,根据用户的配置安装指定位置) ├── package:下面放着应用软件的配置文件,每个应用软件的配置文件有Config.in和soft_name.mk。 ├── README ├── support ├── system └── toolchain
1.2 buildroot配置
通过make xxx_defconfig来选择一个defconfig,这个文件在config目录下。
然后通过make menuconfig进行配置。
Target options --->选择目标板架构特性。 Build options --->配置编译选项。 Toolchain ---> 配置交叉工具链,使用buildroot工具链还是外部提供。 System configuration ---> Kernel ---> Target packages ---> Filesystem images ---> Bootloaders ---> Host utilities ---> Legacy config options --->
1.3 make命令使用
通过make help可以看到buildroot下make的使用细节,包括对package、uclibc、busybox、linux以及文档生成等配置。
Cleaning: clean - delete all files created by build distclean - delete all non-source files (including .config) Build: all - make world toolchain - build toolchain Configuration: menuconfig - interactive curses-based configurator--------------------------------对整个buildroot进行配置 savedefconfig - Save current config to BR2_DEFCONFIG (minimal config)----------------保存menuconfig的配置 Package-specific:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------对package配置 <pkg> - Build and install <pkg> and all its dependencies---------------------单独编译对应APP <pkg>-source - Only download the source files for <pkg> <pkg>-extract - Extract <pkg> sources <pkg>-patch - Apply patches to <pkg> <pkg>-depends - Build <pkg>‘s dependencies <pkg>-configure - Build <pkg> up to the configure step <pkg>-build - Build <pkg> up to the build step <pkg>-show-depends - List packages on which <pkg> depends <pkg>-show-rdepends - List packages which have <pkg> as a dependency <pkg>-graph-depends - Generate a graph of <pkg>‘s dependencies <pkg>-graph-rdepends - Generate a graph of <pkg>‘s reverse dependencies <pkg>-dirclean - Remove <pkg> build directory-----------------------------------------清除对应APP的编译目录 <pkg>-reconfigure - Restart the build from the configure step <pkg>-rebuild - Restart the build from the build step--------------------------------单独重新编译对应APP busybox: busybox-menuconfig - Run BusyBox menuconfig uclibc: uclibc-menuconfig - Run uClibc menuconfig linux: linux-menuconfig - Run Linux kernel menuconfig-----------------------------------------配置Linux并保存设置 linux-savedefconfig - Run Linux kernel savedefconfig linux-update-defconfig - Save the Linux configuration to the path specified by BR2_LINUX_KERNEL_CUSTOM_CONFIG_FILE Documentation: manual - build manual in all formats manual-pdf - build manual in PDF graph-build - generate graphs of the build times----------------------------------对编译时间、编译依赖、文件系统大小生成图标 graph-depends - generate graph of the dependency tree graph-size - generate stats of the filesystem size
2. buildroot框架
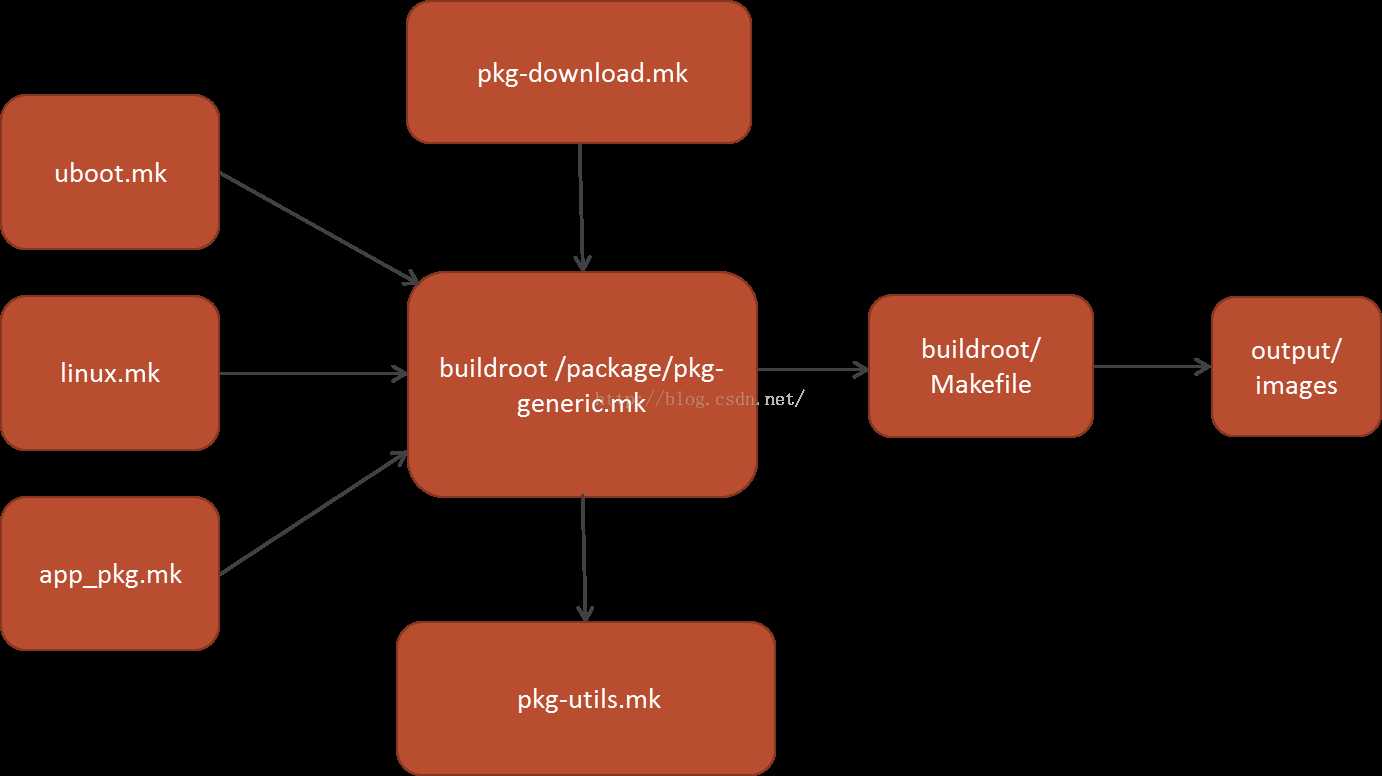
Buildroot提供了函数框架和变量命令框架(下一篇文章将介绍细节),采用它的框架编写的app_pkg.mk这种Makefile格式的自动构建脚本,将被package/pkg-generic.mk 这个核心脚本展开填充到buildroot主目录下的Makefile中去。
最后make all执行Buildroot主目录下的Makefile,生成你想要的image。 package/pkg-generic.mk中通过调用同目录下的pkg-download.mk、pkg-utils.mk文件,已经帮你自动实现了下载、解压、依赖包下载编译等一系列机械化的流程。
