第43课 继承的概念和意义
Posted wanmeishenghuo
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了第43课 继承的概念和意义相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
面向对象的高端课程都是和继承相关的,例如设计模式。
思考:
类与类之间是否存在直接的关联关系?
生活中的例子:
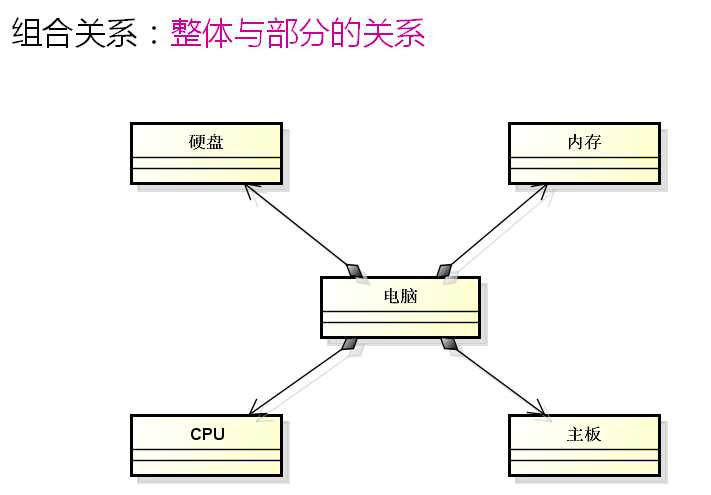
组合关系的程序描述:
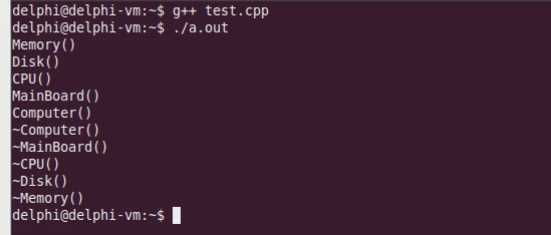
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class Memory 7 { 8 public: 9 Memory() 10 { 11 cout << "Memory()" << endl; 12 } 13 ~Memory() 14 { 15 cout << "~Memory()" << endl; 16 } 17 }; 18 19 class Disk 20 { 21 public: 22 Disk() 23 { 24 cout << "Disk()" << endl; 25 } 26 ~Disk() 27 { 28 cout << "~Disk()" << endl; 29 } 30 }; 31 32 class CPU 33 { 34 public: 35 CPU() 36 { 37 cout << "CPU()" << endl; 38 } 39 ~CPU() 40 { 41 cout << "~CPU()" << endl; 42 } 43 }; 44 45 class MainBoard 46 { 47 public: 48 MainBoard() 49 { 50 cout << "MainBoard()" << endl; 51 } 52 ~MainBoard() 53 { 54 cout << "~MainBoard()" << endl; 55 } 56 }; 57 58 class Computer 59 { 60 Memory mMem; 61 Disk mDisk; 62 CPU mCPU; 63 MainBoard mMainBoard; 64 public: 65 Computer() 66 { 67 cout << "Computer()" << endl; 68 } 69 void power() 70 { 71 cout << "power()" << endl; 72 } 73 void reset() 74 { 75 cout << "reset()" << endl; 76 } 77 ~Computer() 78 { 79 cout << "~Computer()" << endl; 80 } 81 }; 82 83 int main() 84 { 85 Computer c; 86 87 return 0; 88 }
运行结果如下:
组合关系的特点:

