tensorflow学习之使用tensorboard 展示神经网络的graph/histogram/scalar
Posted harriett-lin
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了tensorflow学习之使用tensorboard 展示神经网络的graph/histogram/scalar相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
# 创建神经网络, 使用tensorboard 展示graph/histogram/scalar import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 若没有 pip install matplotlib # 定义一个神经层 def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size,n_layer, activation_function=None): #add one more layer and return the output of this layer layer_name="layer%s"%n_layer with tf.name_scope(layer_name): with tf.name_scope(‘Weights‘): Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]),name=‘W‘) tf.summary.histogram(layer_name+‘/weights‘,Weights) with tf.name_scope(‘biases‘): biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1,name=‘b‘) tf.summary.histogram(layer_name + ‘/biases‘, biases) with tf.name_scope(‘Wx_plus_b‘): Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + biases if activation_function is None: outputs = Wx_plus_b else: outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b) tf.summary.histogram(layer_name + ‘/outputs‘, outputs) return outputs #make up some real data x_data = np.linspace(-1, 1, 300)[:, np.newaxis] # x_data值为-1到1之间,有300个单位(例子),再加一个维度newaxis,即300行*newaxis列 noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.05, x_data.shape) # 均值为0.方差为0.05,格式和x_data一样 y_data = np.square(x_data) - 0.5 + noise #define placeholder for inputs to network with tf.name_scope(‘inputs‘): xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1],name=‘x_input1‘) # none表示无论给多少个例子都行 ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1],name=‘y_input1‘) # add hidden layer l1 = add_layer(xs, 1, 10, n_layer=1,activation_function=tf.nn.relu) # add output layer prediction = add_layer(l1, 10, 1,n_layer=2, activation_function=None) #the error between prediction and real data with tf.name_scope(‘loss‘): loss = tf.reduce_mean( tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys - prediction), reduction_indices=[1])) # 对每个例子进行求和并取平均值 reduction_indices=[1]指按行求和 tf.summary.scalar(‘loss‘,loss) with tf.name_scope(‘train‘): train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss) # 以0.1的学习效率对误差进行更正和提升 #两种初始化的方式 #init = tf.initialize_all_variables() init = tf.global_variables_initializer() sess = tf.Session() sess.run(init) #把所有的summary合并在一起 merged = tf.summary.merge_all() #把整个框架加载到一个文件中去,再从文件中加载出来放到浏览器中查看 #writer=tf.train.SummaryWriter("logs/",sess.graph) #首先找到tensorboard.exe的路径并进入c:AnacondaScripts,执行tensorboard.exe --logdir=代码生成的图像的路径(不能带中文) writer=tf.summary.FileWriter("../../logs/",sess.graph) fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1) ax.scatter(x_data, y_data) plt.ion() plt.show() #show()是一次性的展示,为了使连续的展示,加入plt.ion() for i in range(1000): sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data}) if i % 50 == 0: result = sess.run(merged,feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data}) writer.add_summary(result,i)
实验结果图:
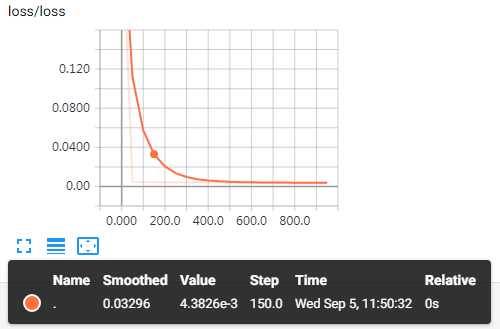
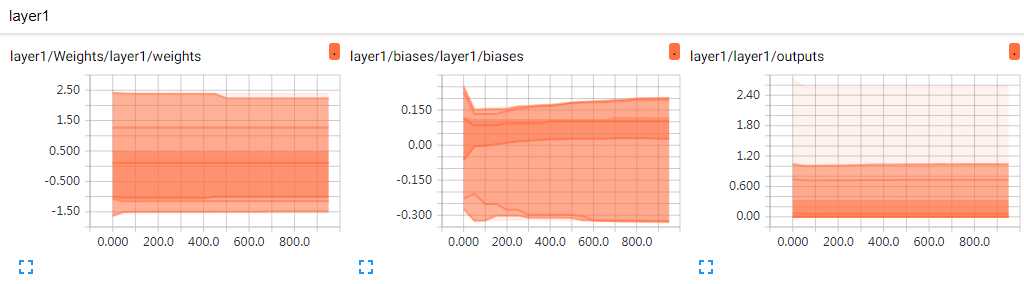
以上是关于tensorflow学习之使用tensorboard 展示神经网络的graph/histogram/scalar的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章