面试题——ArrayList和LinkedList的区别
Posted kunrong
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了面试题——ArrayList和LinkedList的区别相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
List概括
先回顾一下List在Collection的框架图:
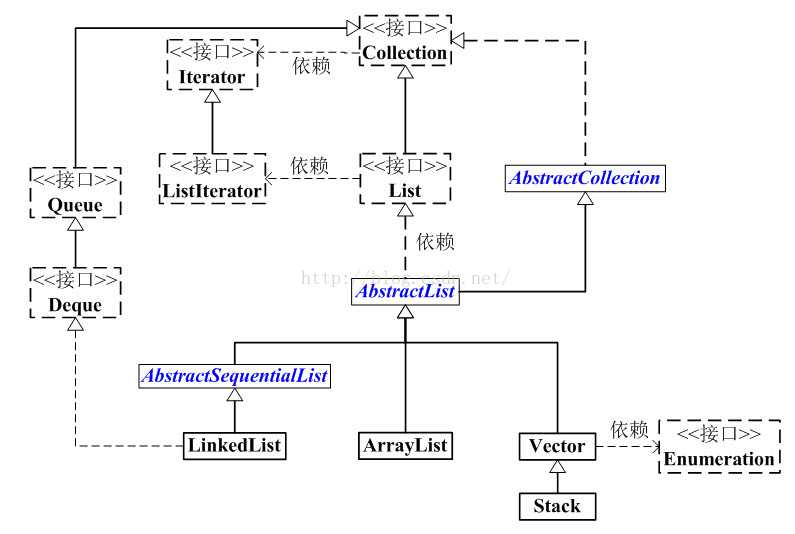
从图中可以看出:
- List是一个接口,他继承Collection接口,代表有序的队列。
- AbstractList是一个抽象类, ,它继承与AbstractCollection。AbstractList实现了List接口中除了size()、get(int location)之外的方法。
- AbstractSequentialList是一个抽象类,它继承与AbstrctList。AbstractSequentialList实现了“链表中,根据index索引值操作链表的全部方法”
- ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector和Stack是List的四个实现类,其中Vector是基于JDK1.0,虽然实现了同步,但是效率低,已经不用了,Stack继承与Vector,所以不再赘述。
- LinkList是个双向链表,它同样可以被当做栈,队列,或者双端队列。
ArrayList 和 LinkList区别
ArrayList是实现了基于动态数组的数据结构,而LinkedList是基于链表的数据结构,。
对于随机访问的get和set,ArrayList要优于LinkedList,因为LinkedList基于指针的移动。
对于添加和删除操作add和remove,一般大家都会说LinkedList要比ArrayList快,因为ArrayList要移动数据。但是实际情况并非这样,对于添加或删除,LinkedList和ArrayList并不能明确说明谁快谁慢,下面会详细分析。
我们结合之前分析的源码,来看看为什么是这样的: ArrayList中的随机访问、添加和删除部分源码如下:*** //获取index位置的元素值
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index); //首先判断index的范围是否合法return elementData(index);
}
//将index位置的值设为element,并返回原来的值
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue; }
//将element添加到ArrayList的指定位置
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
//将index以及index之后的数据复制到index+1的位置往后,即从index开始向后挪了一位
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element; //然后在index处插入element
size++; }
//删除ArrayList指定位置的元素
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
//向左挪一位,index位置原来的数据已经被覆盖了
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
//多出来的最后一位删掉
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue; }
***
LinkedList中的随机访问、添加和删除部分源码如下:
//获得第index个节点的值
*** public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
//设置第index元素的值
public E set(int index, E element) {
checkElementIndex(index);
Node
//在index个节点之前添加新的节点
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index)); }
//删除第index个节点
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
//定位index处的节点
Node
从源码可以看出,ArrayList想要get(int index)元素时,直接返回index位置上的元素,而LinkedList需要通过for循环进行查找,虽然LinkedList已经在查找方法上做了优化,比如index < size / 2,则从左边开始查找,反之从右边开始查找,但是还是比ArrayList要慢。这点是毋庸置疑的。
ArrayList想要在指定位置插入或删除元素时,主要耗时的是System.arraycopy动作,会移动index后面所有的元素;LinkedList主耗时的是要先通过for循环找到index,然后直接插入或删除。这就导致了两者并非一定谁快谁慢,下面通过一个测试程序来测试一下两者插入的速度:
*** import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
/*
- @description 测试ArrayList和LinkedList插入的效率
@eson_15
*/
public class ArrayOrLinked {
static Listpublic static void main(String[] args) {
//首先分别给两者插入10000条数据 for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){ array.add(i); linked.add(i); } //获得两者随机访问的时间 System.out.println("array time:"+getTime(array)); System.out.println("linked time:"+getTime(linked)); //获得两者插入数据的时间 System.out.println("array insert time:"+insertTime(array)); System.out.println("linked insert time:"+insertTime(linked));}
public static long getTime(List//插入数据
public static long insertTime(List}
}
***
****
index = 1000的时候
array time:7
linked time:567
array insert time:29
linked insert time:37
index = 5000的时候
array time:5
linked time:415
array insert time:15
linked insert time:128
index = 9000的时候
array time:6
linked time:443
array insert time:12
linked insert time:152
从运行结果看,LinkedList的效率是越来越差。
所以当插入的数据量很小时,两者区别不太大,当插入的数据量大时,大约在容量的1/10之前,LinkedList会优于ArrayList,在其后就劣与ArrayList,且越靠近后面越差。所以个人觉得,一般首选用ArrayList,由于LinkedList可以实现栈、队列以及双端队列等数据结构,所以当特定需要时候,使用LinkedList,当然咯,数据量小的时候,两者差不多,视具体情况去选择使用;当数据量大的时候,如果只需要在靠前的部分插入或删除数据,那也可以选用LinkedList,反之选择ArrayList反而效率更高。以上是关于面试题——ArrayList和LinkedList的区别的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章