线性表之数组描述
Posted zhaobinyouth
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了线性表之数组描述相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.线性表的描述可以分为两种
- 数组描述:StaticList和DynamicList(动态数组)
- 链式描述
2.数组描述
- 数组描述方法将元素存储在一个数组中,通过一个索引以确定每个元素存储的位置
- 所有元素依次存储在一片连续的存储空间中
- 线性表中的每一个元素对应数组中的一个位置
3.创建一个数组类
要创建一个数组类必须确定数组类型和确定数组长度,所以针对以上两个问题有以下解决:
- 模板类
- 动态数组(数组空间不够的情况下动态增加数组长度)
4. StaticList类实现
- 使用原生数组作为顺序存储空间
- 使用模板参数决定数组大小(数组固定不可以改变)
#ifndef STATICLIST_H #define STATICLIST_H #include "Seqlist.h" namespace DataStructureLib { template <typename T, int N> class StaticList: public SeqList<T> { protected: T m_space[N];//顺序存储空间,N为模板的参数 (类成员m_space是一个原生的数组,原生数组的类型是T类型)在此静态的定义了一个原生数组存储空间 public: StaticList()// 指定父类成员的具体值 { this->m_array=m_space; this->m_length=0; } int capacity() const//int capacity() { return N; } }; } #endif // STATICLIST_H
测试
#include <iostream> #include "StaticList.h" #include "Exception.h" using namespace std; using namespace DataStructureLib; int main() { StaticList<int,5> l; for(int i=0;i<l.capacity(); i++) { l.insert(0,i); } for(int i=0;i<l.capacity();i++) { cout<<l[i]<<endl; } try { l[5]=9; } catch(const Exception& e) { cout<<e.message()<<endl; cout<<e.location()<<endl; } system("pause"); return 0; }
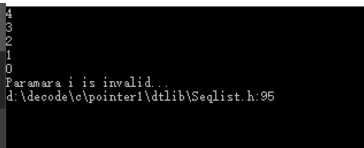
5.DynamicList设计要点(DynamicList 是一个类模板)
- 动态申请连续的堆空间作为顺序存储空间
- 动态设置顺序存储空间的大小
- 保证重置顺序存储空间时的异常安全性
函数调用前和函数调用后
- 不泄露任何资源
- 不允许破坏数据
函数异常安全的保证:
如果异常被抛出:
- 对象里面的任何成员仍能保持有效状态(即异常被抛出后该对象依然可以用)
- 没有数据的破坏和资源的泄漏
DynamicList.h
1 #ifndef DYNAMICLIST_H 2 #define DYNAMICLIST_H 3 #include "seqlist.h" 4 5 namespace DTLib 6 { 7 template<typename T> 8 class DynamicList:public Seqlist<T> 9 { 10 private: 11 int m_capacity ;//顺序存储空间的大小 12 public: 13 DynamicList(int capacity) //申请空间 14 { 15 this->m_array=new T[capacity]; 16 if(m_array!=NULL) 17 { 18 //、赋初始值 19 this->m_length=0; 20 this->m_capacity=capacity; 21 } 22 else 23 { 24 THROW_EXCEPTION(NotEnoughMemoryException,"No Enough Memory to Create DynamicList..."); 25 } 26 } 27 28 int capacity() const 29 { 30 return this->m_capacity; 31 } 32 33 //重新设置存储空间的大小 34 void resize(int capacity) 35 { 36 if(capacity!=this->m_capacity) 37 { 38 T* array=new T[capacity]; 39 if(array!=NULL) 40 { 41 int length=(this->m_capacity<capacity?this->m_capacity:capacity);//判断当前线性表里的个数 42 //如果this->m_capacity<capacity当前线性表里的存储的元素的个数小于新的目标大小capacity的,所有的数据元素都可以保存下来 43 //否则就以新的大小capacity为准 44 45 //复制 数据元素的 当前线性表中的元素复制到新申请到的堆空间 46 //因为需要保证数据元素不丢失 47 for(int i=0;i<length;i++) 48 { 49 array[i]=this->m_array[i]; 50 //T类在赋值时,可能产生异常!但是,即使这里发生了异常,由于 51 //下列的m_array、m_length、m_capacity还没被改变。所以,仍然可以 52 //保证DynamicList类是安全可用的,只是会造成array这个空间的内泄漏。 53 //这里作为T类的使用者,无须替T类的设计者考虑当赋值中出现问题时是要抛 54 //异常通知使用者,还是采用其它处理办法。如果T类的设计者以抛异常处理, 55 //则这里可以通过try-catch捕获这个赋值异常,然后在catch语句块中将 56 //array这个临时空间释放掉。 57 } 58 59 //这里不能先delete[] this->m_array,再给m_array、m_length、m_capacity 60 //赋值,因为delete可能会引起T调用析构函数,而如果在析构函数中抛出异常,以下对 61 //成员变量的赋值都将无法进行,从而造成函数异常时的不安全。因此,正确的顺序应该是 62 //先对成员变量赋值,最后再释放m_array的旧空间。 63 T* tmp=this->m_array; 64 65 m_array=array; 66 this->m_length=length; 67 this->m_capacity=capacity; 68 69 delete[] tmp;//重置前的顺序存储空间 70 71 } 72 73 else 74 { 75 THROW_EXCEPTION(NotEnoughMemoryException,"No Enough Memory to Resize Create DynamicList Objesct..."); 76 } 77 } 78 } 79 80 ~DynamicList() 81 { 82 delete[] this->m_array; 83 } 84 }; 85 } 86 87 #endif // DYNAMICLIST_H
测试
#include <iostream> #include "staticlist.h" #include "Exception.h" #include "dynamiclist.h" using namespace std; using namespace DTLib; int main() { DynamicList<int> l(5); for(int i=0;i<l.capacity(); i++) { l.insert(0,i); } for(int i=0;i<l.capacity();i++) { cout<<l[i]<<endl; } try { l[5]=9; } catch(const Exception& e) { cout<<e.message()<<endl; cout<<e.location()<<endl; } l.resize(3); for(int i=0;i<l.capacity();i++) { cout<<l[i]<<endl; } return 0; }
其他几个设计代码
List.h

