数据分析---用pandas进行数据清洗(Data Analysis Pandas Data Munging/Wrangling)
Posted huzihu
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据分析---用pandas进行数据清洗(Data Analysis Pandas Data Munging/Wrangling)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
这里利用ben的项目(https://github.com/ben519/DataWrangling/blob/master/Python/README.md),在此基础上增添了一些内容,来演示数据清洗的主要工作。
以下是一份简单的交易数据,包括交易单号,交易日期,产品序号,交易数量,单价,总价。
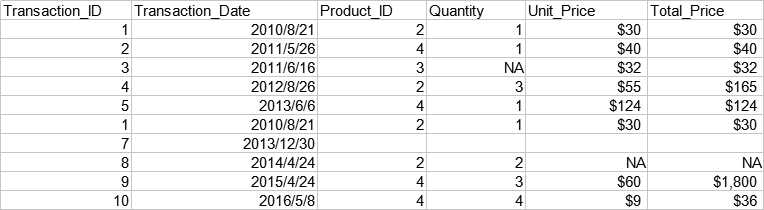
准备工作:导入pandas
import pandas as pd
数据读取: pd.read_excel, pd.read_csv, pd.read_json, pd.read_sql...
transactions=pd.read_excel(r‘... ransactions.xlsx‘)
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Total_Price 0 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 30 1 2 2011-05-26 4 1 40 40 2 3 2011-06-16 3 NaN 32 32 3 4 2012-08-26 2 3 55 165 4 5 2013-06-06 4 1 124 124 5 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 30 6 7 2013-12-30 7 8 2014-04-24 2 2 NaN NaN 8 9 2015-04-24 4 3 60 1800 9 10 2016-05-08 4 4 9 36
获取数据信息:xx.info()
print(transactions.info())
RangeIndex: 10 entries, 0 to 9 Data columns (total 6 columns): Transaction_ID 10 non-null int64 Transaction_Date 10 non-null datetime64[ns] Product_ID 10 non-null object Quantity 9 non-null object Unit_Price 9 non-null object Total_Price 9 non-null object dtypes: datetime64[ns](1), int64(1), object(4) memory usage: 560.0+ bytes None
显示了数据各列的基本信息,比如:Transaction_ID有10个不为空的值,数据类型是int64; Quantity有9个不为空的值(说明有一个缺失值),数据类型是object;等等。
获取数据总行列数信息: xx.shape
print(transactions.shape)
(10, 6)
显示了数据共有10行6列。
获取所有行索引: xx.index.values
print(transactions.index.values)
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
获取所有列名: xx.columns.values
print(transactions.columns.values)
[‘Transaction_ID‘ ‘Transaction_Date‘ ‘Product_ID‘ ‘Quantity‘ ‘Unit_Price‘ ‘Total_Price‘]
选取某一行: xx.loc([row_index_name]) 显式 ; xx.iloc([row_index_from_zero]) 隐式
print(transactions.loc[1])
Transaction_ID 2 Transaction_Date 2011-05-26 00:00:00 Product_ID 4 Quantity 1 Unit_Price 40 Total_Price 40 Name: 1, dtype: object
选取了数据的第二行。此数据行索引是从0开始一直到9,因此显式选取和隐式选取都一样。
选取某一列: xx[‘column_name‘]
print(transactions[‘Product_ID‘])
0 2
1 4
2 3
3 2
4 4
5 2
6
7 2
8 4
9 4
Name: Product_ID, dtype: object
选取连续多行: xx.loc([row_index_name1: row_index_name2]) 显式 ; xx.iloc([row_index_from_zero1: row_index_from_zero2]) 隐式
print(transactions.iloc[2:4])
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Total_Price
2 3 2011-06-16 3 NaN 32 32
3 4 2012-08-26 2 3 55 165
选取连续多列: xx.loc([ :, ‘column_name1‘: ‘column_name2‘]) 显式 ; xx.iloc([ :, column_index_from_zero1: column_index_from_zero2]) 隐式
print(transactions.loc[:,‘Product_ID‘:‘Total_Price‘])
Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Total_Price 0 2 1 30 30 1 4 1 40 40 2 3 NaN 32 32 3 2 3 55 165 4 4 1 124 124 5 2 1 30 30 6 7 2 2 NaN NaN 8 4 3 60 1800 9 4 4 9 36
选取连续某几行某几列的数据: xx.loc([row_index_name1: row_index_name2, ‘column_name1‘: ‘column_name2‘]) 显式 ; xx.iloc([row_index_from_zero1: row_index_from_zero2, column_index_from_zero1: column_index_from_zero2]) 隐式
print(transactions.iloc[2:4,2:4])
Product_ID Quantity 2 3 NaN 3 2 3
选取不连续的多行: xx.loc([[row_index_name1,row_index_name2, ...]]) 显式 ; xx.iloc([[row_index_from_zero1, row_index_from_zero2, ...]]) 隐式
