非阻塞 Connect
Posted tattoo-welkin
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了非阻塞 Connect相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.非阻塞Connect有什么用?
- 可以让三路握手的处理等同与一般数据的处理,而不是一直让
connect一直尝试重连或者花费一个RTT时间。而且RTT时间从几毫秒到几秒不等,万一有许多连接,不论是尝试重连还是花费一个RTT时间,都将是致命的延时。 - 可以使用该技术同时建立多个连接。Web浏览器中常用。
- 既然使用
select等待连接的建立,我们就可以质地不嗯一个时间限制,使得我们能够缩短connect的超时。
2.必须去处理的细节:
- 处理
connect立即建立的情况。(比如我们连接的是同一个主机时) 使用
selcet与非阻塞connect的一些注意事项:2.1. 当连接成功建立后,描述符变为可写。
2.2 当遇到错误时,描述符变为即可写又可读。
3. 两个例子:
(1)非阻塞connect:时间获取客户程序
int Connect_nonblock(int sockfd, const SA *saptr, socklen_t salen, int nsec) //返回 -1 失败
{
int flags, n, error;
socklen_t len;
fd_set rset, wset;
struct timeval tval;
flags = Fcntl(sockfd, F_GETFL, 0);
Fcntl(sockfd, F_SETFL, flags | O_NONBLOCK);
error = 0;
if ((n = connect(sockfd, saptr, salen)) < 0)
{
if (errno != EINPROGRESS) //表示连接已经启动但是还没有完成
return (-1);
}
if (n == 0) //表示连接建立 立即完成
goto done;
FD_ZERO(&rset);
FD_SET(sockfd, &rset);
wset = rset;
tval.tv_sec = nsec;
tval.tv_usec = 0;
if ((n = Select(sockfd + 1, &rset, &wset, NULL, nsec ? &tval : NULL)) == 0)//返回0,超时,关闭套接字
{
Close(sockfd);
errno = ETIMEDOUT;
return (-1);
}
if (FD_ISSET(sockfd, &rset) || FD_ISSET(sockfd, &wset))
{
len = sizeof(error);
if (getsockopt(sockfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_ERROR, &error, &len) < 0)
return (-1);
}
else
err_quit("selcet error :sockfd not set
");
done: //直到建立才返回
Fcntl(sockfd, F_SETFL, flags);
if (error)
{
Close(sockfd);
errno = error;
return (-1);
}
return 0; //成功连接
}一些说明:
??其实比较简单,就是connect去连接,如果能够连上就连接即可,如果没有连上就让select当作一般数据去处理即可!对于连接,select有两种情况,成功就是可写,失败即可读又可写。那么问题来了?
??如何去判断成功还是失败呐?emmmm,所谓的失败就是发生了错误,那么我们直接检测是否有错误即可 。使用getsockopt函数 。
<1> getsockopt函数说明:获取某个套接字关联的选项
int getsockopt(int socket, int level, int option_name,
void *restrict option_value, socklen_t *restrict option_len);
getcoksopt和setsockopt都只用于套接字level指定系统中解释选项的代码或为通用套接字代码,或为特定于某个协议的代码 。option_value将已获取的选项当前值,存放在*option_value中,option_len为*option_value的大小 。option_name代表选项 。
返回值:
RETURN VALUE
Upon successful completion, getsockopt() shall return 0; otherwise, ?1 shall be returned and errno set to indicate the
error.
Berkeley系统中:在*option_value中返回待处理错误,函数返回 0Solaris系统中:将errno置为待处理错误,函数返回 -1
所以在我们的代码中,我们将这两种情况都进行处理 。
<2>测试:
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int sockfd, n;
char recvline[MAXLINE + 1] = {0};
struct sockaddr_in servaddr;
if (argc != 2)
err_quit("usage: a.out <IPaddress>");
if ((sockfd = Socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) < 0)
err_sys("Socket error");
bzero(&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr));
servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
servaddr.sin_port = htons(13); /* daytime server */
if (inet_pton(AF_INET, argv[1], &servaddr.sin_addr) <= 0)
err_quit("inet_pton error for %s", argv[1]);
if (Connect_nonblock(sockfd, (SA *)&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr), 10) < 0)
err_sys("connect error");
while ((n = recv(sockfd, recvline, MAXLINE, 0)) > 0)
{
recvline[n] = 0; /* null terminate */
printf("recvline == %s
", recvline);
}
if (n < 0)
err_sys("read error");
return 0;
}(2)非阻塞Connect : Web 客户程序
??先获取一个主页,然后并行多个连接获取主页的其他网络资源。很显然,这样子的并行连接序列要比串行获取资源来的快。
- 结构体设计
#define MAXFILES 20
#define SERV "80"
struct file
{
char *f_name; //资源路径
char *f_host; //主机
int f_fd;//套接字
int f_flags; //当前状态,有四种值,分别是 { 0, F_CONNECTING, F_READING, F_DONE }
}
file[MAXFILES];- 大致思路:
// 假设我们下载 10 资源
初始化 struct file files[10];
先成功建立第一个连接(获取主页)
while(xxx) {
使用非阻塞I/O, 同时建立多个连接,每一个 f_flags = F_CONNECTING.
