《VGG in TensorFlow Demo》
Posted welcome-xwell
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了《VGG in TensorFlow Demo》相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文献来源: https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~frossard/post/vgg16/
VGG卷积神经网络是牛津大学在2014年提出来的模型。当这个模型被提出时,由于它的简洁性和实用性,马上成为了当时最流行的卷积神经网络模型。它在图像分类和目标检测任务中都表现出非常好的结果。在2014年的ILSVRC比赛中,VGG 在Top-5中取得了92.3%的正确率。
众所周知,VGG是一个良好的特征提取器,其与训练好的模型也经常被用来做其他事情,比如计算perceptual loss(风格迁移和超分辨率任务中),尽管现在resnet和inception网络等等具有很高的精度和更加简便的网络结构,但是在特征提取上,VGG一直是一个很好的网络,所以说,当你的某些任务上resnet或者inception等表现并不好时,不妨试一下VGG,或许会有意想不到的结果。
VGG之所以是一个很好的特征提取器,除了和它的网络结构有关,还和它的训练方式有关系,VGG并不是直接训练完成的,它使用了逐层训练的方法。
另外,VGG对于Alexnet来说,改进并不是很大,主要改进就在于使用了小卷积核,网络是分段卷积网络,通过maxpooling过度,同时网络更深更宽。
VGG16命名由来即该神经网络层结构为:13层卷积层,3层链接层。
运行环境:python3,Ubuntu
文件列表:
2:TensorFlow模型:vgg16.py
3:类名列表:imagenet_classes.py
4:输入实例:m1.jpg
代码实例:
vgg16.py
######################################################################################## # Davi Frossard, 2016 # # VGG16 implementation in TensorFlow # # Details: # # http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~frossard/post/vgg16/ # # # # Model from https://gist.github.com/ksimonyan/211839e770f7b538e2d8#file-readme-md # # Weights from Caffe converted using https://github.com/ethereon/caffe-tensorflow # ######################################################################################## import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np from scipy.misc import imread, imresize from imagenet_classes import class_names class vgg16: def __init__(self, imgs, weights=None, sess=None): self.imgs = imgs self.convlayers() self.fc_layers() self.probs = tf.nn.softmax(self.fc3l) if weights is not None and sess is not None: self.load_weights(weights, sess) def convlayers(self): self.parameters = [] # zero-mean input with tf.name_scope(‘preprocess‘) as scope: mean = tf.constant([123.68, 116.779, 103.939], dtype=tf.float32, shape=[1, 1, 1, 3], name=‘img_mean‘) images = self.imgs-mean # conv1_1 with tf.name_scope(‘conv1_1‘) as scope: kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 3, 64], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name=‘weights‘) conv = tf.nn.conv2d(images, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[64], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name=‘biases‘) out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases) self.conv1_1 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope) self.parameters += [kernel, biases] # conv1_2 with tf.name_scope(‘conv1_2‘) as scope: kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 64, 64], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name=‘weights‘) conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv1_1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[64], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name=‘biases‘) out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases) self.conv1_2 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope) self.parameters += [kernel, biases] # pool1 self.pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(self.conv1_2, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding=‘SAME‘, name=‘pool1‘) # conv2_1 with tf.name_scope(‘conv2_1‘) as scope: kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 64, 128], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name=‘weights‘) conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.pool1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[128], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name=‘biases‘) out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases) self.conv2_1 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope) self.parameters += [kernel, biases] # conv2_2 with tf.name_scope(‘conv2_2‘) as scope: kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 128, 128], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name=‘weights‘) conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv2_1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[128], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name=‘biases‘) out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases) self.conv2_2 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope) self.parameters += [kernel, biases] # pool2 self.pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(self.conv2_2, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding=‘SAME‘, name=‘pool2‘) # conv3_1 with tf.name_scope(‘conv3_1‘) as scope: kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 128, 256], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name=‘weights‘) conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.pool2, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[256], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name=‘biases‘) out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases) self.conv3_1 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope) self.parameters += [kernel, biases] # conv3_2 with tf.name_scope(‘conv3_2‘) as scope: kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 256, 256], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name=‘weights‘) conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv3_1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[256], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name=‘biases‘) out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases) self.conv3_2 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope) self.parameters += [kernel, biases] # conv3_3 with tf.name_scope(‘conv3_3‘) as scope: kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 256, 256], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name=‘weights‘) conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv3_2, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[256], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name=‘biases‘) out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases) self.conv3_3 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope) self.parameters += [kernel, biases] # pool3 self.pool3 = tf.nn.max_pool(self.conv3_3, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding=‘SAME‘, name=‘pool3‘) # conv4_1 with tf.name_scope(‘conv4_1‘) as scope: kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 256, 512], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name=‘weights‘) conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.pool3, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[512], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name=‘biases‘) out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases) self.conv4_1 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope) self.parameters += [kernel, biases] # conv4_2 with tf.name_scope(‘conv4_2‘) as scope: kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 512, 512], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name=‘weights‘) conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv4_1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[512], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name=‘biases‘) out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases) self.conv4_2 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope) self.parameters += [kernel, biases] # conv4_3 with tf.name_scope(‘conv4_3‘) as scope: kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 512, 512], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name=‘weights‘) conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv4_2, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[512], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name=‘biases‘) out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases) self.conv4_3 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope) self.parameters += [kernel, biases] # pool4 self.pool4 = tf.nn.max_pool(self.conv4_3, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding=‘SAME‘, name=‘pool4‘) # conv5_1 with tf.name_scope(‘conv5_1‘) as scope: kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 512, 512], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name=‘weights‘) conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.pool4, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[512], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name=‘biases‘) out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases) self.conv5_1 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope) self.parameters += [kernel, biases] # conv5_2 with tf.name_scope(‘conv5_2‘) as scope: kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 512, 512], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name=‘weights‘) conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv5_1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[512], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name=‘biases‘) out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases) self.conv5_2 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope) self.parameters += [kernel, biases] # conv5_3 with tf.name_scope(‘conv5_3‘) as scope: kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 512, 512], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name=‘weights‘) conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv5_2, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[512], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name=‘biases‘) out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases) self.conv5_3 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope) self.parameters += [kernel, biases] # pool5 self.pool5 = tf.nn.max_pool(self.conv5_3, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding=‘SAME‘, name=‘pool4‘) def fc_layers(self): # fc1 with tf.name_scope(‘fc1‘) as scope: shape = int(np.prod(self.pool5.get_shape()[1:])) fc1w = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([shape, 4096], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name=‘weights‘) fc1b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(1.0, shape=[4096], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name=‘biases‘) pool5_flat = tf.reshape(self.pool5, [-1, shape]) fc1l = tf.nn.bias_add(tf.matmul(pool5_flat, fc1w), fc1b) self.fc1 = tf.nn.relu(fc1l) self.parameters += [fc1w, fc1b] # fc2 with tf.name_scope(‘fc2‘) as scope: fc2w = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([4096, 4096], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name=‘weights‘) fc2b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(1.0, shape=[4096], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name=‘biases‘) fc2l = tf.nn.bias_add(tf.matmul(self.fc1, fc2w), fc2b) self.fc2 = tf.nn.relu(fc2l) self.parameters += [fc2w, fc2b] # fc3 with tf.name_scope(‘fc3‘) as scope: fc3w = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([4096, 1000], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name=‘weights‘) fc3b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(1.0, shape=[1000], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name=‘biases‘) self.fc3l = tf.nn.bias_add(tf.matmul(self.fc2, fc3w), fc3b) self.parameters += [fc3w, fc3b] def load_weights(self, weight_file, sess): weights = np.load(weight_file) keys = sorted(weights.keys()) for i, k in enumerate(keys): print(i, k, np.shape(weights[k])) sess.run(self.parameters[i].assign(weights[k])) if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: sess = tf.Session() imgs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 224, 224, 3]) vgg = vgg16(imgs, ‘vgg16_weights.npz‘, sess) img1 = imread(‘m1.jpg‘, mode=‘RGB‘) img1 = imresize(img1, (224, 224)) prob = sess.run(vgg.probs, feed_dict={vgg.imgs: [img1]})[0] preds = (np.argsort(prob)[::-1])[0:5] for p in preds: print (class_names[p], prob[p])
效果展示:
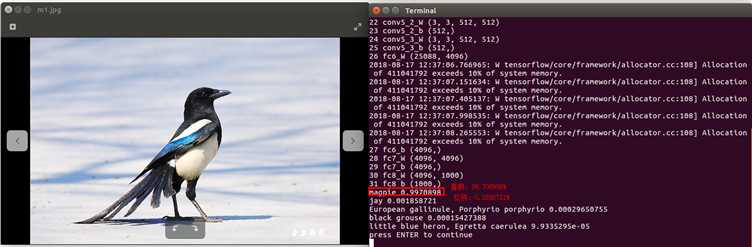
由图可见,识别效果还是可以滴!
关于VGG16具体实现见链接:https://blog.csdn.net/errors_in_life/article/details/65950699
另一详细介绍见:http://www.360doc.com/content/17/0624/10/10408243_666125650.shtml
以上是关于《VGG in TensorFlow Demo》的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章