print(transactions.iloc[[1,4]])
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Total_Price
1 2 2011-05-26 4 1 40 40
4 5 2013-06-06 4 1 124 124
选取不连续的多列: xx.loc([ :, [column_name1, column_name2, ...]]) 显式 ; xx.iloc([ :, [column_index_from_zero1, column_index_from_zero2, ...]]) 隐式
print(transactions.iloc[:,[1,4]])
Transaction_Date Unit_Price 0 2010-08-21 30 1 2011-05-26 40 2 2011-06-16 32 3 2012-08-26 55 4 2013-06-06 124 5 2010-08-21 30 6 2013-12-30 7 2014-04-24 NaN 8 2015-04-24 60 9 2016-05-08 9
添加行: xx.loc(new_row_index)=[.....]
transactions.loc[10]=[11,"2018-9-9",1,4,2,8]
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price 0 1 2010-08-21 00:00:00 2 1 30 1 2 2011-05-26 00:00:00 4 1 40 2 3 2011-06-16 00:00:00 3 NaN 32 3 4 2012-08-26 00:00:00 2 3 55 4 5 2013-06-06 00:00:00 4 1 124 5 1 2010-08-21 00:00:00 2 1 30 6 7 2013-12-30 00:00:00 7 8 2014-04-24 00:00:00 2 2 NaN 8 9 2015-04-24 00:00:00 4 3 60 9 10 2016-05-08 00:00:00 4 4 9 10 11 2018-9-9 1 4 2 Total_Price 0 30 1 40 2 32 3 165 4 124 5 30 6 7 NaN 8 1800 9 36 10 8
添加列:xx[‘new_column_name‘]=[.....]
transactions[‘Unit_Profit‘]=[3,5,8,20,9,4,"",33,5,1]
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Total_Price 0 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 30 1 2 2011-05-26 4 1 40 40 2 3 2011-06-16 3 NaN 32 32 3 4 2012-08-26 2 3 55 165 4 5 2013-06-06 4 1 124 124 5 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 30 6 7 2013-12-30 7 8 2014-04-24 2 2 NaN NaN 8 9 2015-04-24 4 3 60 1800 9 10 2016-05-08 4 4 9 36 Unit_Profit 0 3 1 5 2 8 3 20 4 9 5 4 6 7 33 8 5 9 1
在指定位置插入列: xx.insert(column_index, ‘new_column_name‘,[...])
transactions.insert(5,‘Unit_Profit‘,[3,5,8,20,9,4,"",33,5,1])
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Unit_Profit 0 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 3 1 2 2011-05-26 4 1 40 5 2 3 2011-06-16 3 NaN 32 8 3 4 2012-08-26 2 3 55 20 4 5 2013-06-06 4 1 124 9 5 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 4 6 7 2013-12-30 7 8 2014-04-24 2 2 NaN 33 8 9 2015-04-24 4 3 60 5 9 10 2016-05-08 4 4 9 1 Total_Price 0 30 1 40 2 32 3 165 4 124 5 30 6 7 NaN 8 1800 9 36
删除行:xx.drop(row_index_from_zero,axis=0)
transactions=transactions.drop(8,axis=0)
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Total_Price 0 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 30 1 2 2011-05-26 4 1 40 40 2 3 2011-06-16 3 NaN 32 32 3 4 2012-08-26 2 3 55 165 4 5 2013-06-06 4 1 124 124 5 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 30 6 7 2013-12-30 7 8 2014-04-24 2 2 NaN NaN 9 10 2016-05-08 4 4 9 36
删除列: xx.drop(‘column_name‘,axis=1)
transactions=transactions.drop(‘Total_Price‘,axis=1)
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price 0 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 1 2 2011-05-26 4 1 40 2 3 2011-06-16 3 NaN 32 3 4 2012-08-26 2 3 55 4 5 2013-06-06 4 1 124 5 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 6 7 2013-12-30 7 8 2014-04-24 2 2 NaN 8 9 2015-04-24 4 3 60 9 10 2016-05-08 4 4 9
数据转置: xx.T
print(transactions.T)
