8.26校内测试重构树求直径BFS模拟线段树维护DP
Posted wans-caesar-02111007
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了8.26校内测试重构树求直径BFS模拟线段树维护DP相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
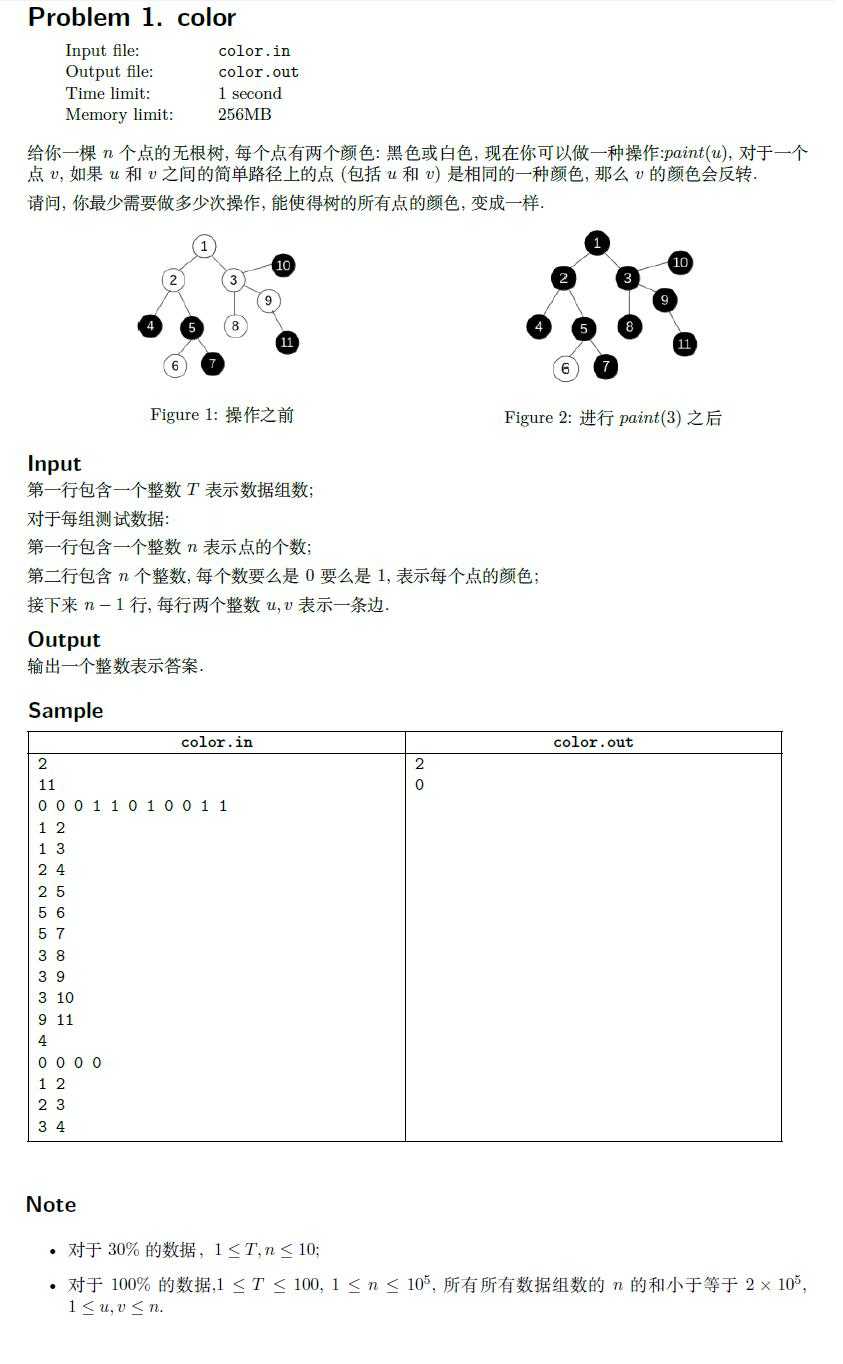
题目性质比较显然,相同颜色联通块可以合并成一个点,重新建树后,发现相邻两个点的颜色一定是不一样的。
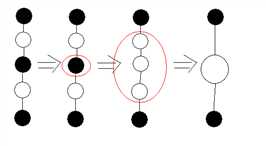
然后发现,对于一条链来说,每次把一个点反色,实际上使点数少了2个。如下图
而如果一条链上面有分支,也是一样:
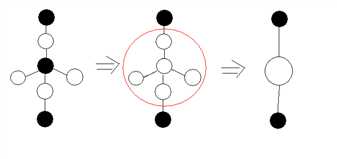
所以我们实际上只需要把最长链上的变成一种颜色就可以了。最长链就是直径,需要改动的点就是$frac{tot+1}{2}$,$tot$就是直径的点数。
(话说$stl$好慢aaa!!!要克制住我自己少用$map$叻!
