Xiangqi UVa1589(多次WA)
Posted dreamworldclark
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Xiangqi UVa1589(多次WA)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
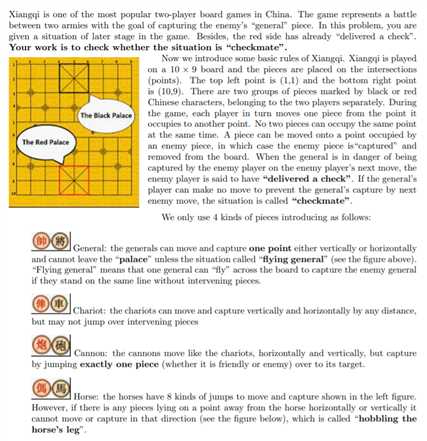
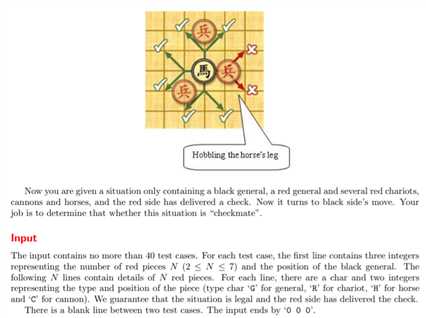
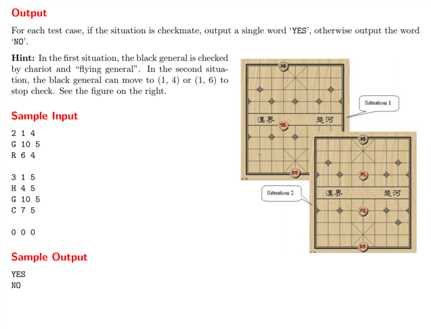

1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<string.h> 3 #define maxn 8 4 //#define LOCAL 5 #include<iostream> 6 using namespace std; 7 int test(); 8 int count(int,int); 9 int horse_judge(int); 10 int hobble(int,int); 11 12 int G1, G2; //(G1,G2) of black general. 13 int N; //the number of pieces of red. 14 char a[maxn]; //store the pieces name in red. # i to (2*i,2*i+1) 15 int pos[2*maxn]; //record the point. 16 17 //judge YES(1) or NO(0) 18 int judgement() 19 { //if the black and red general in the same line and do not have pieces between them. 20 //black win. 21 int index = strchr(a,‘G‘)-a; 22 if( pos[2*index+1] == G2 && count(2,index) == 0) {return 0;} 23 24 //move up, down, left, right to try if the black general can save itself. 25 //if this move is a life way, the program will return 0; 26 //else the program will go back to the original position and then try different directions. 27 if( G1-1 >= 1 ){ G1 -= 1; if(test()) return 0; G1 += 1; } 28 29 if( G1+1 <= 3 ){ G1 += 1; if(test()) return 0; G1 -= 1; } 30 31 if( G2-1 >= 4 ){ G2 -= 1; if(test()) return 0; G2 += 1; } 32 33 if( G2+1 <= 6 ){ G2 += 1; if(test()) return 0; G2 -= 1; } 34 return 1; 35 } 36 37 //test if the black general will die(4 possibilities). 38 //when the black general do not die, the program will return 1 39 //when die, return 0 40 int test() 41 { 42 int n = strlen(a); 43 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) 44 { 45 //if two generals in the same line, I will count the number of pieces between them. 46 //if the number is zero, I‘m sorry to say that the black general die. 47 if( a[i] == ‘G‘ && G2 == pos[2*i+1] ) 48 { 49 if( count(2,i) == 0 ) return 0; 50 } 51 52 if( a[i] == ‘R‘ && (G1 == pos[2*i] || G2 == pos[2*i+1]) ) 53 { 54 int flag = 0; //used to judge if they are in the same row or col. 55 if(G1 == pos[2*i] && G2 == pos[2*i+1])continue;//eat the piece. 56 if(G1 == pos[2*i]) flag = 1; 57 if(G2 == pos[2*i+1]) flag = 2; 58 if( count(flag,i) == 0 ) { return 0;} 59 } 60 if( a[i] == ‘C‘ && (G1 == pos[2*i] || G2 == pos[2*i+1]) ) 61 { 62 int flag = 0; 63 if(G1 == pos[2*i] && G2 == pos[2*i+1]) continue; 64 if(G1 == pos[2*i]) flag = 1; 65 if(G2 == pos[2*i+1]) flag = 2; 66 if( count(flag,i) == 1 ) { return 0;} 67 68 } 69 if( a[i] == ‘H‘ ) 70 { 71 if(G1 == pos[2*i] && G2 == pos[2*i+1]) continue; 72 if(horse_judge(i)){ return 0; } //judge by other functions. 73 } 74 } 75 return 1;//if the black survive after all the test, return 1; 76 } 77 78 //count the number of other pieces between these two pieces. 