你只要需要按照格式写Makefile脚app_pkg.mk,填充下载地址,链接依赖库的名字等一些特有的构建细节即可。 总而言之,Buildroot本身提供构建流程的框架,开发者按照格式写脚本,提供必要的构建细节,配置整个系统,最后自动构建出你的系统。
3. 配置Linux Kernel
对Linux内核的配置包括两部分:通过make menuconfig进入Kernel对内核进行选择,通过make linux-menuconfig对内核内部进行配置。
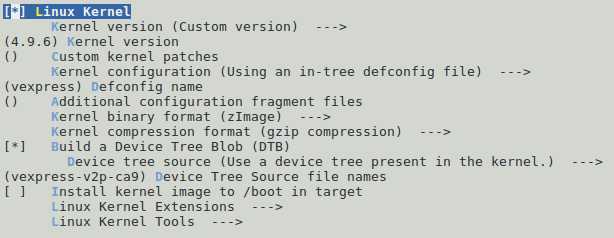
3.1 选择Linux内核版本
如下“Kernel version”选择内核的版本、“Defconfig name”选择内核config文件、“Kernel binary formant”选择内核格式、“Device tree source file names”选择DT文件,
在“Linux Kernel Tools”中选择内核自带的工具,比如perf。
3.2 对Kernel进行配置
通过make linux-menuconfig可以对内核内部细节进行配置。
4. 配置文件系统APP
对目标板文件系统内容进行配置主要通过make menuconfig进入Target packages进行。
5. 添加自己的APP
要添加自己的本地APP, 首先在package/Config.in中添加指向新增APP目录的Config.in;
然后在package中新增目录helloworld,并在里面添加Config.in和helloworld.mk;
最后添加对应的helloworld目录。
5.1 添加package/Config.in入口
系统在make menuconfig的时候就可以找到对应的APP的Config.in。
diff --git a/package/Config.in b/package/Config.in index 43d75a9..6ef9fad 100644 --- a/package/Config.in +++ b/package/Config.in @@ -1868,5 +1868,8 @@ menu "Text editors and viewers" source "package/uemacs/Config.in" source "package/vim/Config.in" endmenu +menu "Private package" + source "package/helloworld/Config.in" +endmenu
5.2 配置APP对应的Config.in和mk文件
helloworld/Config.in文件,通过make menuconfig可以对helloworld进行选择。
config BR2_PACKAGE_HELLOWORLD bool "helloworld" help This is a demo to add local app.
buildroot编译helloworld所需要的设置helloworld.mk,包括源码位置、安装目录、权限设置等。
下面的HELLOWORLD的开头也是必须的。
################################################################################ # # helloworld # ################################################################################ HELLOWORLD_VERSION:= 1.0.0 HELLOWORLD_SITE:= $(CURDIR)/work/helloworld HELLOWORLD_SITE_METHOD:=local HELLOWORLD_INSTALL_TARGET:=YES define HELLOWORLD_BUILD_CMDS $(MAKE) CC="$(TARGET_CC)" LD="$(TARGET_LD)" -C $(@D) all endef define HELLOWORLD_INSTALL_TARGET_CMDS $(INSTALL) -D -m 0755 $(@D)/helloworld $(TARGET_DIR)/bin endef define HELLOWORLD_PERMISSIONS /bin/helloworld f 4755 0 0 - - - - - endef $(eval $(generic-package))
5.3 编写APP源码
简单的编写一个helloworld.c文件:
#include <stdio.h> void main(void) { printf("Hello world. "); }
然后编写Makefile文件:
CPPFLAGS += LDLIBS += all: helloworld analyzestack: helloworld.o $(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) -o [email protected] $^ $(LDLIBS) clean: rm -f *.o helloworld .PHONY: all clean
5.4 通过make menuconfig选中APP
通过Target packages -> Private package进入,选中helloworld。

然后make savedefconfig,对helloworld的配置就会保存到qemu_arm_vexpress_defconfig中。

5.5 编译APP
可以和整个平台一起编译APP;或者make helloworld单独编译。
这两个文件在选中此APP之后,都会被拷贝到output/build/helloworld-1.0.0文件夹中。
然后生成的bin文件拷贝到output/target/bin/helloworld,这个文件会打包到文件系统中。
如果需要清空相应的源文件,通过make helloworld-dirclean。
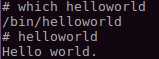
5.6 运行APP
在shell中输入helloworld,可以得到如下结果。
添加APP工作完成。
以上是关于buildroot使用介绍的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章