1 #ifndef _LIST_H_ 2 #define _LIST_H_ 3 4 #include "Object.h" 5 6 namespace DataStructureLib { 7 8 template <typename T> 9 class List : public Object 10 { 11 public: 12 virtual bool insert(int index, const T& elem) = 0; 13 virtual bool remove(int index) = 0; 14 virtual bool get(int index, T& elem) const = 0; 15 virtual int length() const = 0; 16 virtual void clear() = 0; 17 }; 18 19 } 20 21 #endif // _LIST_H_
Seqlist.h

#ifndef _SEQLIST_H_ #define _SEQLIST_H_ #include "list.h" #include "Exception.h" namespace DataStructureLib { template <typename T> class SeqList : public List<T> { protected: T* m_array; //顺序存储空间 int m_length; //当前线性表长度 public: //插入元素 bool insert(int index, const T &elem) { bool ret = ((0 <= index)&&(index <= m_length)); ret = ret && (m_length < capacity()); if(ret){ //将index及其之后的元素向后移动一个位置 for(int pos=m_length-1; pos>=index; pos--){ m_array[pos + 1] = m_array[pos]; } //新元素插入在index位置 m_array[index] = elem; m_length++; } return ret; } //删除元素 bool remove(int index) { bool ret = ((0 <= index)&&(index < m_length)); if(ret){ for(int pos=index; pos<m_length-1; pos++){ m_array[pos] = m_array[pos + 1]; } m_length--; } return ret; } //设置元素 bool set(int index, const T& elem) { bool ret = ((0 <= index)&&(index < m_length)); if(ret){ m_array[index] = elem; } return ret; } //获取元素 bool get(int index, T &elem) const { bool ret = ((0 <= index)&&(index < m_length)); if(ret){ elem = m_array[index]; } return ret; } //当前长度 int length()const { return m_length; } //清空线性表 void clear() { m_length = 0; } //顺序存储线性表的数组访问方式 T& operator[](int index) { if((0<=index) && (index<m_length)){ return m_array[index]; }else{ THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Parameter index is invalid ..."); } } T operator [](int index) const { return (const_cast<SeqList<T>&>(*this))[index]; } //顺序存储空间的容量 virtual int capacity()const = 0; }; } #endif // _SEQLIST_H_
object.h