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<map> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; int n, a[100005]; int stot, tov[200005], nex[200005], h[100005]; map < pair < int, int >, int > G; void add ( int u, int v ) { tov[++stot] = v; nex[stot] = h[u]; h[u] = stot; } int stot_co, tov_co[200005], nex_co[200005], h_co[100005]; void add_co ( int u, int v ) { tov_co[++stot_co] = v; nex_co[stot_co] = h_co[u]; h_co[u] = stot_co; } int fa[100005]; int find ( int x ) { if ( x != fa[x] ) fa[x] = find ( fa[x] ); return x; } void unionn ( int x, int y ) { int xx = find ( x ), yy = find ( y ); fa[xx] = yy; } int opt, color[100005]; void dfs1 ( int u, int f ) { for ( int i = h[u]; i; i = nex[i] ) { int v = tov[i]; if ( v == f ) continue; color[v] = 0; if ( a[v] == a[u] ) color[v] = color[u]; else color[v] = ++ opt; dfs1 ( v, u ); int x = find ( color[v] ), y = find ( color[u] ); if ( color[v] != color[u] && x != y ) { add_co ( color[v], color[u] ); add_co ( color[u], color[v] ); unionn ( x, y ); } } } int dis[100005], rt; void dfs ( int u, int f ) { for ( int i = h_co[u]; i; i = nex_co[i] ) { int v = tov_co[i]; if ( v == f ) continue; dis[v] = dis[u] + 1; dfs ( v, u ); } if ( dis[u] > dis[rt] ) rt = u; } int main ( ) { freopen ( "color.in", "r", stdin ); freopen ( "color.out", "w", stdout ); int T; scanf ( "%d", &T ); while ( T -- ) { G.clear ( ); stot = 0, stot_co = 0, opt = 0; scanf ( "%d", &n ); for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) h[i] = 0; for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) h_co[i] = 0; for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) color[i] = 0; for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) scanf ( "%d", &a[i] ); for ( int i = 1; i < n; i ++ ) { int u, v; scanf ( "%d%d", &u, &v ); add ( u, v ); add ( v, u ); } for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) fa[i] = i; color[1] = ++opt; dfs1 ( 1, 0 ); rt = 0; for ( int i = 1; i <= opt; i ++ ) dis[i] = 0; dfs ( 1, 0 ); for ( int i = 1; i <= opt; i ++ ) dis[i] = 0; dfs ( rt, 0 ); printf ( "%d ", ( dis[rt] + 1 ) / 2 ); } return 0; }
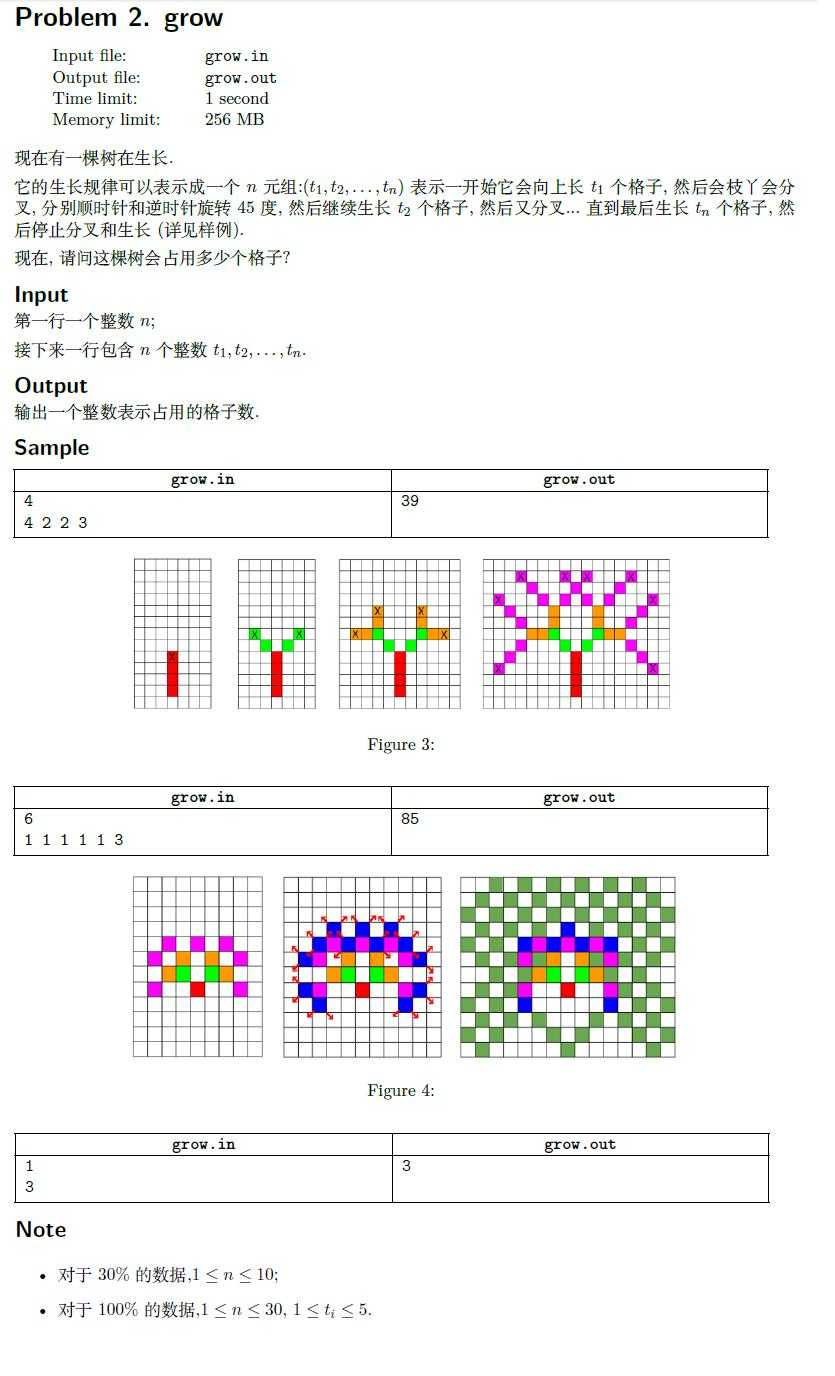
小模拟,考试的时候觉得状态太多,不可能重复???然后就没有写$vis$打标记,下来一加就...(辛酸泪QAQ
