数据结构 - 单源最短路径之迪杰斯特拉(Dijkstra)算法详解(Java)
Posted gnlin0820
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构 - 单源最短路径之迪杰斯特拉(Dijkstra)算法详解(Java)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
给出一个图,求某个端点(goal)到其余端点或者某个端点的最短路径,最容易想到的求法是利用DFS,假设求起点到某个端点走过的平均路径为n条,每个端点的平均邻接端点为m,那求出这个最短路径使用DFS算法的时间复杂度为O(mn), 这显然是十分不理想的。
于是提出迪杰斯特拉(Dijkstra)算法,为解决有向图中某个端点到其余端点的最短路径, 在端点数为m,时间复杂度为O(m2)的情况下求出结果,前提条件是每条边的权重不能使负值。
接下来讲述算法细节:
1、把所有端点划分为两个集合,所有已找到最短路径的端点集合和未找到最短路径的端点集合(初始只有起点在已找到最短路线端点集合中)。
2、维护一个长度为m的距离数组(下面均用这个表达,都是指这个东西),存储当前所有端点的最短距离。当一个新的端点找到最短路径的时候,即更新该端点所能到达的其余未找到最短路径的端点的当前最短距离(初始值是起点到所能到达的端点的距离)。
3、循环m-1次,每次从距离数组中找到最小的数值,该数值即为该端点的最短路径(比如起点为A,遍历的时候找到最小数值是B,那么这个值就是B点的最短距离,因为不可能从A出去的其他路径再经过其他路径再到达B的距离比这个距离更小,除非有路径的权重的负值,但这与Dijkstra的前提条件相悖)。
4、对当前找到最短路径的端点,如果从该点出发,所能到达的未找到最短路径的端点小于当前距离数组里面的值,则更新这个值。
5、循环m-1次找到所有端点的最短路径,或者在某个循环未能找到符合要求的端点,则说明剩下的端点不可到达,都结束此次计算。
过程被我表达有点晦涩...下面可以通过代码理解。
1 // calculate the shortest distance from start point to end point 2 public void calcDistance(int start, int[][] matrix) { 3 this.matrix = matrix; 4 this.start = start; 5 int cnt = matrix.length; //Point count 6 this.goalCnt = cnt; 7 boolean[] found = new boolean[cnt]; //true value indicate the shortest distance from start to n have been found 8 int[] dis = new int[cnt]; // store the shortest distance from start to n, initial as INT_MAX 9 int[] preRoute = new int[cnt]; //preRoute[u] = v represent that the previous goal of shortest path to u is v 10 for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) { 11 dis[i] = start == i ? 0 : matrix[start][i] != 0 ? matrix[start][i] : Integer.MAX_VALUE; 12 preRoute[i] = -1; 13 } 14 found[start] = true; 15 // find out one shortest path in one iteration 16 for (int i = 0; i < cnt - 1; i++) { 17 // the shortest distance of the index of goal was found in current iteration 18 int tDis = Integer.MAX_VALUE, 19 tInd = -1; 20 for (int j = 0; j < cnt; j++) { 21 if (!found[j] && dis[j] < tDis) { 22 tInd = j; 23 tDis = dis[j]; 24 } 25 } 26 if (-1 == tInd) { 27 //The left goal is unreachable 28 break; 29 } 30 found[tInd] = true; 31 distance.put(tInd, dis[tInd]); 32 // find out the route of the tInd goal 33 int e = tInd; 34 Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); 35 while (-1 != e) { 36 stack.push(e); 37 e = preRoute[e]; 38 } 39 route.put(tInd, stack); 40 //update the shorter path 41 for (int j = 0; j < cnt; j ++) { 42 if (matrix[tInd][j] != 0) { 43 int newDis = dis[tInd] + matrix[tInd][j]; 44 if (!found[j] && newDis < dis[j]) { 45 dis[j] = newDis; 46 preRoute[j] = tInd; // tInd is the previous goal of the shortest path to j goal 47 } 48 } 49 } 50 } 51 }