0 1 Transaction_ID 1 2 Transaction_Date 2010-08-21 00:00:00 2011-05-26 00:00:00 Product_ID 2 4 Quantity 1 1 Unit_Price 30 40 Total_Price 30 40 2 3 Transaction_ID 3 4 Transaction_Date 2011-06-16 00:00:00 2012-08-26 00:00:00 Product_ID 3 2 Quantity NaN 3 Unit_Price 32 55 Total_Price 32 165 4 5 Transaction_ID 5 1 Transaction_Date 2013-06-06 00:00:00 2010-08-21 00:00:00 Product_ID 4 2 Quantity 1 1 Unit_Price 124 30 Total_Price 124 30 6 7 Transaction_ID 7 8 Transaction_Date 2013-12-30 00:00:00 2014-04-24 00:00:00 Product_ID 2 Quantity 2 Unit_Price NaN Total_Price NaN 8 9 Transaction_ID 9 10 Transaction_Date 2015-04-24 00:00:00 2016-05-08 00:00:00 Product_ID 4 4 Quantity 3 4 Unit_Price 60 9 Total_Price 1800 36
有时候需要把行和列进行交换,数据才更容易看懂(尽管这里不需要)。
查找重复值: xx.duplicated()
print(transactions.duplicated())
0 False 1 False 2 False 3 False 4 False 5 True 6 False 7 False 8 False 9 False dtype: bool
数据第6行(索引为5)是重复的(需要每列的数据都重复)。
删除重复值: xx.drop_duplicates()
transactions=transactions.drop_duplicates()
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Total_Price 0 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 30 1 2 2011-05-26 4 1 40 40 2 3 2011-06-16 3 NaN 32 32 3 4 2012-08-26 2 3 55 165 4 5 2013-06-06 4 1 124 124 6 7 2013-12-30 7 8 2014-04-24 2 2 NaN NaN 8 9 2015-04-24 4 3 60 1800 9 10 2016-05-08 4 4 9 36
数据第6行已被删除。
查找缺失值: xx.isnull() ; xx.notnull()
print(transactions[transactions[‘Unit_Price‘].isnull()])
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Total_Price
7 8 2014-04-24 2 2 NaN NaN
显示了Unit_Price有缺失值的一行数据。
删除缺失值: xx.dropna(how=..., axis=...) 注:how="any"或"all", axis=0或1
transactions=transactions.dropna(axis=0)
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Total_Price
0 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 30
1 2 2011-05-26 4 1 40 40
3 4 2012-08-26 2 3 55 165
4 5 2013-06-06 4 1 124 124
5 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 30
6 7 2013-12-30
8 9 2015-04-24 4 3 60 1800
9 10 2016-05-08 4 4 9 36
填补缺失值: xx.fillna(value=..., axis=...) 注:axis=0或1
transactions[‘Unit_Price‘]=transactions[‘Unit_Price‘].fillna(value=35)
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Total_Price 0 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 30 1 2 2011-05-26 4 1 40 40 2 3 2011-06-16 3 NaN 32 32 3 4 2012-08-26 2 3 55 165 4 5 2013-06-06 4 1 124 124 5 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 30 6 7 2013-12-30 7 8 2014-04-24 2 2 35 NaN 8 9 2015-04-24 4 3 60 1800 9 10 2016-05-08 4 4 9 36
去除空格: 先把空格替换成NaN,再提取没有缺失值的数据
import numpy as np transactions=transactions.applymap(lambda x: np.NaN if str(x).isspace() else x)
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price 0 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0 1 2 2011-05-26 4.0 1.0 40.0 2 3 2011-06-16 3.0 NaN 32.0 3 4 2012-08-26 2.0 3.0 55.0 4 5 2013-06-06 4.0 1.0 124.0 5 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0 6 7 2013-12-30 NaN NaN NaN 7 8 2014-04-24 2.0 2.0 NaN 8 9 2015-04-24 4.0 3.0 60.0 9 10 2016-05-08 4.0 4.0 9.0 Total_Price 0 30.0 1 40.0 2 32.0 3 165.0 4 124.0 5 30.0 6 NaN 7 NaN 8 1800.0 9 36.0
注:如果替换某行或某列的空格,用apply;如果替换整体数据的空格,则用applymap
大小写转换: xx.str.lower() ; xx.str.upper()
演示省略。。
转换数据类型:xx.astype(data_type_to_be_transferred_to) 注:可转换的数据类型有:int, str, float ... ; 转换成时间序列: pd.to_datetime(...)