79 //1 is row; 2 is col 80 int count(int flag, int index) 81 { 82 int n = strlen(a); 83 int num = 0; 84 int t(0); 85 //count the row. 86 if(flag == 1) 87 { 88 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++ ) 89 { 90 if(pos[2*i] == G1 ) 91 { 92 //on the left. 93 if(pos[2*i+1]<G2 && (pos[2*i+1] > pos[2*index+1])) 94 num++; 95 //on the right. 96 if(pos[2*i+1]>G2 && (pos[2*i+1] < pos[2*index+1])) 97 num++; 98 } 99 } 100 return num; 101 } 102 //count the column. 103 if(flag == 2) 104 { 105 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) 106 { 107 if(pos[2*i+1] == G2) 108 { 109 //above the of general 110 if(pos[2*i] < G1 && pos[2*i] > pos[2*index]) 111 num++; 112 //under the general 113 if(pos[2*i] > G1 && pos[2*i] < pos[2*index]) 114 num++; 115 } 116 } 117 return num; 118 } 119 } 120 121 //judge if the black general will be killed by horse. 122 //return 0 live. 123 //return 1 die. 124 int horse_judge(int index) 125 { 126 //cx,cy are uesed to know the horse‘s direction to the black general. 127 int cx, cy; 128 int x(pos[index*2]), y(pos[index*2+1]); //the point of the horse. 129 if( G1 > x ) cx = -1; 130 else if( G1 < x ) cx = 1; 131 else return 0; 132 if( G2 > y ) cy = -1; 133 else if( G2 < y ) cy = 1; 134 else return 0; 135 if( (G1+ cx*1 == x && G2 + cy*2 == y)|| (G1 + cx*2 == x && G2 + cy*1 == y) ) 136 { 137 int point1 = G1+1*cx; 138 int point2 = G2+1*cy; 139 if(hobble(point1, point2) ) return 0; 140 else return 1; 141 } 142 else return 0; 143 } 144 145 int hobble(int x, int y) 146 { 147 for(int i = 0; i < strlen(a); i++) 148 { 149 if( pos[2*i]==x && pos[2*i+1] == y) return 1; 150 } 151 return 0; 152 } 153 154 int main() 155 { 156 #ifdef LOCAL 157 freopen("data.in", "r", stdin); 158 freopen("data.out", "w", stdout); 159 #endif 160 161 while( cin>>N>>G1>>G2 && N != 0) //!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! 162 { 163 //initialize two arraies. 164 memset(a,0,sizeof(a)); 165 memset(pos,0,sizeof(pos)); 166 for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) 167 { 168 cin>>a[i]; 169 cin>>pos[2*i]>>pos[2*i+1]; 170 } 171 if(judgement()) 172 printf("YES "); 173 else 174 printf("NO "); 175 } 176 return 0; 177 }
思路分析:
- 用数字构建一个虚拟的棋盘,将红方的每一个棋子会攻击到的点都用1表示,而攻击不到的点用0表示,这样黑色的将军在移动的时候就可以通过虚拟棋盘的所对应的位置的值来判断会不会死亡。当然这个方案需要构建多个数组,用的内存比较大。
- 每一次移动黑色的将军之后,判断它的生死,这样的话更加方便一些
问题:
- 使用scanf("%c",&a[i])的时候会读取回车,如果要使用的话需要用getchar()吃掉回车,或者干脆使用iostream,那个输入输出都不要控制,很方便。
- 判断马在将的哪个方位的时候讲cx,cy弄反了,这个问题一方面是疏忽,另一方面是注释写的不清楚。清晰的使用注释,不仅能够让代码更容易阅读,而且便于自己在写代码的时候弄清楚变量的关系。
- 几个连续的if,千万要注意会不会有互相干扰的问题。应该在一开始就养成分类的良好习惯,如果应该分类,应该毫不犹豫的分类,而不是想当然的认为没有影响。这样的错误十分十分的难查出来,这让调试得难度极大。
改进:
希望有一天能够写出令自己惊叹的美丽的程序,只要前进就会离目标越来越近!
以上是关于Xiangqi UVa1589(多次WA)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