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<queue> #include<map> using namespace std; int n, t[35], G[400][400]; map < int, int > mx, my; struct node { int x, y, opt, id; node ( int x = 0, int y = 0, int opt = 0, int id = 0 ) : x ( x ), y ( y ), opt ( opt ), id ( id ) { } }; queue < node > q; int vis[404][404][31][9]; struct QAQ { int x, y; QAQ ( int x = 0, int y = 0 ) : x ( x ), y ( y ) { } }; QAQ print ( int x, int y, int opt, int id ) { for ( int i = 1; i <= t[id]; i ++ ) { G[x][y] = 1; x = x + mx[opt]; y = y + my[opt]; } return QAQ ( x - mx[opt], y - my[opt] ); } void BFS ( int sx, int sy ) { q.push ( node ( sx, sy + t[1] - 1, 0, 1 ) ); QAQ a = print ( sx, sy, 0, 1 ); vis[sx][sy+t[1]-1][1][0] = 1; while ( !q.empty ( ) ) { node x = q.front ( ); q.pop ( ); if ( x.id == n ) break; if ( x.opt != -3 && x.opt != 4 ) { int L = x.opt - 1, R = x.opt + 1; int id = x.id + 1; int lsx = x.x + mx[L], lsy = x.y + my[L]; int rsx = x.x + mx[R], rsy = x.y + my[R]; QAQ ll = print ( lsx, lsy, L, id ); QAQ rr = print ( rsx, rsy, R, id ); if ( !vis[ll.x][ll.y][id][L] ) { q.push ( node ( ll.x, ll.y, L, id ) ); vis[ll.x][ll.y][id][L] = 1; } if ( !vis[rr.x][rr.y][id][R] ) { q.push ( node ( rr.x, rr.y, R, id ) ); vis[rr.x][rr.y][id][R] = 1; } } else if ( x.opt == -3 ) { int L = 4, R = x.opt + 1; int id = x.id + 1; int lsx = x.x + mx[L], lsy = x.y + my[L]; int rsx = x.x + mx[R], rsy = x.y + my[R]; QAQ ll = print ( lsx, lsy, L, id ); QAQ rr = print ( rsx, rsy, R, id ); if ( !vis[ll.x][ll.y][id][L] ) { q.push ( node ( ll.x, ll.y, L, id ) ); vis[ll.x][ll.y][id][L] = 1; } if ( !vis[rr.x][rr.y][id][R] ) { q.push ( node ( rr.x, rr.y, R, id ) ); vis[rr.x][rr.y][id][R] = 1; } } else if ( x.opt == 4 ) { int L = x.opt - 1, R = -3; int id = x.id + 1; int lsx = x.x + mx[L], lsy = x.y + my[L]; int rsx = x.x + mx[R], rsy = x.y + my[R]; QAQ ll = print ( lsx, lsy, L, id ); QAQ rr = print ( rsx, rsy, R, id ); if ( !vis[ll.x][ll.y][id][L] ) { q.push ( node ( ll.x, ll.y, L, id ) ); vis[ll.x][ll.y][id][L] = 1; } if ( !vis[rr.x][rr.y][id][R] ) { q.push ( node ( rr.x, rr.y, R, id ) ); vis[rr.x][rr.y][id][R] = 1; } } } } int main ( ) { freopen ( "grow.in", "r", stdin ); freopen ( "grow.out", "w", stdout ); scanf ( "%d", &n ); mx[0] = 0, mx[1] = 1, mx[2] = 1, mx[3] = 1, mx[4] = 0, mx[-1] = -1, mx[-2] = -1, mx[-3] = -1; my[0] = 1, my[1] = 1, my[2] = 0, my[3] = -1, my[4] = -1, my[-1] = 1, my[-2] = 0, my[-3] = -1; for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) scanf ( "%d", &t[i] ); BFS ( 150, 150 ); int ans = 0; for ( int i = 0; i < 400; i ++ ) for ( int j = 0; j < 400; j ++ ) if ( G[i][j] ) ans ++; printf ( "%d", ans ); }
有关串用$dp$解决是很显然的(?$idy$题解原话),定义$dp[s][t]$表示从$s$状态转移到$t$状态最少的修改数。关于状态定义代码有注释。用线段树维护区间状态转移$dp$值,每个节点保存一个矩阵,节点合并时类似$floyed$,枚举断点转移。查询时查询区间即可。