实际工程中先考虑组合关系。组合关系能满足需求就用组合关系。
继承关系:
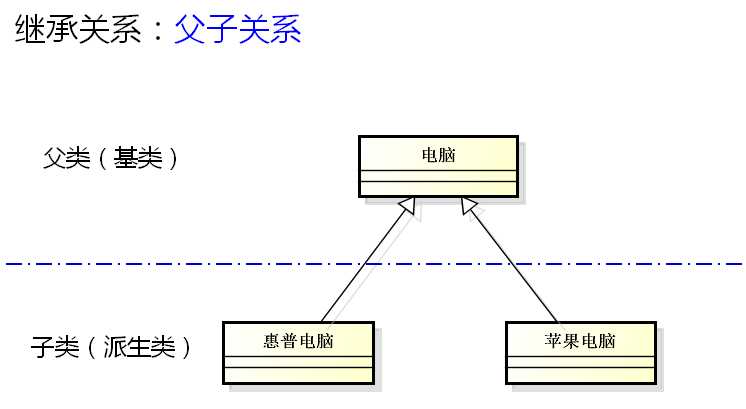


示例:
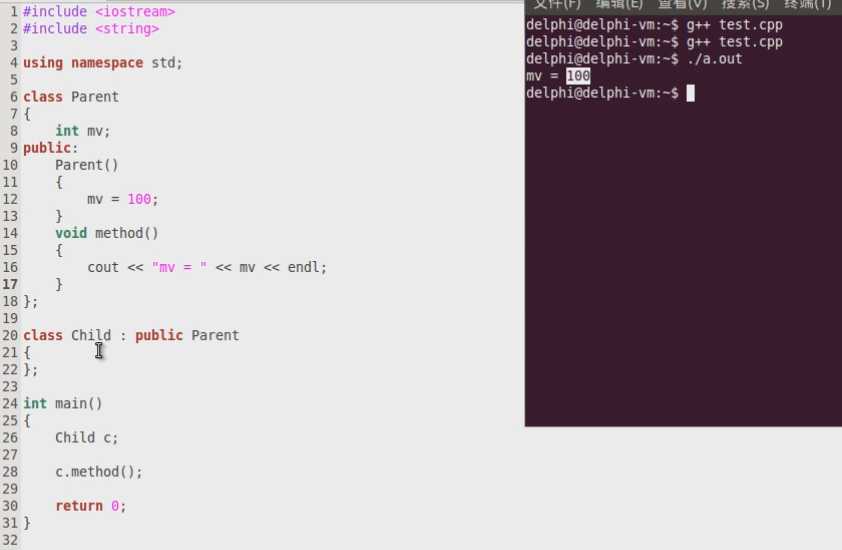
子类继承了父类的mv和其他成员函数,所以打印出100。
子类不但可以继承父类的代码,而且还可以添加新代码,继承还有另一个层面的意义,那就是代码复用,如下:
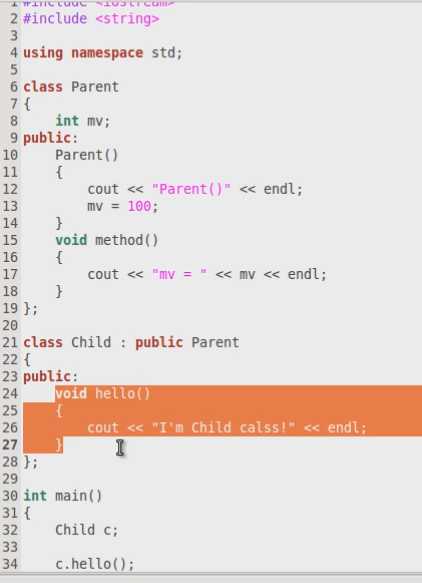
C语言使用已经存在的代码只能复制粘贴,C++则可以通过继承。
完成的程序如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class Parent 7 { 8 int mv; 9 public: 10 Parent() 11 { 12 cout << "Parent()" << endl; 13 mv = 100; 14 } 15 void method() 16 { 17 cout << "mv = " << mv << endl; 18 } 19 }; 20 21 class Child : public Parent 22 { 23 public: 24 void hello() 25 { 26 cout << "I‘m Child calss!" << endl; 27 } 28 }; 29 30 int main() 31 { 32 Child c; 33 34 c.hello(); 35 c.method(); 36 37 return 0; 38 }
重要规则:

示例程序:
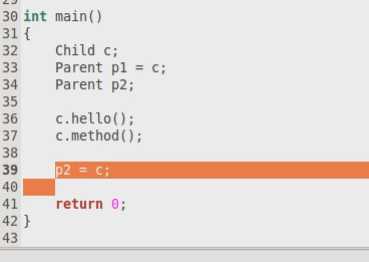
Child对象可以直接当做Parent对象使用的。
继承的意义:

继承示例:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class Memory 7 { 8 public: 9 Memory() 10 { 11 cout << "Memory()" << endl; 12 } 13 ~Memory() 14 { 15 cout << "~Memory()" << endl; 16 } 17 }; 18 19 class Disk 20 { 21 public: 22 Disk() 23 { 24 cout << "Disk()" << endl; 25 } 26 ~Disk() 27 { 28 cout << "~Disk()" << endl; 29 } 30 }; 31 32 class CPU 33 { 34 public: 35 CPU() 36 { 37 cout << "CPU()" << endl; 38 } 39 ~CPU() 40 { 41 cout << "~CPU()" << endl; 42 } 43 }; 44 45 class MainBoard 46 { 47 public: 48 MainBoard() 49 { 50 cout << "MainBoard()" << endl; 51 } 52 ~MainBoard() 53 { 54 cout << "~MainBoard()" << endl; 55 } 56 }; 57 58 class Computer 59 { 60 Memory mMem; 61 Disk mDisk; 62 CPU mCPU; 63 MainBoard mMainBoard; 64 public: 65 Computer() 66 { 67 cout << "Computer()" << endl; 68 } 69 void power() 70 { 71 cout << "power()" << endl; 72 } 73 void reset() 74 { 75 cout << "reset()" << endl; 76 } 77 ~Computer() 78 { 79 cout << "~Computer()" << endl; 80 } 81 }; 82 83 class HPBook : public Computer 84 { 85 string mOS; 86 public: 87 HPBook() 88 { 89 mOS = "Windows 8"; 90 } 91 void install(string os) 92 { 93 mOS = os; 94 } 95 void OS() 96 { 97 cout << mOS << endl; 98 } 99 }; 100 101 class MacBook : public Computer 102 { 103 public: 104 void OS() 105 { 106 cout << "Mac OS" << endl; 107 } 108 }; 109 110 int main() 111 { 112 HPBook hp; 113 114 hp.power(); 115 hp.install("Ubuntu 16.04 LTS"); 116 hp.OS(); 117 118 cout << endl; 119 120 MacBook mac; 121 122 mac.OS(); 123 124 return 0; 125 }
运行结果如下:
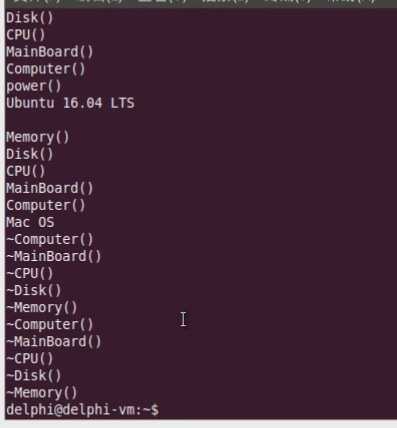
小结:

以上是关于第43课 继承的概念和意义的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章