UVA12569-Planning mobile robot on Tree (EASY Version)(BFS+状态压缩)
Posted npugen
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了UVA12569-Planning mobile robot on Tree (EASY Version)(BFS+状态压缩)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Problem UVA12569-Planning mobile robot on Tree (EASY Version)
Accept:138 Submit:686
Time Limit: 3000 mSec
 Problem Description
Problem Description
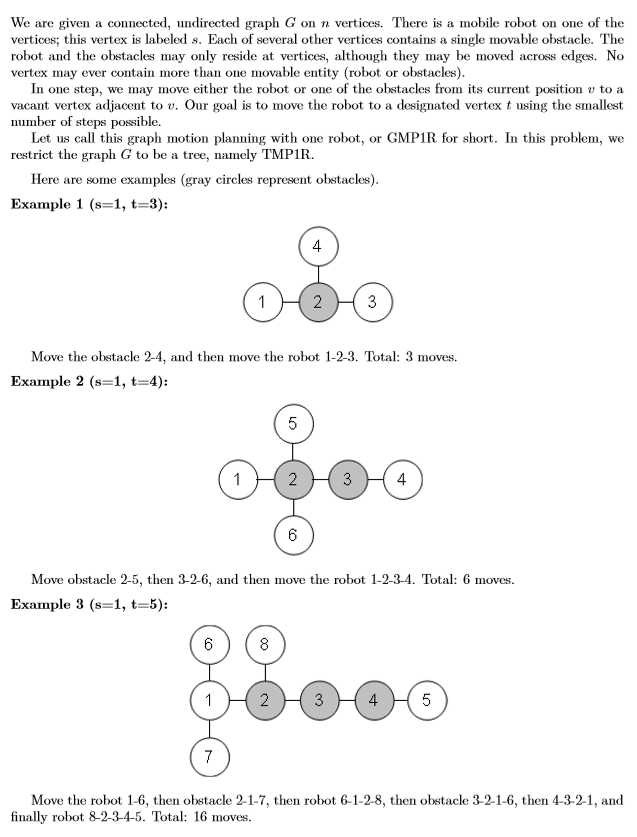
 Input
Input
The first line contains the number of test cases T (T ≤ 340). Each test case begins with four integers n, m, s, t (4 ≤ n ≤ 15, 0 ≤ m ≤ n?2, 1 ≤ s,t ≤ n, s ?= t), the number of vertices, the number of obstacles and the label of the source and target. Vertices are numbered 1 to n. The next line contains m different integers not equal to s, the vertices containing obstacles. Each of the next n ? 1 lines contains two integers u and v (1 ≤ u < v ≤ n), that means there is an edge u?v in the tree.
 Output
Output
For each test case, print the minimum number of moves k in the first line. Each of the next k lines containstwointegers a and b,thatmeanstomovetherobot/obstaclefrom a to b. Ifthereisnosolution, print ‘-1’. If there are multiple solutions, any will do. Print a blank line after each test case.
 Sample Input
Sample Input
4 1 1 3
2
1 2
2 3
2 4
6 2 1 4
2 3
1 2
2 3
3 4
2 5
2 6
8 3 1 5
2 3 4
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
1 6
1 7
2 8
 Sample Ouput
Sample Ouput
2 4
1 2
2 3
2 6
3 2
2 5
1 2
2 3
3 4
1 7
2 1
1 6
7 1
1 2
2 8
3 2
2 1
1 7
4 3
3 2
2 1
8 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 const int maxn = 16; 6 int n, m, s, t; 7 int ori; 8 9 struct Edge { 10 int to, next; 11 }edge[maxn << 1]; 12 13 struct Node { 14 int sit, robot; 15 int time; 16 Node(int sit = 0, int robot = 0, int time = 0) : 17 sit(sit), robot(robot), time(time) {} 18 }; 19 20 int tot, head[maxn]; 21 pair<int,int> pre[40000][maxn]; 22 bool vis[40000][maxn]; 23 24 void init() { 25 tot = 1; 26 memset(head, -1, sizeof(head)); 27 memset(pre, -1, sizeof(pre)); 28 memset(vis, false, sizeof(vis)); 29 } 30 31 void AddEdge(int u, int v) { 32 edge[tot].to = v; 33 edge[tot].next = head[u]; 34 head[u] = tot++; 35 } 36 37 inline int get_pos(int x) { 38 return 1 << x; 39 } 40 41 int bfs(pair<int,int> &res) { 42 queue<Node> que; 43 que.push(Node(ori, s, 0)); 44 vis[ori][s] = true; 45 46 while (!que.empty()) { 47 Node first = que.front(); 48 que.pop(); 49 if (first.robot == t) { 50 res.first = first.sit, res.second = first.robot; 51 return first.time; 52 } 53 int ssit = first.sit, rrob = first.robot; 54 //printf("%d %d ", ssit, rrob); 55 56 for (int i = head[rrob]; i != -1; i = edge[i].next) { 57 int v = edge[i].to; 58 if (ssit&get_pos(v) || vis[ssit][v]) continue; 59 vis[ssit][v] = true; 60 que.push(Node(ssit, v, first.time + 1)); 61 pre[ssit][v] = make_pair(ssit, rrob); 62 } 63 64 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 65 if (ssit&(get_pos(i))) { 66 for (int j = head[i]; j != -1; j = edge[j].next) { 67 int v = edge[j].to; 68 if (v == rrob || (ssit & get_pos(v))) continue; 69 int tmp = ssit ^ get_pos(v); 70 tmp ^= get_pos(i); 71 if (vis[tmp][rrob]) continue; 72 vis[tmp][rrob] = true; 73 que.push(Node(tmp, rrob, first.time + 1)); 74 pre[tmp][rrob] = make_pair(ssit, rrob); 75 } 76 } 77 } 78 } 79 return -1; 80 } 81 82 void output(pair<int,int> a) { 83 if (a.first == ori && a.second == s) return; 84 output(pre[a.first][a.second]); 85 int ppre = pre[a.first][a.second].first, now = a.first; 86 87 if (ppre^now) { 88 int b = -1, c = -1; 89 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 90 if (((ppre & (1 << i)) == (1 << i)) && ((now & (1 << i)) == 0)) { 91 b = i; 92 } 93 else if (((ppre & (1 << i)) == 0) && ((now & (1 << i)) == (1 << i))) { 94 c = i; 95 } 96 } 97 printf("%d %d ", b + 1, c + 1); 98 } 99 else { 100 printf("%d %d ", pre[a.first][a.second].second + 1, a.second + 1); 101 } 102 } 103 104 int con = 1; 105 106 int main() 107 { 108 int iCase; 109 scanf("%d", &iCase); 110 while (iCase--) { 111 init(); 112 scanf("%d%d%d%d", &n, &m, &s, &t); 113 s--, t--; 114 ori = 0; 115 int x; 116 for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { 117 scanf("%d", &x); 118 x--; 119 ori ^= get_pos(x); 120 } 121 122 int u, v; 123 for (int i = 1; i <= n - 1; i++) { 124 scanf("%d%d", &u, &v); 125 u--, v--; 126 AddEdge(u, v); 127 AddEdge(v, u); 128 } 129 130 pair<int, int> res; 131 int ans = bfs(res); 132 printf("Case %d: %d ", con++, ans); 133 if (ans != -1) output(res); 134 printf(" "); 135 } 136 return 0; 137 }
以上是关于UVA12569-Planning mobile robot on Tree (EASY Version)(BFS+状态压缩)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章