第41课 内存操作经典问题分析1
Posted wanmeishenghuo
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了第41课 内存操作经典问题分析1相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
野指针:

野指针的由来:

示例程序:
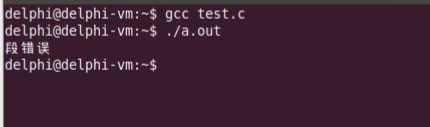
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <malloc.h> 3 4 5 int main() 6 { 7 int* p1 = (int*)malloc(40); 8 int* p2 = (int*)1234567; 9 int i = 0; 10 11 for(i=0; i<40; i++) 12 { 13 *(p1 + i) = 40 - i; 14 } 15 16 free(p1); 17 18 for(i=0; i<40; i++) 19 { 20 p1[i] = p2[i]; 21 } 22 23 return 0; 24 }
第13行越界之后就相当于操作野指针了。第8行将随意一个地址转换为指针,也相当于野指针。
运行结果如下:
基本原则:

示例:
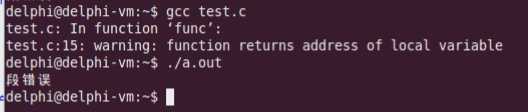
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <malloc.h> 4 5 struct Student 6 { 7 char* name; 8 int number; 9 }; 10 11 char* func() 12 { 13 char p[] = "D.T.Software"; 14 15 return p; 16 } 17 18 void del(char* p) 19 { 20 printf("%s ", p); 21 22 free(p); 23 } 24 25 int main() 26 { 27 struct Student s; 28 char* p = func(); 29 30 strcpy(s.name, p); 31 32 s.number = 99; 33 34 p = (char*)malloc(5); 35 36 strcpy(p, "D.T.Software"); 37 38 del(p); 39 40 return 0; 41 }
第15行返回局部字符数组,是不正确的。结构体s中的name没有初始化,s.name和p都是野指针。
34-36行的内存拷贝也会产生越界。和“任何与内存操作相关的函数必须指定长度信息”原则相违背。
运行结果如下:
小结:

以上是关于第41课 内存操作经典问题分析1的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章