select 监听套接字
for (f in files) { // 遍历所有文件
if (f.f_flags == F_CONNECTING) {
// 检查连接是否成功或失败。使用我们上面用到的知识,主要是 getsockopt 函数
如果连接成功,则发起 GET 请求,同时 f_flags = F_READING.
如果连接失败,f_flags = F_DONE;
}
else if (f.f_flags == F_READING) {
// 下载资源
nr = read(f.f_fd, buf);
if (nr == 0) {
对端关闭, f.f_flags = F_DONE;
}
}
}
}web.h文件
#ifndef _WEB_H
#define _WEB_H
#include "../myhead.h"
#define MAXFILES 20
#define SERV "80"
struct file
{
char *f_name;
char *f_host;
int f_fd;
int f_flags;
}
file[MAXFILES];
#define F_CONNECTING 1
#define F_READING 2
#define F_DONE 4
#define GET_CMD "GET %s HTTP/1.0
"
int nconn, nfiles, nlefttoconn, nlefttoread, maxfd;
fd_set rset, wset;
/*
nconn:当前打开的连接数,不超过第一个命令行参数
nlefttoread:待读取的文件数量
nlefttoconn:尚未连接的文件数
nfiles:文件数量
*/
#endif
web.c文件
#include "web.h"
struct addrinfo *Host_serv(const char *host, const char *serv, int family, int socktype);
void home_pages(const char *host, const char *fname);
void start_connect(struct file *fptr); //非阻塞连接;
void write_get_cmd(struct file *fptr);
int Tcp_connect(const char *host, const char *serv)
{
int sockfd, n;
struct addrinfo hints, *res, *ressave;
bzero(&hints, sizeof(struct addrinfo));
hints.ai_family = AF_UNSPEC;
hints.ai_socktype = SOCK_STREAM;
if ((n = getaddrinfo(host, serv, &hints, &res)) != 0)
err_quit("tcp_connect error for %s ,%s,%s : %s", host, serv, gai_strerror(n));
ressave = res;
do
{
sockfd = Socket(res->ai_family, res->ai_socktype, res->ai_protocol);
if (sockfd < 0)
continue;
if (connect(sockfd, res->ai_addr, res->ai_addrlen) == 0)
break;
Close(sockfd);
} while ((res = res->ai_next) != NULL);
if (res == NULL)
err_sys("tcp_coonnect error for %s,%s", host, serv);
freeaddrinfo(ressave);
return (sockfd);
}
struct addrinfo *Host_serv(const char *host, const char *serv, int family, int socktype)
{
int n;
struct addrinfo hints, *res;
bzero(&hints, sizeof(struct addrinfo));
hints.ai_flags = AI_CANONNAME;
hints.ai_family = family;
hints.ai_socktype = socktype;
if ((n = getaddrinfo(host, serv, &hints, &res)) != 0)
err_quit("host_serv error for %s, %s: %s",
(host == NULL) ? "(no hostname)" : host,
(serv == NULL) ? "(no service name)" : serv,
gai_strerror(n));
return (res);
}
void home_pages(const char *host, const char *fname)
{
int fd, n;
char line[MAXLINE] = {0};
fd = Tcp_connect(host, SERV);
n = snprintf(line, sizeof(line), GET_CMD, fname);
Sendlen(fd, line, n, 0);
for (;;)
{
if ((n = Recvlen(fd, line, MAXLINE, 0)) == 0)
break; //serv closed
fprintf(stderr, "recv %d bytes from server
", n);
}
fprintf(stderr, "end-of-home-pages
");
Close(fd);
}
void start_connect(struct file *fptr) //非阻塞连接
{
int fd, flags, n;
struct addrinfo *ai;
ai = Host_serv(fptr->f_host, SERV, 0, SOCK_STREAM);
fd = Socket(ai->ai_family, ai->ai_socktype, ai->ai_protocol);
fptr->f_fd = fd;
fprintf(stderr, "start_connect for %s ,fd %d
", fptr->f_name, fd);
flags = Fcntl(fd, F_GETFL, 0);
Fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flags | O_NONBLOCK);
if ((n = connect(fd, ai->ai_addr, ai->ai_addrlen)) < 0)
{