transactions[‘Transaction_Date‘]=pd.to_datetime(transactions[‘Transaction_Date‘])
注:需要先把数据内的缺失值处理干净,否则会产生错误
使用掩码进行条件筛选: xx[mask] 注:一些条件表示方法:&(and) ,|(or),-(not),isin(in)
print(transactions[(transactions[‘Quantity‘]==1) & (transactions[‘Unit_Price‘]>100)])
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price 4 5 2013-06-06 4.0 1.0 124.0 Total_Price 4 124.0
这里选取了交易数量为1并且单价超过100的数据(删除了所有缺失值后)。
条件筛选后选取符合条件的某一列数据: xx.loc[xx[mask],‘column_name‘]
print(transactions.loc[((transactions[‘Quantity‘]==1) & (transactions[‘Unit_Price‘]>100)),‘Product_ID‘])
4 4.0
Name: Product_ID, dtype: float64
这里选取了交易数量为1并且单价超过100的物品的Produxt_ID(删除了所有缺失值后)。
查找异常值: 通过掩码过滤,在这里以Upper Quartile+1.5*IQR和Lower Quartile-1.5*IQR为上下限
print(transactions.describe()) upper_extrme=144.5+1.5*(144.5-33) lower_extrme=33-1.5*(144.5-33) print(transactions.loc[((transactions[‘Total_Price‘]>upper_extrme) | (transactions[‘Total_Price‘]<lower_extrme))])
Transaction_ID Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Total_Price count 7.000000 7.000000 7.000000 7.000000 7.000000 mean 4.571429 3.142857 2.000000 49.714286 317.857143 std 3.690399 1.069045 1.290994 36.926568 655.752095 min 1.000000 2.000000 1.000000 9.000000 30.000000 25% 1.500000 2.000000 1.000000 30.000000 33.000000 50% 4.000000 4.000000 1.000000 40.000000 40.000000 75% 7.000000 4.000000 3.000000 57.500000 144.500000 max 10.000000 4.000000 4.000000 124.000000 1800.000000 Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price 8 9 2015-04-24 4.0 3.0 60.0 Total_Price 8 1800.0
先通过describe函数查看数据整体分布情况,然后计算出Total_Price的上下限,通过掩码选取Total_Price超过上限或低于下限的行。在这里可以看到,有一个异常值1800,原因是多写了一个0。
替换异常值: xx.replace(to_replace, old_value, inplace=True)
transactions[‘Total_Price‘].replace(1800,180,inplace=True)
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price 0 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0 1 2 2011-05-26 4.0 1.0 40.0 3 4 2012-08-26 2.0 3.0 55.0 4 5 2013-06-06 4.0 1.0 124.0 5 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0 8 9 2015-04-24 4.0 3.0 60.0 9 10 2016-05-08 4.0 4.0 9.0 Total_Price 0 30.0 1 40.0 3 165.0 4 124.0 5 30.0 8 180.0 9 36.0
把上面查找出来的异常值1800替换成了180。
累计: 累计方法有:count(), mean(), median(), min(), max(), std(), prod(), sum(), ...
print(transactions[‘Total_Price‘].sum())
2225.0
显示了Total_Price的合计数目。
数据分组:xx.groupby(...)