1 #ifndef OBJECT_H 2 #define OBJECT_H 3 4 5 namespace DataStructureLib 6 { 7 8 class Object 9 { 10 public: 11 //以下四个重载函数用于统一不同编译器new失败时的结果不同的问题。 12 //throw()表示不抛出异常,即如果申请内请失败时,统一返回NULL而不抛异常 13 void* operator new(size_t size) throw(); 14 void operator delete(void* p); 15 16 void* operator new[](size_t size) throw(); 17 void operator delete[](void* p); 18 19 virtual ~Object()=0; 20 }; 21 } 22 #endif // OBJECT_H
object.cpp

#include "object.h" #include "cstdlib" #include<iostream> using namespace std; namespace DataStructureLib { void* Object::operator new(size_t size) throw() { cout<<"Object::operator new : "<< size<<endl; return malloc(size);//这里的size代表申请内存空间的字节数 } void Object::operator delete(void* p) { cout<<"Object::operator delete : "<<p<<endl; free(p); } void* Object::operator new[](size_t size) throw() { cout<<"Object::operator new[]"<<endl; return malloc(size);//此时的size代表申请对象的数量 } void Object::operator delete[](void* p) { cout<<"Object::operator delete[]:"<<p<<endl; free(p); } Object::~Object() { } }
SmartPointer.h

#ifndef _SMARTPOINTER_H_ #define _SMARTPOINTER_H_ #include<stdio.h > #include"object.h" namespace DataStructureLib { template<typename T> class SmartPointer:public Object { T* m_pointer; public: SmartPointer(T* pointer= NULL) { m_pointer=pointer; } SmartPointer(const SmartPointer<T>& obj) { m_pointer=obj.m_pointer; const_cast<SmartPointer<T>&>(obj).m_pointer=NULL; } SmartPointer& operator=(const SmartPointer<T>& obj) { if (m_pointer!=obj.m_pointer) { m_pointer=obj.m_pointer; const_cast<SmartPointer<T>&>(obj).m_pointer=NULL; } return *this; } T* operator ->() { return m_pointer; } T& operator *() { return *m_pointer; } bool isNull() { return (m_pointer==NULL); } T* get() { return m_pointer; } ~SmartPointer(void) { delete m_pointer; } }; } #endif
Exception.h