if (errno != EINPROGRESS) // EINPROGRESS套接字为非阻塞套接字,且连接请求没有立即完成
err_sys("nonblocking connect error ", __LINE__);
fptr->f_flags = F_CONNECTING;
FD_SET(fd, &rset);
FD_SET(fd, &wset);
if (fd > maxfd)
maxfd = fd;
}
else if (n >= 0)
{ /* connect is already done */
write_get_cmd(fptr);
}
}
void write_get_cmd(struct file *fptr)
{
int n;
char line[MAXLINE];
n = snprintf(line, sizeof(line), GET_CMD, fptr->f_name);
Writen(fptr->f_fd, line, n);
fprintf(stderr, "send %d bytes for %s
", n, fptr->f_name);
fptr->f_flags = F_READING; /* clears F_CONNECTING */
FD_SET(fptr->f_fd, &rset); /* will read server‘s reply */
if (fptr->f_fd > maxfd)
maxfd = fptr->f_fd;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int i, fd, n, maxconn, flags, error;
char buf[MAXLINE] = {0};
fd_set rs, ws;
if (argc < 5)
{
fprintf(stderr, "use :web conns hostname homepages files.....");
return 0;
}
maxconn = atoi(argv[1]);
nfiles = min(argc - 4, MAXFILES);
for (i = 0; i < nfiles; i++)
{
file[i].f_name = argv[i + 4];
file[i].f_host = argv[2];
file[i].f_flags = 0;
}
fprintf(stderr, "nfiles == %d
", nfiles);
home_pages(argv[2], argv[3]); //建立第一个连接
FD_ZERO(&rset);
FD_ZERO(&wset);
maxfd = -1;
nlefttoread = nlefttoconn = nfiles;
nconn = 0;
/*
nconn :当前打开的连接数,不超过第一个命令行参数
nlefttoread:待读取的文件数量
nlefttoconn:尚未连接的文件数
nfiles:文件数量
*/
while (nlefttoread > 0)
{
while (nconn < maxconn && nlefttoconn > 0)
{
/* 4find a file to read */
for (i = 0; i < nfiles; i++)
if (file[i].f_flags == 0)
break;
if (i == nfiles)
err_quit("nlefttoconn = %d but nothing found", nlefttoconn);
start_connect(&file[i]);
nconn++;
nlefttoconn--;
}
rs = rset;
ws = wset;
n = Select(maxfd + 1, &rs, &ws, NULL, NULL);
for (i = 0; i < nfiles; i++)
{
flags = file[i].f_flags;
if (flags == 0 || flags & F_DONE)
continue;
fd = file[i].f_fd;
if (flags & F_CONNECTING &&
(FD_ISSET(fd, &rs) || FD_ISSET(fd, &ws)))
{
n = sizeof(error);
if (getsockopt(fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_ERROR, &error, &n) < 0 ||
error != 0)
{
err_ret("nonblocking connect failed for %s",
file[i].f_name);
file[i].f_flags = F_DONE;
}
/* 4connection established */
fprintf(stderr, "connection established for %s
", file[i].f_name);
FD_CLR(fd, &wset); /* no more writeability test */
write_get_cmd(&file[i]); /* write() the GET command */
}
else if (flags & F_READING && FD_ISSET(fd, &rs))
{
if ((n = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf))) == 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "end-of-file on %s
", file[i].f_name);
Close(fd);
file[i].f_flags = F_DONE; /* clears F_READING */
FD_CLR(fd, &rset);
nconn--;
nlefttoread--;
}
else
{
fprintf(stderr, "read %d bytes from %s
", n, file[i].f_name);
}
}
}
}
exit(0);
}测试:
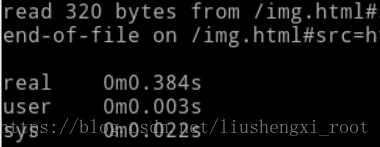
这是最大并行连接数是3时的情况:
附录:
1. connect函数说明(总结unp connect 即可 )
connect激发TCP的三路握手过程,而且仅在连接建立成功或者出错后才会返回。在一个非阻塞的套接字上调用
connect时,connect将立即返回一个EINPROGRESS错误,不过三路握手会继续进行。然后我们通过select去检测该连接成功或者失败。如果
connect连接失败,则该套接字不能再用,必须关闭! 不能对这样的套接字再次调用connect。
讨论:
以上是关于非阻塞 Connect的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章