print(transactions.groupby(‘Product_ID‘)[‘Quantity‘].sum())
Product_ID 2.0 5.0 4.0 9.0 Name: Quantity, dtype: float64
显示了按照Product_ID分组的交易数量的总和。(注:transactions.groupby(‘Product_ID‘)是一个数据分组的对象,它实际上还没有进行任何计算,只是一个暂时存储的容器,要使用累计函数后才会进行计算。因此,groupby一般与累计函数搭配使用。)
print(transactions.groupby(‘Product_ID‘)[‘Quantity‘].agg([‘sum‘,‘mean‘]))
sum mean
Product_ID
2.0 5.0 1.666667
4.0 9.0 2.250000
如果需要进行两个及以上项目的累计,可以使用agg函数。
计数: xx.value_counts()
print(transactions[‘Product_ID‘].value_counts())
4.0 4
2.0 3
Name: Product_ID, dtype: int64
更改某个列名: xx.rename(columns={‘old_column_name‘:‘new_column_name‘}, inplace=True)
transactions.rename(columns={‘Unit_Price‘:‘UP‘},inplace=True)
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity UP Total_Price
0 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0 30.0
1 2 2011-05-26 4.0 1.0 40.0 40.0
3 4 2012-08-26 2.0 3.0 55.0 165.0
4 5 2013-06-06 4.0 1.0 124.0 124.0
5 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0 30.0
8 9 2015-04-24 4.0 3.0 60.0 1800.0
9 10 2016-05-08 4.0 4.0 9.0 36.0
更改索引: xx.set_index()
transactions.set_index(‘Transaction_Date‘,inplace=True)
Transaction_ID Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Transaction_Date 2010-08-21 1 2.0 1.0 30.0 2011-05-26 2 4.0 1.0 40.0 2012-08-26 4 2.0 3.0 55.0 2013-06-06 5 4.0 1.0 124.0 2010-08-21 1 2.0 1.0 30.0 2015-04-24 9 4.0 3.0 60.0 2016-05-08 10 4.0 4.0 9.0 Total_Price Transaction_Date 2010-08-21 30.0 2011-05-26 40.0 2012-08-26 165.0 2013-06-06 124.0 2010-08-21 30.0 2015-04-24 1800.0 2016-05-08 36.0
以交易日期为索引。
按索引排序: xx.sort_index()
transactions.sort_index(ascending=False, inplace=True)
Transaction_ID Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Transaction_Date 2016-05-08 10 4.0 4.0 9.0 2015-04-24 9 4.0 3.0 60.0 2013-06-06 5 4.0 1.0 124.0 2012-08-26 4 2.0 3.0 55.0 2011-05-26 2 4.0 1.0 40.0 2010-08-21 1 2.0 1.0 30.0 2010-08-21 1 2.0 1.0 30.0 Total_Price Transaction_Date 2016-05-08 36.0 2015-04-24 1800.0 2013-06-06 124.0 2012-08-26 165.0 2011-05-26 40.0 2010-08-21 30.0 2010-08-21 30.0
以交易日期为索引,倒序排列。
按内容排序: xx.sort_values()
transactions.sort_values(by=[‘Quantity‘,‘Total_Price‘], inplace=True)
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price 0 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0 5 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0 1 2 2011-05-26 4.0 1.0 40.0 4 5 2013-06-06 4.0 1.0 124.0 3 4 2012-08-26 2.0 3.0 55.0 8 9 2015-04-24 4.0 3.0 60.0 9 10 2016-05-08 4.0 4.0 9.0 Total_Price 0 30.0 5 30.0 1 40.0 4 124.0 3 165.0 8 1800.0 9 36.0
更新索引: xx.reset_index()
transactions.reset_index(inplace=True)
index Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price 0 0 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0 1 5 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0 2 1 2 2011-05-26 4.0 1.0 40.0 3 4 5 2013-06-06 4.0 1.0 124.0 4 3 4 2012-08-26 2.0 3.0 55.0 5 8 9 2015-04-24 4.0 3.0 60.0 6 9 10 2016-05-08 4.0 4.0 9.0 Total_Price 0 30.0 1 30.0 2 40.0 3 124.0 4 165.0 5 1800.0 6 36.0
上面按内容排序后,索引顺序变乱了,如果数据就需要按此顺序排列,那么可以更新索引。
透视表: pd.pivot_table(xx, values=..., index=..., columns=..., aggfunc=...)