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #define oo 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std; // 0 1 2 3 4 // $ 2 20 201 2017 const int N = 100005; struct Info { int dp[5][5]; void init ( int cur ) { memset ( dp, 0x3f, sizeof ( dp ) ); if ( cur == 3 || cur == 4 || cur == 5 || cur == 8 || cur == 9 ) { for ( int i = 0; i <= 4; i ++ ) dp[i][i] = 0; } else if ( cur == 2 ) { dp[0][0] = 1; dp[0][1] = 0; dp[1][1] = dp[2][2] = dp[3][3] = dp[4][4] = 0; } else if ( cur == 0 ) { dp[1][2] = 0; dp[1][1] = 1; dp[0][0] = dp[2][2] = dp[3][3] = dp[4][4] = 0; } else if ( cur == 1 ) { dp[2][2] = 1; dp[2][3] = 0; dp[0][0] = dp[1][1] = dp[3][3] = dp[4][4] = 0; } else if ( cur == 7 ) { dp[3][3] = 1; dp[3][4] = 0; dp[0][0] = dp[1][1] = dp[2][2] = dp[4][4] = 0; } else if ( cur == 6 ) { dp[3][3] = 1; dp[4][4] = 1; dp[0][0] = dp[1][1] = dp[2][2] = 0; } } }; Info operator + ( const Info &r, const Info &s ) { Info rt; memset ( &rt, 0x3f, sizeof ( rt ) ); for ( int i = 0; i <= 4; i ++ ) for ( int j = 0; j <= 4; j ++ ) for ( int k = i; k <= j; k ++ ) { rt.dp[i][j] = min ( rt.dp[i][j], r.dp[i][k] + s.dp[k][j] ); } return rt; } struct node { Info info; node *ls, *rs; } pool[N*4], *tail = pool, *root; int a[N]; char s[N]; node *build ( int l, int r ) { node *nd = ++tail; if ( l == r ) { nd -> info.init ( a[l] ); return nd; } int mid = ( l + r ) >> 1; nd -> ls = build ( l, mid ); nd -> rs = build ( mid + 1, r ); nd -> info = nd -> ls -> info + nd -> rs -> info; return nd; } Info query ( node *nd, int l, int r, int L, int R ) { if ( l >= L && r <= R ) return nd -> info; int mid = ( l + r ) >> 1; if ( R <= mid ) return query ( nd -> ls, l, mid, L, R ); else if ( L > mid ) return query ( nd -> rs, mid + 1, r, L, R ); else return query ( nd -> ls, l, mid, L, R ) + query ( nd -> rs, mid + 1, r, L, R ); } int n, q; int query ( int l, int r ) { Info info = query ( root, 1, n, l, r ); return info.dp[0][4] == oo ? -1 : info.dp[0][4]; } int main ( ) { freopen ( "year.in", "r", stdin ); freopen ( "year.out", "w", stdout ); scanf ( "%s", s + 1 ); scanf ( "%d", &q ); n = strlen ( s + 1 ); for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) a[i] = s[i] - ‘0‘; root = build ( 1, n ); while ( q -- ) { int l, r; scanf ( "%d%d", &l, &r ); printf ( "%d ", query ( l, r ) ); } return 0; }
以上是关于8.26校内测试重构树求直径BFS模拟线段树维护DP的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章