以上为Dijkstra的核心算法,传入一个图一个起点,求出这个起点到其余端点的最短路径,found[n]为true表示下标为n的端点的最短路径已经找到,dis数组即为上文所提距离数组,32~39行以及preRoute数组只是为了找出路径所经节点,不属于算法内容。
下面我们找一张图检验一下算法结果,S(N0)为起点。
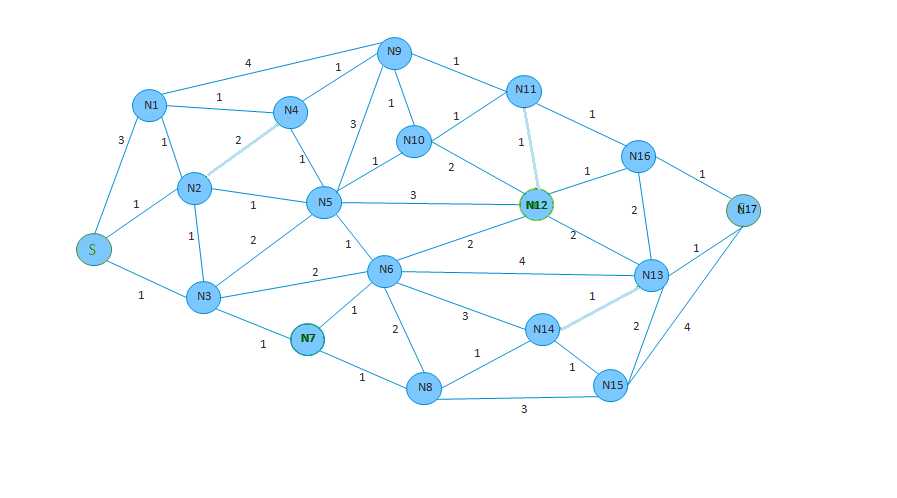
化为矩阵形式如下:
public static void main(String[] args) { // test data int[][] matrix = { {0,3,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0}, {3,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,4,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0}, {1,1,0,1,2,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0}, {1,0,1,0,0,2,2,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0}, {0,1,2,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0}, {0,0,1,2,1,0,1,0,0,3,1,0,3,0,0,0,0,0}, {0,0,0,2,0,1,0,1,2,0,0,0,2,4,3,0,0,0}, {0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0}, {0,0,0,0,0,0,2,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,3,0,0}, {0,4,0,0,1,3,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0}, {0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,2,0,0,0,0,0}, {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0}, {0,0,0,0,0,3,2,0,0,0,2,1,0,2,0,0,1,0}, {0,0,0,0,0,0,4,0,0,0,0,0,2,0,1,2,2,1}, {0,0,0,0,0,0,3,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0}, {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,3,0,0,0,0,2,1,0,0,4}, {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,2,0,0,0,1}, {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,4,1,0}}; Dijkstra dijkstra = new Dijkstra(); dijkstra.calcDistance(0, matrix); for (int i = 1; i < dijkstra.getGoalCnt(); i++) { System.out.println("Destination: " + i); System.out.println("Distance: " + dijkstra.getDistance(i)); System.out.println("Path: " + dijkstra.getRouteMap(i)); System.out.println(); } }
运算结果:
Destination: 1 Distance: 2 Path: 0->2->1 Destination: 2 Distance: 1 Path: 0->2 Destination: 3 Distance: 1 Path: 0->3 Destination: 4 Distance: 3 Path: 0->2->4 Destination: 5 Distance: 2 Path: 0->2->5 Destination: 6 Distance: 3 Path: 0->3->6 Destination: 7 Distance: 2 Path: 0->3->7 Destination: 8 Distance: 3 Path: 0->3->7->8 Destination: 9 Distance: 4 Path: 0->2->4->9 Destination: 10 Distance: 3 Path: 0->2->5->10 Destination: 11 Distance: 4 Path: 0->2->5->10->11 Destination: 12 Distance: 5 Path: 0->2->5->12 Destination: 13 Distance: 5 Path: 0->3->7->8->14->13 Destination: 14 Distance: 4 Path: 0->3->7->8->14 Destination: 15 Distance: 5 Path: 0->3->7->8->14->15 Destination: 16 Distance: 5 Path: 0->2->5->10->11->16 Destination: 17 Distance: 6 Path: 0->3->7->8->14->13->17
初步检验结果是正确的。
至此,以上为个人对Dijkstra算法的理解,如有不妥之处,欢迎指出斧正。
尊重知识产权,转载引用请通知作者并注明出处!
以上是关于数据结构 - 单源最短路径之迪杰斯特拉(Dijkstra)算法详解(Java)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章