print(pd.pivot_table(transactions,values=‘Total_Price‘,index=[‘Product_ID‘,‘Quantity‘],aggfunc=‘sum‘))
Total_Price
Product_ID Quantity
2.0 1.0 60.0
3.0 165.0
4.0 1.0 164.0
3.0 1800.0
4.0 36.0
多级索引行列转换: stack() ; unstack()
print(pd.pivot_table(transactions,values=‘Total_Price‘,index=[‘Product_ID‘,‘Quantity‘],aggfunc=‘sum‘).unstack())
Total_Price Quantity 1.0 3.0 4.0 Product_ID 2.0 60.0 165.0 NaN 4.0 164.0 1800.0 36.0
将上面的透视表展开。
数据分列: xx.str.split()
假如我们要把交易日期里的年份提取出来,变成单独的列。---> 先把交易日期这一列的数据格式变为str,再按照‘-‘进行切割,当参数expand为True时,会把切割出来的内容分别当做一列。因此,如果只需要年份,那么就只需要提取第一列。
year=transactions[‘Transaction_Date‘].astype(str).str.split(‘-‘,expand=True)[0] transactions[‘Year‘]=year
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price 0 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0 1 2 2011-05-26 4.0 1.0 40.0 3 4 2012-08-26 2.0 3.0 55.0 4 5 2013-06-06 4.0 1.0 124.0 5 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0 8 9 2015-04-24 4.0 3.0 60.0 9 10 2016-05-08 4.0 4.0 9.0 Total_Price Year 0 30.0 2010 1 40.0 2011 3 165.0 2012 4 124.0 2013 5 30.0 2010 8 1800.0 2015 9 36.0 2016
这样,以后可以方便按年份或月份进行分组。
数据分区: pd.cut(xx, bins, labels=...) ; xx.qcut(xx, bins, labels=...) 注:cut 是根据每个值的大小来进行分区的,qcut 是根据每个值出现的次数来进行分区的。
cut=pd.cut(transactions[‘Unit_Price‘],3,labels=[‘low‘,‘median‘,‘high‘]) transactions.insert(5,‘Price_Range‘,cut)
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price 0 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0 1 2 2011-05-26 4.0 1.0 40.0 3 4 2012-08-26 2.0 3.0 55.0 4 5 2013-06-06 4.0 1.0 124.0 5 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0 8 9 2015-04-24 4.0 3.0 60.0 9 10 2016-05-08 4.0 4.0 9.0 Price_Range Total_Price 0 low 30.0 1 low 40.0 3 median 165.0 4 high 124.0 5 low 30.0 8 median 1800.0 9 low 36.0
在这里把Unit_Price分成了3挡。
合并:
把列作为键进行合并: pd.merge(xx, xx, on=..., how=...)
假设我们现在有另外一张表,记载的是产品序号对应的产品名称。现在把这两张表合并在一起:
product_name=pd.DataFrame({"Product_ID":[1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0],"Product_Name":["candy","pen","stapler","toy"]})
merged=pd.merge(transactions,product_name,on=‘Product_ID‘,how="inner")
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price 0 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0 1 4 2012-08-26 2.0 3.0 55.0 2 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0 3 2 2011-05-26 4.0 1.0 40.0 4 5 2013-06-06 4.0 1.0 124.0 5 9 2015-04-24 4.0 3.0 60.0 6 10 2016-05-08 4.0 4.0 9.0 Total_Price Product_Name 0 30.0 pen 1 165.0 pen 2 30.0 pen 3 40.0 toy 4 124.0 toy 5 1800.0 toy 6 36.0 toy
假如两张表作为键的列名称不一致,那么可以通过设置left_on和left_on来解决:
product_name=pd.DataFrame({"Product_Identity":[1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0],"Product_Name":["candy","pen","stapler","toy"]})
merged=pd.merge(transactions,product_name,left_on=‘Product_ID‘,right_on="Product_Identity",how="inner")
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price 0 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0 1 4 2012-08-26 2.0 3.0 55.0 2 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0 3 2 2011-05-26 4.0 1.0 40.0 4 5 2013-06-06 4.0 1.0 124.0 5 9 2015-04-24 4.0 3.0 60.0 6 10 2016-05-08 4.0 4.0 9.0 Total_Price Product_Identity Product_Name 0 30.0 2.0 pen 1 165.0 2.0 pen 2 30.0 2.0 pen 3 40.0 4.0 toy 4 124.0 4.0 toy 5 1800.0 4.0 toy 6 36.0 4.0 toy
注:how可选"left", "right", "outer", "inner"
"left":类似于SQL的left outer join;
"right":类似于SQL的right outer join;
"outer":并集,类似于SQL的full outer join;
"inner":交集,类似于SQL的inner join;
按索引进行合并: xx.join(xx, on=..., how=...)
假设有另外几张表(t1, t2)记载有交易记录,如果需要把这几张表合并在一起:transactions.join([t1,t2], how="outer")。这里不再做演示。
以上是关于数据分析---用pandas进行数据清洗(Data Analysis Pandas Data Munging/Wrangling)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章