#ifndef _EXCEPTION_H_ #define _EXCEPTION_H_ #include"object.h" namespace DataStructureLib { #define THROW_EXCEPTION(e,m) throw e(m,__FILE__,__LINE__) class Exception:public Object { protected: char* m_message; char* m_location; protected: void init(const char*,const char*,int);//由于三个构造函数中的逻辑很相似,所以可以将相似的部分统一放到一个函数init() public: Exception(const char* message); Exception(const char* file,int line); Exception(const char* message,const char* file,int line); //涉及到堆空间即需进行深拷贝,拷贝构造函数和"=" Exception(const Exception& e); Exception& operator =(const Exception& e); virtual const char* message() const; virtual const char* location() const; virtual ~Exception(void)= 0; }; //计算异常类 class ArithmeticException: public Exception { public: ArithmeticException():Exception(0){} ArithmeticException(const char* message):Exception(message){} ArithmeticException(const char*file, int line):Exception(file, line){} ArithmeticException(const char *message, const char* file, int line):Exception(message, file, line){} ArithmeticException(const ArithmeticException& e): Exception(e){} ArithmeticException& operator=(const ArithmeticException& e) { Exception::operator =(e); return *this; } }; //空指针异常 class NullPointerException: public Exception { public: NullPointerException():Exception(0){} NullPointerException(const char* message):Exception(message){} NullPointerException(const char*file, int line):Exception(file, line){} NullPointerException(const char *message, const char* file, int line):Exception(message, file, line){} NullPointerException(const NullPointerException& e): Exception(e){} NullPointerException& operator=(const NullPointerException& e) { Exception::operator =(e); return *this; } }; //越界异常类 class IndexOutOfBoundsException: public Exception { public: IndexOutOfBoundsException():Exception(0){} IndexOutOfBoundsException(const char* message):Exception(message){} IndexOutOfBoundsException(const char*file, int line):Exception(file, line){} IndexOutOfBoundsException(const char *message, const char* file, int line):Exception(message, file, line){} IndexOutOfBoundsException(const IndexOutOfBoundsException& e): Exception(e){} IndexOutOfBoundsException& operator=(const IndexOutOfBoundsException& e) { Exception::operator =(e); return *this; } }; //内存不足异常类 class NotEnoughMemoryException: public Exception { public: NotEnoughMemoryException():Exception(0){} NotEnoughMemoryException(const char* message):Exception(message){} NotEnoughMemoryException(const char*file, int line):Exception(file, line){} NotEnoughMemoryException(const char *message, const char* file, int line):Exception(message, file, line){} NotEnoughMemoryException(const NotEnoughMemoryException& e): Exception(e){} NotEnoughMemoryException& operator=(const NotEnoughMemoryException& e) { Exception::operator =(e); return *this; } }; //参数错误异常类 class InvalidParameterException: public Exception { public: InvalidParameterException():Exception(0){} InvalidParameterException(const char* message):Exception(message){} InvalidParameterException(const char*file, int line):Exception(file, line){} InvalidParameterException(const char *message, const char* file, int line):Exception(message, file, line){} InvalidParameterException(const InvalidParameterException& e): Exception(e){} InvalidParameterException& operator=(const InvalidParameterException& e) { Exception::operator =(e); return *this; } }; } #endif
Exception.cpp

#include "Exception.h" #include <cstring> #include <cstdlib> namespace DataStructureLib { void Exception::init(const char* message,const char* file,int line) { m_message=strdup(message);//这里不能直接使用m_message=message, //因为message指针指向的数据有可能会在栈、堆、全局区,如果是在栈上,局部变量可能会消失,如果直接使用m_message=message就会不安全 if(file!=NULL) { char sl[16]={0}; itoa(line,sl,10);//将line转为char类型 10代表十进制 m_location=static_cast<char* >(malloc(strlen(file)+strlen(sl)+2));//加2表示后面的":"和结束符即“/0” m_location=strcpy(m_location,file); m_location=strcat(m_location,":"); m_location=strcat(m_location,sl); } } Exception:: Exception(const char* message) { init(message,NULL,0); } Exception::Exception(const char* file,int line) { init(NULL,file,line); } Exception::Exception(const char* message,const char* file,int line) { init(message,file,line); } Exception::~Exception(void) { free(m_message); free(m_location); } const char* Exception::message() const { return m_message; } const char* Exception::location() const { return m_location; } Exception::Exception(const Exception& e) { m_message=strdup(e.m_message); m_location=strdup(e.m_location); } Exception& Exception::operator =(const Exception& e) { if (this!=&e) { free(m_message); free(m_location); m_message=strdup(e.m_message); m_location=strdup(e.m_location); } return *this; } }
以上是关于线性表之数组描述的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
